Abstract
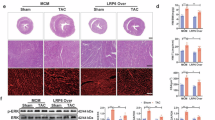
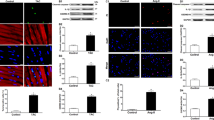
Inflammation and apoptosis are main pathological processes that lead to the development of cardiac hypertrophy. Lupeol, a natural triterpenoid, has shown anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic activities as well as potential protective effects on cardiovascular diseases. In this study we investigated whether lupeol attenuated cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis induced by pressure overload in vivo and in vitro, and explored the underlying mechanisms. Cardiac hypertrophy was induced in mice by transverse aortic constriction (TAC) surgery, and in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCMs) by stimulation with phenylephrine (PE) in vitro. We showed that administration of lupeol (50 mg ·kg-1· d-1, i.g., for 4 weeks) prevented the morphological changes and cardiac dysfunction and remodeling in TAC mice, and treatment with lupeol (50 μg/mL) significantly attenuated the hypertrophy of PE-stimulated NRCMs, and blunted the upregulated hypertrophic markers ANP, BNP, and β-MHC. Furthermore, lupeol treatment attenuated the apoptotic and inflammatory responses in the heart tissue. We revealed that lupeol attenuated the inflammatory responses including the reduction of inflammatory cytokines and inhibition of NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation, which was mediated by the TLR4-PI3K-Akt signaling. Administration of a PI3K/Akt agonist 740 Y-P reversed the protective effects of lupeol in TAC mice as well as in PE-stimulated NRCMs. Moreover, pre-treatment with a TLR4 agonist RS 09 abolished the protective effects of lupeol and restored the inhibition of PI3K-Akt-NF-κB signaling by lupeol in PE-stimulated NRCMs. Collectively, our results demonstrate that the lupeol protects against cardiac hypertrophy via anti-inflammatory mechanisms, which results from inhibiting the TLR4-PI3K-Akt-NF-κB signaling.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Nakamura M, Sadoshima J. Mechanisms of physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018;15:387–407.
Lei H, Hu J, Sun K, Xu D. The role and molecular mechanism of epigenetics in cardiac hypertrophy. Heart Fail Rev. 2021;26:1505–14.
Camici PG, Tschöpe C, Di Carli MF, Rimoldi O, Van Linthout S. Coronary microvascular dysfunction in hypertrophy and heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116:806–16.
Tschöpe C, Ammirati E, Bozkurt B, Caforio ALP, Cooper LT, Felix SB, et al. Myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy: current evidence and future directions. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021;18:169–93.
Bacmeister L, Schwarzl M, Warnke S, Stoffers B, Blankenberg S, Westermann D, et al. Inflammation and fibrosis in murine models of heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol. 2019;114:19.
Xiao Z, Kong B, Yang H, Dai C, Fang J, Qin TY, et al. Key player in cardiac hypertrophy, emphasizing the role of toll-like receptor 4. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020;7:579036.
Dai W, Tang T, Dai Z, Shi D, Mo L, Zhang Y. Probing the mechanism of hepatotoxicity of hexabromocyclododecanes through toxicological network analysis. Environ Sci Technol. 2020;54:15235–45.
Wang X, Chen L, Zhao X, Xiao LL, Yi ST, Kong YW, et al. A cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide suppresses cardiac hypertrophy induced by pressure overload by regulating IGFR1/PI3K/Akt and TLR9/AMPKα. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:96.
Yu H, Lin L, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Hu H. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:209.
Lin K, Luo W, Yan J, Shen SY, Shen QR, Wang J, et al. TLR2 regulates angiotensin II-induced vascular remodeling and EndMT through NF-κB signaling. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;13:2553–74.
Lee TL, Lai TC, Lin SR, Lin SW, Chen YC, Pu CM, et al. Conditioned medium from adipose-derived stem cells attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury through the microRNA-221/222/PUMA/ETS-1 pathway. Theranostics. 2021;11:3131–49.
Surai PF, Kochish II, Kidd MT. Redox homeostasis in Poultry: Regulatory roles of NF-κB. Antioxid (Basel). 2021;10:186.
Chen Y, Yang B, Stanton C, Ross RP, Zhao JX, Zhang H, et al. Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum ameliorates DSS-induced colitis by maintaining intestinal mechanical barrier, blocking proinflammatory cytokines, inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling, and altering gut microbiota. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69:1496–512.
Perez-Cornago A, Crowe FL, Appleby PN, Bradbury KE, Wood AM, Jakobsen MU, et al. Plant foods, dietary fibre and risk of ischaemic heart disease in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohort. Int J Epidemiol. 2021;50:212–22.
