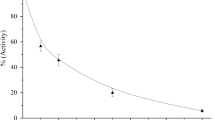
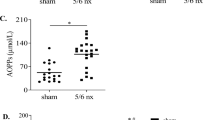
Abstract
Cytochrome P450s are important phase I metabolic enzymes located on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) involved in the metabolism of endogenous and exogenous substances. Our previous study showed that a hepatoprotective agent silybin restored CYP3A expression in mouse nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In this study we investigated how silybin regulated P450s activity during NAFLD. C57BL/6 mice were fed a high-fat-diet (HFD) for 8 weeks to induce NAFLD, and were administered silybin (50, 100 mg ·kg−1 ·d−1, i.g.) in the last 4 weeks. We showed that HFD intake induced hepatic steatosis and ER stress, leading to significant inhibition on the activity of five primary P450s including CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A in liver microsomes. These changes were dose-dependently reversed by silybin administration. The beneficial effects of silybin were also observed in TG-stimulated HepG2 cells in vitro. To clarify the underlying mechanism, we examined the components involved in the P450 catalytic system, membrane phospholipids and ER membrane fluidity, and found that cytochrome b5 (cyt b5) was significantly downregulated during ER stress, and ER membrane fluidity was also reduced evidenced by DPH polarization and lower polyunsaturated phospholipids levels. The increased ratios of NADP+/NADPH and PC/PE implied Ca2+ release and disruption of cellular Ca2+ homeostasis resulted from mitochondria dysfunction and cytochrome c (cyt c) release. The interaction between cyt c and cyt b5 under ER stress was an important reason for P450s activity inhibition. The effect of silybin throughout the whole course suggested that it regulated P450s activity through its anti-ER stress effect in NAFLD. Our results suggest that ER stress may be crucial for the inhibition of P450s activity in mouse NAFLD and silybin regulates P450s activity by attenuating ER stress.

Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Pavlides M, Cobbold J. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Medicine. 2019;47:728–33.
Li H, Canet MJ, Clarke JD, Billheimer D, Xanthakos SA, Lavine JE, et al. Pediatric cytochrome P450 activity alterations in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Drug Metab Dispos. 2017;45:1317–25.
Cobbina E, Akhlaghi F. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)—pathogenesis, classification, and effect on drug metabolizing enzymes and transporters. Drug Metab Rev. 2017;49:197–211.
Stiborova M, Indra R, Moserova M, Frei E, Schmeiser HH, Kopka K, et al. NADH: cytochrome b5 reductase and cytochrome b5 can act as sole electron donors to human cytochrome P450 1A1-mediated oxidation and DNA adduct formation by benzo[a]pyrene. Chem Res Toxicol. 2016;29:1325–34.
Hedison TM, Scrutton NS. Tripping the light fantastic in membrane redox biology: linking dynamic structures to function in ER electron transfer chains. FEBS J. 2019;286:2004–17.
Barnaba C, Martinez MJ, Taylor E, Barden AO, Brozik JA. Single-protein tracking reveals that NADPH mediates the insertion of cytochrome P450 reductase into a biomimetic of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139:5420–30.
Bhatt MR, Khatri Y, Rodgers RJ, Martin LL. Role of cytochrome b5 in the modulation of the enzymatic activities of cytochrome P450 17alpha-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase (P450 17A1). J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017;170:2–18.
Baylon JL, Lenov IL, Sligar SG, Tajkhorshid E. Characterizing the membrane-bound state of cytochrome P450 3A4: structure, depth of insertion, and orientation. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:8542–51.
Aghazadeh S, Amini R, Yazdanparast R, Ghaffari SH. Anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of Silybum marianum in treatment of experimental steatohepatitis. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2011;63:569–74.
Pradhan SC, Girish C. Hepatoprotective herbal drug, silymarin from experimental pharmacology to clinical medicine. Indian J Med Res. 2006;124:491–504.
Feng YY, Yan JY, Xia X, Liang JQ, Li F, Xie TF, et al. Effect and mechanism of total flavonoids of Lichi Semen on CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats, and prediction of Q-marker. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020;45:5722–31.
Wang H, Yan T, Xie Y, Zhao M, Che Y, Zhang J, et al. Mechanism-based inhibitory and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha-dependent modulating effects of silybin on principal hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015;43:444–54.
Gufford BT, Chen G, Lazarus P, Graf TN, Oberlies NH, Paine MF. Identification of diet-derived constituents as potent inhibitors of intestinal glucuronidation. Drug Metab Dispos. 2014;42:1675–83.
