Abstract
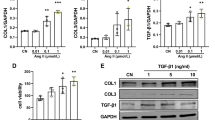
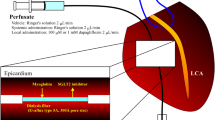
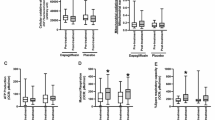
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis plays a vital role in the occurrence and development of heart failure. Dapagliflozin (DAPA), a new type of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, is an oral hypoglycemic drug that reduces glucose reabsorption by the kidneys and increases glucose excretion in the urine. Studies have shown that DAPA may have the potential to treat heart failure in addition to controlling blood sugar. This study explored the effect of DAPA on endoplasmic reticulum stress-related apoptosis caused by heart failure. In vitro, we found that DAPA inhibited the expression of cleaved caspase 3, Bax, C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), and glucose-regulated protein78 (GRP78) and upregulated the cardiomyoprotective protein Bcl-2 in angiotensin II (Ang II)-treated cardiomyocytes. In addition, DAPA promoted the expression of silent information regulator factor 2-related enzyme 1 (SIRT1) and suppressed the expression of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) and the ratios p-PERK/PERK and p-eIF2α/eIF2α. Notably, the therapeutic effect of DAPA was weakened by pretreatment with the SIRT1 inhibitor EX527 (10 μM). Simultaneous administration of DAPA inhibited the Ang II-induced transformation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts and inhibited fibroblast migration. In summary, our present findings first indicate that DAPA could inhibit the PERK-eIF2α-CHOP axis of the ER stress response through the activation of SIRT1 in Ang II-treated cardiomyocytes and ameliorate heart failure development in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Hill JA, Olson EN. Cardiac plasticity. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1370–80.
Wang L, Wang J, Cretoiu D, Li G, Xiao J. Exercise-mediated regulation of autophagy in the cardiovascular system. J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9:203–10.
Abbate A, Toldo S, Marchetti C, Kron J, Van Tassell BW, Dinarello CA. Interleukin-1 and the inflammasome as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2020;126:1260–80.
Lund LH, Savarese G. Global public health burden of heart failure. Cardiac Fail Rev. 2017;3:7–11.
Coeytaux RR, Williams JW, Gray RN, Wang A. Percutaneous heart valve replacement for aortic stenosis: state of the evidence. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153:314–24.
van Empel VP, Bertrand AT, Hofstra L, Crijns HJ, Doevendans PA, De Windt LJ. Myocyte apoptosis in heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;67:21–9.
Sadoshima J, Montagne O, Wang Q, Yang G, Warden J, Liu J, et al. The MEKK1-JNK pathway plays a protective role in pressure overload but does not mediate cardiac hypertrophy. J Clin Invest. 2002;110:271–9.
Lin JH, Li H, Yasumura D, Cohen HR, Zhang C, Panning B, et al. IRE1 signaling affects cell fate during the unfolded protein response. Science. 2007;318:944–9.
Sundaresan NR, Pillai VB, Gupta MP. Emerging roles of SIRT1 deacetylase in regulating cardiomyocyte survival and hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;51:614–8.
Nadtochiy SM, Urciuoli W, Zhang J, Schafer X, Munger J, Brookes PS. Metabolomic profiling of the heart during acute ischemic preconditioning reveals a role for SIRT1 in rapid cardioprotective metabolic adaptation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015;88:64–72.
Ding M, Lei J, Han H, Li W, Qu Y, Fu E, et al. SIRT1 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via activating eNOS in diabetic rats. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015;14:143.
Akkafa F, Halil Altiparmak I, Erkus ME, Aksoy N, Kaya C, Ozer A, et al. Reduced SIRT1 expression correlates with enhanced oxidative stress in compensated and decompensated heart failure. Redox Biol. 2015;6:169–73.
Vikram A, Lewarchik CM, Yoon JY, Naqvi A, Kumar S, Morgan GM, et al. Sirtuin 1 regulates cardiac electrical activity by deacetylating the cardiac sodium channel. Nat Med. 2017;23:361–7.
Vrhovac I, Balen Eror D, Klessen D, Burger C, Breljak D, Kraus O, et al. Localizations of Na+-D-glucose cotransporters SGLT1 and SGLT2 in human kidney and of SGLT1 in human small intestine, liver, lung, and heart. Pflug Arch. 2015;467:1881–98.
Cowie MR, Fisher M. SGLT2 inhibitors: mechanisms of cardiovascular benefit beyond glycaemic control. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17:761–72.
Yurista SR, Silljé H, Oberdorf-Maass SU, Schouten EM, Pavez Giani MG, Hillebrands JL, et al. Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibition with empagliflozin improves cardiac function in non-diabetic rats with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019;21:862–73.
Jaikumkao K, Pongchaidecha A, Chueakula N, Thongnak LO, Wanchai K, Chatsudthipong V, et al. Dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, slows the progression of renal complications through the suppression of renal inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in prediabetic rats. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20:2617–26.