Zou LX, Chen C, Yan X, Lin QY, Fang J, Li PB, et al. Resveratrol attenuates pressure overload-induced cardiac fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction via PTEN/Akt/Smad2/3 and NF-κB signaling pathways. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019;63:e1900418.
Zhang X, Zhu JX, Ma ZG, Wu HM, Xu SC, Song P, et al. Rosmarinic acid alleviates cardiomyocyte apoptosis via cardiac fibroblast in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15:556–67.
Liu K, Zhang X, Xie L, Deng M, Chen HJ, Song JW, et al. Lupeol and its derivatives as anticancer and anti-inflammatory agents: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic efficacy. Pharmacol Res. 2021;164:105373.
Tsai FS, Lin LW, Wu CR. Lupeol and its role in chronic diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;929:145–75.
Wang XT, Gong Y, Zhou B, Yang JJ, Cheng Y, Zhao JG, et al. Ursolic acid ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation and fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:1461–7.
Ma ZG, Dai J, Wei WY, Zhang WB, Xu SC, Liao HH, et al. Asiatic acid protects against cardiac hypertrophy through activating AMPKα signalling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12:861–71.
Beserra FP, Vieira AJ, Gushiken LFS, Souza EOD, Hussni MF, Hussni CA, et al. Lupeol, a dietary triterpene, enhances wound healing in streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemic rats with modulatory effects on inflammation, oxidative stress, and angiogenesis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:3182627.
Kim SJ, Cho HI, Kim SJ, Kim JS, Kwak JH, Lee DU, et al. Protective effects of lupeol against D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced fulminant hepatic failure in mice. J Nat Prod. 2014;77:2383–8.
Saleem M, Afaq F, Adhami VM, Mukhtar H. Lupeol modulates NF-kappaB and PI3K/Akt pathways and inhibits skin cancer in CD-1 mice. Oncogene. 2004;23:5203–14.
Pereira Beserra F, Xue M, Maia GLA, Leite Rozza A, Helena Pellizzon C, Jackson CJ. Lupeol, a pentacyclic triterpene, promotes migration, wound closure, and contractile effect in vitro: possible involvement of PI3K/Akt and p38/ERK/MAPK pathways. Molecules. 2018;23:2819.
Sudhahar V, Kumar SA, Sudharsan PT, Varalakshmi P. Protective effect of lupeol and its ester on cardiac abnormalities in experimental hypercholesterolemia. Vasc Pharmacol. 2007;46:412–8.
Bacmeister L, Schwarzl M, Warnke S, Stoffers B, Blankenberg S, Westermann D, et al. Inflammation and fibrosis in murine models of heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol. 2019;114:19.
Burke RM, Burgos Villar KN, Small EM. Fibroblast contributions to ischemic cardiac remodeling. Cell Signal. 2021;77:109824.
Martinelli I, Timotin A, Moreno-Corchado P, Marsal D, Kramar S, Loy H, et al. Galanin promotes autophagy and alleviates apoptosis in the hypertrophied heart through FoxO1 pathway. Redox Biol. 2021;40:101866.
Kumari S, Katare PB, Elancheran R, Nizami HL, Paramesha B, Arava S, et al. Musa balbisiana fruit rich in polyphenols attenuates isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats via inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:7147498.
Deng S, Hu Y, Zhou J, Wang YF, Wang YG, Li SC, et al. TLR4 mediates alveolar bone resorption in experimental peri-implantitis through regulation of CD45+ cell infiltration, RANKL/OPG ratio, and inflammatory cytokine production. J Periodontol. 2020;91:671–82.
Wang D, Jin M, Zhao X, Zhao TY, Lin W, He ZL, et al. FGF1ΔHBS ameliorates chronic kidney disease via PI3K/Akt mediated suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:464.
Liu Y, Tong C, Tang Y, Liu Y, Shi XY, Shi L, et al. Tanshinone IIA alleviates blast-induced inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice partly by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;152:52–60.
Li B, Leung JCK, Chan LYY, Yiu WH, Tang SCW. A global perspective on the crosstalk between saturated fatty acids and toll-like receptor 4 in the etiology of inflammation and insulin resistance. Prog Lipid Res. 2020;77:101020.
Iannucci A, Caneparo V, Raviola S, Debernardi I, Colangelo D, Miggiano R, et al. Toll-like receptor 4-mediated inflammation triggered by extracellular IFI16 is enhanced by lipopolysaccharide binding. PLoS Pathog. 2020;16:e1008811.
Zhong J, Qiu X, Yu Q, Chen H, Yan C. A novel polysaccharide from acorus tatarinowii protects against LPS-induced neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity by inhibiting TLR4-mediated MyD88/NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;163:464–75.
Wen J, Shen J, Zhou Y, Zhao X, Dai Z, Jin Y. Pyrroloquinoline quinone attenuates isoproterenol hydrochloride‑induced cardiac hypertrophy in AC16 cells by inhibiting the NF‑κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45:873–85.
