Abstract
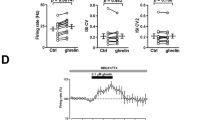
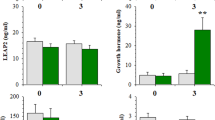
Ghrelin is a circulating orexigenic hormone that promotes feeding behavior and regulates metabolism in humans and rodents. We previously reported that local infusion of ghrelin into the basolateral amygdala (BLA) blocked memory acquisition for conditioned taste aversion (CTA) by activating growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a. In this study, we further explored the underlying mechanism and signaling pathways mediating ghrelin modulation of CTA memory in rats. Pharmacological agents targeting distinct signaling pathways were infused into the BLA during conditioning. We showed that preadministration of the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 abolished the repressive effect of ghrelin on CTA memory. Moreover, LY294002 pretreatment prevented ghrelin from inhibiting Arc and zif268 mRNA expression in the BLA triggered by CTA memory retrieval. Preadministration of rapamycin eliminated the repressive effect of ghrelin, while Gsk3 inhibitors failed to mimic ghrelin’s effect. In addition, PLC and PKC inhibitors microinfused in the BLA blocked ghrelin’s repression of CTA acquisition. These results demonstrate that ghrelin signaling in the BLA shapes CTA memory via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and PLC/PKC pathways. We conducted in vivo multichannel recordings from mouse BLA neurons and found that microinjection of ghrelin (20 µM) suppressed intrinsic excitability. By means of whole-cell recordings from rat brain slices, we showed that bath application of ghrelin (200 nM) had no effect on basal synaptic transmission or synaptic plasticity of BLA pyramidal neurons. Together, this study reveals the mechanism underlying ghrelin-induced interference with CTA memory acquisition in rats, i.e., suppression of intrinsic excitability of BLA principal neurons via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and PLC/PKC pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402:656–60.
Perello M, Cabral A, Cornejo MP, De Francesco PN, Fernandez G, Uriarte M. Brain accessibility delineates the central effects of circulating ghrelin. J Neuroendocrinol. 2019;31:e12677.
Murtuza MI, Isokawa M. Endogenous ghrelin-O-acyltransferase (GOAT) acylates local ghrelin in the hippocampus. J Neurochem. 2018;144:58–67.
Abizaid A, Hougland JL. Ghrelin Signaling: GOAT and GHS-R1a take a LEAP in complexity. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020;31:107–17.
Stevanovic DM, Grefhorst A, Themmen AP, Popovic V, Holstege J, Haasdijk E, et al. Unacylated ghrelin suppresses ghrelin-induced neuronal activity in the hypothalamus and brainstem of male rats [corrected]. PLoS One. 2014;9:e98180.
Hornsby AKE, Buntwal L, Carisi MC, Santos VV, Johnston F, Roberts LD, et al. Unacylated-ghrelin impairs hippocampal neurogenesis and memory in mice and is altered in Parkinson’s dementia in humans. Cell Rep Med. 2020;1:100120.
Agosti E, De Feudis M, Angelino E, Belli R, Alves Teixeira M, Zaggia I, et al. Both ghrelin deletion and unacylated ghrelin overexpression preserve muscles in aging mice. Aging. 2020;12:13939–57.
Howard AD, Feighner SD, Cully DF, Arena JP, Liberator PA, Rosenblum CI, et al. A receptor in pituitary and hypothalamus that functions in growth hormone release. Science. 1996;273:974–7.
Shiimura Y, Horita S, Hamamoto A, Asada H, Hirata K, Tanaka M, et al. Structure of an antagonist-bound ghrelin receptor reveals possible ghrelin recognition mode. Nat Commun. 2020;11:4160.
Andrews ZB. The extra-hypothalamic actions of ghrelin on neuronal function. Trends Neurosci. 2011;34:31–40.
Spencer SJ, Emmerzaal TL, Kozicz T, Andrews ZB. Ghrelin’s role in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis stress response: implications for mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2015;78:19–27.
Diano S, Farr SA, Benoit SC, McNay EC, da Silva I, Horvath B, et al. Ghrelin controls hippocampal spine synapse density and memory performance. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:381–8.
Ribeiro LF, Catarino T, Santos SD, Benoist M, van Leeuwen JF, et al. Ghrelin triggers the synaptic incorporation of AMPA receptors in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:E149–58.
Dresler M, Kluge M, Genzel L, Schussler P, Steiger A. Nocturnal administration of ghrelin does not promote memory consolidation. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2010;43:277–8.
Albarran-Zeckler RG, Brantley AF, Smith RG. Growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R1a) knockout mice exhibit improved spatial memory and deficits in contextual memory. Behav Brain Res. 2012;232:13–9.
