Abstract
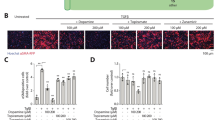
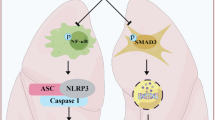
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic fatal lung disease characterized by destruction of lung parenchyma and deposition of extracellular matrix in interstitial and alveolar spaces. But known drugs for IPF are far from meeting clinical demands, validation of drug targets against pulmonary fibrosis is in urgent demand. Tyrosine kinase receptor DDRs has been considered as a potential therapeutic target for pulmonary fibrosis due to its pathological collagen binding property and the roles in regulating extracellular matrix remodeling. In this study we designed and synthesized a new indazole derivative XBLJ-13, and identified XBLJ-13 as a highly specific and potent DDRs inhibitor with anti-inflammation and anti-fibrosis activities. We first demonstrated that DDR1/2 was highly expressed in the lung tissues of IPF patients. Then we showed that XBLJ-13 potently inhibited DDR1 and DDR2 kinases with IC50 values of 17.18 nM and 15.13 nM, respectively. Among a panel of 34 kinases tested, XBLJ-13 displayed relatively high selectivity for DDRs with minimal inhibitory effect on PDGFR family and FGFR1, as well as Abl kinase that had high homology with DDRs. Extensive profiling of XBLJ-13 revealed that the new inhibitor had much lower toxicity than nintedanib and better pharmacokinetic properties in mice. Furthermore, pharmacodynamic evaluation conducted in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis mice showed that administration of XBLJ-13 (30, 60, 90 mg·kg−1·d−1, i.g.) for 12 days significantly and dose-dependently ameliorated lung inflammation and fibrosis. Together, this study confirms that DDRs kinase is a potential target for PF, Particularly, compound XBLJ-13 is a highly potent and specific DDRs inhibitor, along with good pharmacokinetics profiles, and preferable in vivo efficacy, suggesting that it is a potential candidate for the treatment of PF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Zank DC, Bueno M, Mora AL, Rojas M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: aging, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cellular bioenergetics. Front Med. 2018;5:10.
Richeldi L, Collard HR, Jones MG. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 2017;389:1941–52.
Glass DS, Grossfeld D, Renna HA, Agarwala P, Spiegler P, Kasselman LJ, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Molecular mechanisms and potential treatment approaches. Respir Investig. 2020;58:320–35.
Wynn TA. Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. J Exp Med. 2011;208:1339–50.
Byrne AJ, Maher TM, Lloyd CM. Pulmonary macrophages: a new therapeutic pathway in fibrosing lung disease? Trends Mol Med. 2016;22:303–16.
Grimminger F, Günther A, Vancheri C. The role of tyrosine kinases in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2015;45:1426–33.
Avivi-Green C, Singal M, Vogel WF. Discoidin domain receptor 1-deficient mice are resistant to bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Am J respiratory Crit Care Med. 2006;174:420–7.
Flamant M, Placier S, Rodenas A, Curat CA, Vogel WF, Chatziantoniou C, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 1 null mice are protected against hypertension-induced renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:3374–81.
Matsuyama W, Wang L, Farrar WL, Faure M, Yoshimura T. Activation of discoidin domain receptor 1 isoform b with collagen up-regulates chemokine production in human macrophages: role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappa B. J Immunol (Baltim, Md: 1950). 2004;172:2332–40.
Zhao H, Bian H, Bu X, Zhang S, Zhang P, Yu J, et al. Targeting of discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) prevents myofibroblast activation and neovessel formation during pulmonary fibrosis. Mol Ther. 2016;24:1734–44.
Poudel B, Yoon DS, Lee JH, Lee YM, Kim DK. Collagen I enhances functional activities of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells via discoidin domain receptor 2. Cell Immunol. 2012;278:95–102.
Ruiz PA, Jarai G. Collagen I induces discoidin domain receptor (DDR) 1 expression through DDR2 and a JAK2-ERK1/2-mediated mechanism in primary human lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:12912–23.
Day E, Waters B, Spiegel K, Alnadaf T, Manley PW, Buchdunger E, et al. Inhibition of collagen-induced discoidin domain receptor 1 and 2 activation by imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;599:44–53.
Jeffries DE, Borza CM, Blobaum AL, Pozzi A, Lindsley CW. Discovery of VU6015929: a selective discoidin domain receptor 1/2 (DDR1/2) Inhibitor to explore the role of DDR1 in antifibrotic therapy. ACS medicinal Chem Lett. 2020;11:29–33.
Ngo P, Ramalingam P, Phillips JA, Furuta GT. Collagen gel contraction assay. Methods Mol Biol. 2006;341:103–9.
Wang Q, Dai Y, Ji Y, Shi H, Guo Z, Chen D, et al. Discovery and optimization of a series of 3-substituted indazole derivatives as multi-target kinase inhibitors for the treatment of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Med Chem. 2019;163:671–89.
Richeldi L, Varone F, Bergna M, de Andrade J, Falk J, Hallowell R, et al. Pharmacological management of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: a review of the current evidence. Eur Respir Rev. 2018;150:21–7.
Moll S, Desmouliere A, Moeller MJ, Pache JC, Badi L, Arcadu F, et al. DDR1 role in fibrosis and its pharmacological targeting. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019;1866:118474.
Borza CM, Pozzi A, Plosa EJ. Discoidin domain receptor 2, a potential therapeutic target in lung fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018;59:277–8.
Guignabert C, Phan C, Seferian A, Huertas A, Tu L, Thuillet R, et al. Dasatinib induces lung vascular toxicity and predisposes to pulmonary hypertension. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:3207–18.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81773779, 81125023, U1703235, 31871414, and 81701220), Shanghai Science and Technology Development Funds (19JC1416300 and 18431907100), Key New Drug Creation and Manufacturing Program of China (2019ZX09201001–004–010, 2019ZX09201001–003–010, and 2018ZX09711002–004–009), Shanghai Aging and Maternal and Child Health Research Program (2020yjzx0136), Backbone Program of Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital (fkgg1809) and K. C. Wong Education Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YD and BXT contributed equally, and they performed biological experiments and drafted the manuscript. DQC, QW and LWZ performed the chemical synthesis. CL performed the kinome selectivity assay. XZ, DDS and XS helped with the animal experiments. HS provided the human lung tissues. YZ, DQC, BX, XMZ and JL corrected the manuscript and directed the study. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Y., Tang, Bx., Wang, Q. et al. Discovery of a novel DDRs kinase inhibitor XBLJ-13 for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43, 1769–1779 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00808-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00808-z
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Conjoint analysis of single-cell sequencing and high-throughput virtual screening regarding DDR2 in osteoarthritis disease models
European Journal of Medical Research (2025)
-
Virtual screening for potential discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) inhibitors based on structural assessment
Molecular Diversity (2023)