Wu JW, Lin LC, Tsai TH. Drug-drug interactions of silymarin on the perspective of pharmacokinetics. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009;121:185–93.
Zhang R, Xu D, Zhang Y, Wang R, Yang N, Lou Y, et al. Silybin restored CYP3A expression through the sirtuin 2/nuclear factor kappa-B pathway in mouse nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Drug Metab Dispos. 2021;49:770–9.
Zhang B, Xu D, She L, Wang Z, Yang N, Sun R, et al. Silybin inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome assembly through the NAD(+)/SIRT2 pathway in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. FASEB J. 2018;32:757–67.
Febvre-James M, Bruyere A, Le Vee M, Fardel O. The JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib reverses interleukin-6-mediated suppression of drug-detoxifying proteins in cultured human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2018;46:131–40.
Morgan ET. Regulation of cytochromes P450 during inflammation and infection. Drug Metab Rev. 1997;29:1129–88.
Renton KW. Cytochrome P450 regulation and drug biotransformation during inflammation and infection. Curr Drug Metab. 2004;5:235–43.
Shi J, Wang X, Lyu L, Jiang H, Zhu HJ. Comparison of protein expression between human livers and the hepatic cell lines HepG2, Hep3B, and Huh7 using SWATH and MRM-HR proteomics: focusing on drug-metabolizing enzymes. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2018;33:133–40.
Wang W, Cai Q, Zhou F, Liu J, Jin X, Ni P, et al. Impaired pentose phosphate pathway in the development of 3D MCF-7 cells mediated intracellular redox disturbance and multi-cellular resistance without drug induction. Redox Biol. 2018;15:253–65.
Gibbons E, Pickett KR, Streeter MC, Warcup AO, Nelson J, Judd AM, et al. Molecular details of membrane fluidity changes during apoptosis and relationship to phospholipase A(2) activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1828:887–95.
Tonshin AA, Saprunova VB, Solodovnikova IM, Bakeeva LE, Yaguzhinsky LS. Functional activity and ultrastructure of mitochondria isolated from myocardial apoptotic tissue. Biochemistry. 2003;68:875–81.
Jancova P, Anzenbacherova E, Papouskova B, Lemr K, Luzna P, Veinlichova A, et al. Silybin is metabolized by cytochrome P450 2C8 in vitro. Drug Metab Dispos. 2007;35:2035–9.
Mitchell KJ, Lai FA, Rutter GA. Ryanodine receptor type I and nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate receptors mediate Ca2+ release from insulin-containing vesicles in living pancreatic beta-cells (MIN6). J Biol Chem. 2003;278:11057–64.
Lee HC. Physiological functions of cyclic ADP-ribose and NAADP as calcium messengers. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001;41:317–45.
Patel S. NAADP-induced Ca2+ release—a new signalling pathway. Biol Cell. 2004;96:19–28.
Castuma CE, Brenner RR. Effect of fatty acid deficiency on microsomal membrane fluidity and cooperativity of the UDP-glucuronyltransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983;729:9–16.
Yang X, Sheng W, Sun GY, Lee JC. Effects of fatty acid unsaturation numbers on membrane fluidity and alpha-secretase-dependent amyloid precursor protein processing. Neurochem Int. 2011;58:321–9.
Fu S, Yang L, Li P, Hofmann O, Dicker L, Hide W, et al. Aberrant lipid metabolism disrupts calcium homeostasis causing liver endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity. Nature. 2011;473:528–31.
Tang L, Xu M, Zhang Y, Liu X, Zhang H. The role of mitochondrial permeability transition pore in chronic heart failure rats and potential protective effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid. J Tongji Univ (Med Sci). 2016;37:18.
Yun B, Lee H, Ghosh M, Cravatt BF, Hsu KL, Bonventre JV, et al. Serine hydrolase inhibitors block necrotic cell death by preventing calcium overload of the mitochondria and permeability transition pore formation. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:1491–504.
Gilabert-Oriol R, Mergel K, Thakur M, von Mallinckrodt B, Melzig MF, Fuchs H, et al. Real-time analysis of membrane permeabilizing effects of oleanane saponins. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013;21:2387–95.
Zhang L, Sanderson MJ. Oscillations in ciliary beat frequency and intracellular calcium concentration in rabbit tracheal epithelial cells induced by ATP. J Physiol. 2003;546:733–49.
Schenkman JB, Jansson I. The many roles of cytochrome b5. Pharmacol Ther. 2003;97:139–52.
Malhi H, Kaufman RJ. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol. 2011;54:795–809.