Song L, Zhu Q, Liu T, Yu M, Xiao K, Kong Q, et al. Ghrelin modulates lateral amygdala neuronal firing and blocks acquisition for conditioned taste aversion. PLoS One. 2013;8:e65422.
Zhu Q, Xiao K, Yu M, Niu M, Li C, Gao Y, et al. Ghrelin but not nesfatin-1 affects certain forms of learning and memory in both rats and mice. Brain Res. 2013;1541:42–51.
Song G, Zhu Q, Han F, Liu S, Zhao C, Zhou Y. Local infusion of ghrelin into the lateral amygdala blocks extinction of conditioned taste aversion in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2018;662:71–6.
Bennett KA, Langmead CJ, Wise A, Milligan G. Growth hormone secretagogues and growth hormone releasing peptides act as orthosteric super-agonists but not allosteric regulators for activation of the G protein Galpha(o1) by the ghrelin receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 2009;76:802–11.
Evron T, Peterson SM, Urs NM, Bai Y, Rochelle LK, Caron MG, et al. G Protein and beta-arrestin signaling bias at the ghrelin receptor. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:33442–55.
Chung H, Li E, Kim Y, Kim S, Park S. Multiple signaling pathways mediate ghrelin-induced proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells. J Endocrinol. 2013;218:49–59.
Kanoski SE, Fortin SM, Ricks KM, Grill HJ. Ghrelin signaling in the ventral hippocampus stimulates learned and motivational aspects of feeding via PI3K-Akt signaling. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;73:915–23.
Cavalier M, Crouzin N, Ben Sedrine A, de Jesus Ferreira MC, Guiramand J, Cohen-Solal C, et al. Involvement of PKA and ERK pathways in ghrelin-induced long-lasting potentiation of excitatory synaptic transmission in the CA1 area of rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 2015;42:2568–76.
Chen L, Xing T, Wang M, Miao Y, Tang M, Chen J, et al. Local infusion of ghrelin enhanced hippocampal synaptic plasticity and spatial memory through activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in the dentate gyrus of adult rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2011;33:266–75.
Schellekens H, van Oeffelen WE, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Promiscuous dimerization of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R1a) attenuates ghrelin-mediated signaling. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:181–91.
Kern A, Mavrikaki M, Ullrich C, Albarran-Zeckler R, Brantley AF, Smith RG. Hippocampal dopamine/DRD1 signaling dependent on the ghrelin receptor. Cell. 2015;163:1176–90.
Li N, Song G, Wang Y, Zhu Q, Han F, Zhang C, et al. Blocking constitutive activity of GHSR1a in the lateral amygdala facilitates acquisition of conditioned taste aversion. Neuropeptides. 2018;68:22–7.
Cui L, Sun W, Yu M, Li N, Guo L, Gu H, et al. Disrupted-in-schizophrenia1 (DISC1) L100P mutation alters synaptic transmission and plasticity in the hippocampus and causes recognition memory deficits. Mol Brain. 2016;9:89.
Jones MW, Errington ML, French PJ, Fine A, Bliss TV, Garel S, et al. A requirement for the immediate early gene Zif268 in the expression of late LTP and long-term memories. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:289–96.
Plath N, Ohana O, Dammermann B, Errington ML, Schmitz D, Gross C, et al. Arc/Arg3.1 is essential for the consolidation of synaptic plasticity and memories. Neuron. 2006;52:437–44.
Lonergan ME, Gafford GM, Jarome TJ, Helmstetter FJ. Time-dependent expression of Arc and zif268 after acquisition of fear conditioning. Neural Plast. 2010;2010:139891.
Carlini VP, Varas MM, Cragnolini AB, Schioth HB, Scimonelli TN, de Barioglio SR. Differential role of the hippocampus, amygdala, and dorsal raphe nucleus in regulating feeding, memory, and anxiety-like behavioral responses to ghrelin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;313:635–41.
Camina JP, Carreira MC, El Messari S, Llorens-Cortes C, Smith RG, Casanueva FF. Desensitization and endocytosis mechanisms of ghrelin-activated growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a. Endocrinology. 2004;145:930–40.
Meyer RM, Burgos-Robles A, Liu E, Correia SS, Goosens KA. A ghrelin-growth hormone axis drives stress-induced vulnerability to enhanced fear. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19:1284–94.
Carlini VP, Monzon ME, Varas MM, Cragnolini AB, Schioth HB, Scimonelli TN, et al. Ghrelin increases anxiety-like behavior and memory retention in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;299:739–43.
Goshadrou F, Ronaghi A. Attenuating the effect of Ghrelin on memory storage via bilateral reversible inactivation of the basolateral amygdale. Behav Brain Res. 2012;232:391–4.