Swe MT, Thongnak L, Jaikumkao K, Pongchaidecha A, Chatsudthipong V, Lungkaphin A. Dapagliflozin not only improves hepatic injury and pancreatic endoplasmic reticulum stress, but also induces hepatic gluconeogenic enzymes expression in obese rats. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019;133:2415–30.
Shi L, Zhu D, Wang S, Jiang A, Li F. Dapagliflozin attenuates cardiac remodeling in mice model of cardiac pressure overload. Am J Hypertens. 2019;32:452–9.
Lahnwong S, Palee S, Apaijai N, Sriwichaiin S, Kerdphoo S, Jaiwongkam T, et al. Acute dapagliflozin administration exerts cardioprotective effects in rats with cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020;19:91.
Kostin S, Pool L, Elsässer A, Hein S, Drexler HC, Arnon E, et al. Myocytes die by multiple mechanisms in failing human hearts. Circ Res. 2003;92:715–24.
Guo X, Zhang Y, Lu C, Qu F, Jiang X. Protective effect of hyperoside on heart failure rats via attenuating myocardial apoptosis and inducing autophagy. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2020;84:714–24.
Whelan RS, Kaplinskiy V, Kitsis RN. Cell death in the pathogenesis of heart disease: mechanisms and significance. Annu Rev Physiol. 2010;72:19–44.
Wencker D, Chandra M, Nguyen K, Miao W, Garantziotis S, Factor SM, et al. A mechanistic role for cardiac myocyte apoptosis in heart failure. J Clin Invest. 2003;111:1497–504.
Razavi HM, Hamilton JA, Feng Q. Modulation of apoptosis by nitric oxide: implications in myocardial ischemia and heart failure. Pharmacol Ther. 2005;106:147–62.
Sin TK, Yu AP, Yung BY, Yip SP, Chan LW, Wong CS, et al. Modulating effect of SIRT1 activation induced by resveratrol on Foxo1-associated apoptotic signalling in senescent heart. J Physiol. 2014;592:2535–48.
Patten RD, Pourati I, Aronovitz MJ, Baur J, Celestin F, Chen X, et al. 17beta-estradiol reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis in vivo and in vitro via activation of phospho-inositide-3 kinase/Akt signaling. Circ Res. 2004;95:692–9.
Patten RD, Denofrio D, El-Zaru M, Kakkar R, Saunders J, Celestin F, et al. Ventricular assist device therapy normalizes inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis in the failing human heart. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45:1419–24.
Liu Q, Chen L, Liang X, Cao Y, Zhu X, Wang S, et al. Exercise attenuates angiotensin-induced muscle atrophy by targeting PPARgamma/miR-29b. J Sport Health Sci. 2021;S2095–2546;00067–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jshs.2021.06.002.
Uehara Y, Hirose J, Yamabe S, Okamoto N, Okada T, Oyadomari S, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis contributes to articular cartilage degeneration via C/EBP homologous protein. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2014;22:1007–17.
Okada K, Minamino T, Tsukamoto Y, Liao Y, Tsukamoto O, Takashima S, et al. Prolonged endoplasmic reticulum stress in hypertrophic and failing heart after aortic constriction: possible contribution of endoplasmic reticulum stress to cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Circulation. 2004;110:705–12.
Hotamisligil GS. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell. 2010;140:900–17.
Li Z, Guo J, Bian Y, Zhang M. Intermedin protects thapsigargininduced endoplasmic reticulum stress in cardiomyocytes by modulating protein kinase A and sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ATPase. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23:107. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11746.
Shibusawa R, Yamada E, Okada S, Nakajima Y, Bastie CC, Maeshima A, et al. Dapagliflozin rescues endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated cell death. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9887.
Li YP, Wang SL, Liu B, Tang L, Kuang RR, Wang XB, et al. Sulforaphane prevents rat cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in vitro via activating SIRT1 and subsequently inhibiting ER stress. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016;37:344–53.
Prola A, Pires Da Silva J, Guilbert A, Lecru L, Piquereau J, Ribeiro M, et al. SIRT1 protects the heart from ER stress-induced cell death through eIF2alpha deacetylation. Cell Death Differ. 2017;24:343–56.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81770292) and Key Projects of Workstation of He Lin (18331101) and Wenzhou Science and Technology Major Projects (2018ZY007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LL, LTF, FFR designed the research, FFR wrote the paper. FFR, ZYX, YNJ, XG, and QYC conducted the experiments. All the authors analyzed the data, revised the paper, and approved the final paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Ff., Xie, Zy., Jiang, Yn. et al. Dapagliflozin attenuates pressure overload-induced myocardial remodeling in mice via activating SIRT1 and inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43, 1721–1732 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00805-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00805-2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Metabo-epigenetic circuits of heart failure: chromatin-modifying enzymes as determinants of metabolic plasticity
EMBO Molecular Medicine (2025)
-
SGLT2 inhibitors: how do they affect the cardiac cells
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2025)
-
Inhibition of SGLT2 protects podocytes in diabetic kidney disease by rebalancing mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
Dapagliflozin improves skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity through SIRT1 activation induced by nutrient deprivation state
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Empagliflozin rescues lifespan and liver senescence in naturally aged mice
GeroScience (2024)