Luciani DS, Gwiazda KS, Yang TL, Kalynyak TB, Bychkivska Y, Frey MH, et al. Roles of IP3R and RyR Ca2+ channels in endoplasmic reticulum stress and beta-cell death. Diabetes. 2009;58:422–32.
Cederbaum AI. Molecular mechanisms of the microsomal mixed function oxidases and biological and pathological implications. Redox Biol. 2015;4:60–73.
Stiborova M, Indra R, Frei E, Kopeckova K, Schmeiser HH, Eckschlager T, et al. Cytochrome b5 plays a dual role in the reaction cycle of cytochrome P450 3A4 during oxidation of the anticancer drug ellipticine. Monatsh Chem. 2017;148:1983–91.
Sung C, Jung E, Choi KY, Bae JH, Kim M, Kim J, et al. The production of omega-hydroxy palmitic acid using fatty acid metabolism and cofactor optimization in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;99:6667–76.
Spector AA, Yorek MA. Membrane lipid composition and cellular function. J Lipid Res. 1985;26:1015–35.
Ahn T, Guengerich FP, Yun CH. Membrane insertion of cytochrome P450 1A2 promoted by anionic phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1998;37:12860–6.
Kim KH, Ahn T, Yun CH. Membrane properties induced by anionic phospholipids and phosphatidylethanolamine are critical for the membrane binding and catalytic activity of human cytochrome P450 3A4. Biochemistry. 2003;42:15377–87.
Park JW, Reed JR, Brignac-Huber LM, Backes WL. Cytochrome P450 system proteins reside in different regions of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 2014;464:241–9.
Strobel HW, Lu AY, Heidema J, Coon MJ. Phosphatidylcholine requirement in the enzymatic reduction of hemoprotein P-450 and in fatty acid, hydrocarbon, and drug hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1970;245:4851–4.
Michell RH. Do inositol supplements enhance phosphatidylinositol supply and thus support endoplasmic reticulum function? Br J Nutr. 2018;120:301–16.
Kirkby B, Roman N, Kobe B, Kellie S, Forwood JK. Functional and structural properties of mammalian acyl-coenzyme A thioesterases. Prog Lipid Res. 2010;49:366–77.
Szabadkai G, Simoni AM, Rizzuto R. Mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake requires sustained Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:15153–61.
Boyman L, Karbowski M, Lederer WJ. Regulation of mitochondrial ATP production: Ca2+ signaling and quality control. Trends Mol Med. 2020;26:21–39.
Szczepanowska J, Malinska D, Wieckowski MR, Duszynski J. Effect of mtDNA point mutations on cellular bioenergetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1817:1740–6.
Yamashita R, Fujii S, Ushioda R, Nagata K. Ca2+ imbalance caused by ERdj5 deletion affects mitochondrial fragmentation. Sci Rep. 2021;11:20772.
Hom JR, Gewandter JS, Michael L, Sheu SS, Yoon Y. Thapsigargin induces biphasic fragmentation of mitochondria through calcium-mediated mitochondrial fission and apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 2007;212:498–508.
Huang R, Zhang M, Rwere F, Waskell L, Ramamoorthy A. Kinetic and structural characterization of the interaction between the FMN binding domain of cytochrome P450 reductase and cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:4843–55.
Gentry KA, Prade E, Barnaba C, Zhang M, Mahajan M, Im SC, et al. Kinetic and structural characterization of the effects of membrane on the complex of cytochrome b 5 and cytochrome c. Sci Rep. 2017;7:7793.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81872932, 81673679), the Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province (SWYY-061), the Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (SZSM201801060), the Project of State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, China Pharmaceutical University (No. SKLNMZZ202001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YX and JW designed this study. JW, YGL, XLY, RW, and RZ conducted the experiments. JW, YGL, and XLY contributed new reagents or analytic tools. JW, YGL, XLY and RZ performed data analysis. YX, JW, JYA, and GJW wrote or contributed to the writing of the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Lou, Yg., Yang, Xl. et al. Silybin regulates P450s activity by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress in mouse nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 44, 133–144 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00924-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00924-4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The synergistic effects of citicoline and silymarin on liver injury and thyroid hormone disturbances in γ-irradiated rats
Molecular Biology Reports (2025)
-
Silybin inhibits succinate production and secretion in hepatocytes to reverse liver fibrosis
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2025)
-
Silybin attenuates avermectin-induced oxidative damage in carp respiration by modulating the cGAS-STING pathway and endoplasmic reticulum stress
Fish Physiology and Biochemistry (2024)
-
Ameliorative effects of silybin against avermectin-triggered carp spleen mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis through inhibition of PERK-ATF4-CHOP signaling pathway
Fish Physiology and Biochemistry (2023)