Cabral A, Lopez Soto EJ, Epelbaum J, Perello M. Is ghrelin synthesized in the central nervous system? Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:638.
Spitznagel MB, Benitez A, Updegraff J, Potter V, Alexander T, Glickman E, et al. Serum ghrelin is inversely associated with cognitive function in a sample of non-demented elderly. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2010;64:608–11.
Bellar D, Glickman EL, Judge LW, Gunstad J. Serum ghrelin is associated with verbal learning and adiposity in a sample of healthy, fit older adults. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:202757.
Yoshino Y, Funahashi Y, Nakata S, Ozaki Y, Yamazaki K, Yoshida T, et al. Ghrelin cascade changes in the peripheral blood of Japanese patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Psychiatr Res. 2018;107:79–85.
Cao X, Zhu M, He Y, Chu W, Du Y, Du H. Increased serum acylated ghrelin levels in patients with mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;61:545–52.
Ghersi MS, Gabach LA, Buteler F, Vilcaes AA, Schioth HB, Perez MF, et al. Ghrelin increases memory consolidation through hippocampal mechanisms dependent on glutamate release and NR2B-subunits of the NMDA receptor. Psychopharmacology. 2015;232:1843–57.
Lynch MA. Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:87–136.
Daoudal G, Debanne D. Long-term plasticity of intrinsic excitability. learning rules and mechanisms. Learn Mem. 2003;10:456–65.
Zhang W, Linden DJ. The other side of the engram. experience-driven changes in neuronal intrinsic excitability. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:885–900.
Disterhoft JF, Oh MM. Learning, aging and intrinsic neuronal plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 2006;29:587–99.
Matthews EA, Linardakis JM, Disterhoft JF. The fast and slow afterhyperpolarizations are differentially modulated in hippocampal neurons by aging and learning. J Neurosci. 2009;29:4750–5.
Oh MM, Oliveira FA, Disterhoft JF. Learning and aging related changes in intrinsic neuronal excitability. Front Aging Neurosci. 2010;2:2.
Oh MM, Disterhoft JF. Increased excitability of both principal neurons and interneurons during associative learning. Neuroscientist. 2015;21:372–84.
Yasoshima Y, Yamamoto T. Short-term and long-term excitability changes of the insular cortical neurons after the acquisition of taste aversion learning in behaving rats. Neuroscience. 1998;84:1–5.
Kim MJ, Mizumori SJ, Bernstein IL. Neuronal representation of conditioned taste in the basolateral amygdala of rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2010;93:406–14.
Chen L, Cummings K, Mau W, Zaki Y, Dong Z, Rabinowitz S, et al. The role of intrinsic excitability in the evolution of memory: significance in memory allocation, consolidation, and updating. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2020;173:107266.
Li N, Xiao K, Mi X, Li N, Guo L, Wang X, et al. Ghrelin signaling in dCA1 suppresses neuronal excitability and impairs memory acquisition via PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β cascades. Neuropharmacology. 2021;203:108871.
Shi L, Bian X, Qu Z, Ma Z, Zhou Y, Wang K, et al. Peptide hormone ghrelin enhances neuronal excitability by inhibition of Kv7/KCNQ channels. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1435.
Soom M, Schonherr R, Kubo Y, Kirsch C, Klinger R, Heinemann SH. Multiple PIP2 binding sites in Kir2.1 inwardly rectifying potassium channels. FEBS Lett. 2001;490:49–53.
Lopez Soto EJ, Agosti F, Cabral A, Mustafa ER, Damonte VM, Gandini MA, et al. Constitutive and ghrelin-dependent GHSR1a activation impairs CaV2.1 and CaV2.2 currents in hypothalamic neurons. J Gen Physiol. 2015;146:205–19.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NNSFC (Grant no. 32071141 and 91732110 to YZ, 31900854 to MY), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant no. 2019M662292 to MY), and NSFC of SD province (Grant no. ZR2019ZD34 and 2019GGX101045 to YZ, ZR201911120651 to NL). We thank Ms. Jennifer Li for native language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ designed and supervised the experiments. MY, QQZ and MLN performed behavioral experiments. ZSZ and JDG designed and performed electrophysiological experiment, NL and BQR helped with data analysis. YZ and TBY wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, M., Zhu, Qq., Niu, Ml. et al. Ghrelin infusion into the basolateral amygdala suppresses CTA memory formation in rats via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and PLC/PKC signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43, 2242–2252 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00859-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00859-w
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Stress-induced GHS-R1a expression in medial prefrontal cortical neurons promotes vulnerability to anxiety in mice
Communications Biology (2025)