Prakoso D, De Blasio MJ, Tate M, Kiriazis H, Donner DG, Qian HW, et al. Gene therapy targeting cardiac phosphoinositide 3-kinase (p110α) attenuates cardiac remodeling in type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020;318:H840–H852.
Mian MOR, He Y, Bertagnolli M, Mai-Vo TA, Fernandes RO, Boudreau F, et al. TLR (toll-like receptor) 4 antagonism prevents left ventricular hypertrophy and dysfunction caused by neonatal hyperoxia exposure in rats. Hypertension. 2019;74:843–53.
Sun J, Niu C, Ye W, An N, Chen G, Huang XZ, et al. FGF13 is a novel regulator of NF-κB and potentiates pathological cardiac hypertrophy. iScience. 2020;23:101627.
Zhou H, Li N, Yuan Y, Jin YG, Wu QQ, Yan L, et al. Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B4 protects against cardiac hypertrophy via SHP-2-dependent inhibition of the NF-κB pathway. J Mol Med (Berl). 2020;98:691–705.
Buakaew W, Pankla Sranujit R, Noysang C, Thongsri Y, Potup P, Nuengchamnong N, et al. Phytochemical constituents of citrus hystrix DC. leaves attenuate inflammation via NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome activity in macrophages. Biomolecules. 2021;11:105.
Yang L, Hu X, Mo YY. Acidosis promotes tumorigenesis by activating Akt/NF-κB signaling. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019;38:179–88.
He L, Pan Y, Yu J, Wang B, Dai G, Ying X. Decursin alleviates the aggravation of osteoarthritis via inhibiting PI3K-Akt and NF-κB signal pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;97:107657.
Pillai VB, Sundaresan NR, Gupta MP. Regulation of Akt signaling by sirtuins: its implication in cardiac hypertrophy and aging. Circ Res. 2014;114:368–78.
Ma ZG, Yuan YP, Zhang X, Xu SC, Wang SS, Tang QZ. Piperine attenuates pathological cardiac fibrosis via PPAR-γ/Akt pathways. EBioMedicine. 2017;18:179–87.
Wang HB, Huang SH, Xu M, Yang J, Yang J, Liu MX, et al. Galangin ameliorates cardiac remodeling via the MEK1/2-ERK1/2 and PI3K-Akt pathways. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:15654–67.
Derossi D, Williams EJ, Green PJ, Dunican DJ, Doherty P. Stimulation of mitogenesis by a cell-permeable PI3-kinase binding peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;251:148–52.
Liu T, Zhang M, Niu H, Jing Liu J, Ma RL, Wang YI, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide from astragalus melittin ameliorates inflammation via suppressing the activation of TLR-4/NF-κB p65 signal pathway and protects mice from CVB3-induced virus myocarditis. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;126:179–86.
Lu X, He Y, Tang C, Wang XY, Que LL, Zhu GQ, et al. Triad3A attenuates pathological cardiac hypertrophy involving the augmentation of ubiquitination-mediated degradation of TLR4 and TLR9. Basic Res Cardiol. 2020;115:19.
Rathore M, Girard C, Ohanna M, Tichet M, Jouira RB, Garcia E, et al. Cancer cell-derived long pentraxin 3 (PTX3) promotes melanoma migration through a toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/NF-κB signaling pathway. Oncogene. 2019;38:5873–89.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Key Project from the National Natural Science Foundation (82000229), National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1311300), Development Center for Medical Science and Technology National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China (The prevention and control project of the cardiovascular disease, 2016ZX-008-01), and Science and Technology Planning Projects of Wuhan (2018061005132295).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DL, MX, and QZT designed research; DL, YYG, XFC, HLQ, SC, XFZ, and QZ performed the experiments; DL and YYG analyzed data; DL and MX wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Guo, Yy., Cen, Xf. et al. Lupeol protects against cardiac hypertrophy via TLR4-PI3K-Akt-NF-κB pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43, 1989–2002 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00820-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-021-00820-3
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lupeol: an updated review utilizing AI-assisted predictive tools for enhanced therapeutic insights into lupeol’s potential for alopecia management
Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (2025)
-
Soluble CSF1R alleviates microgliopathy in a CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy (CRL) mouse model
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2025)
-
Low intensity pulsed ultrasound alleviates synovial fibrosis in osteoarthritis via the PI3K/AKT pathway
Scientific Reports (2025)
-
PHB2 protects against pressure overload-induced myocardial remodeling in mice via stabilizing TOMM40 and regulating mitochondrial morphofunctional homeostasis
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2025)
-
Inflammation in cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome: key roles and underlying mechanisms–a comprehensive review
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2025)