Abstract
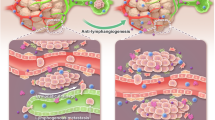
The high incidence of lymphatic metastasis is closely related to poor prognosis and mortality in cancers. Potent inhibitors to prevent pathological lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic spread are urgently needed. The VEGF-C-VEGFR3 pathway plays a vital role in driving lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis. In addition, COX2 in tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) facilitates lymphangiogenesis. We recently reported that aiphanol, a natural stilbenolignan, attenuates tumor angiogenesis by repressing VEGFR2 and COX2. In this study, we evaluated the antilymphangiogenic and antimetastatic potency of aiphanol using in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo systems. We first demonstrated that aiphanol directly bound to VEGFR3 and blocked its kinase activity with an half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value of 0.29 μM in an in vitro ADP-GloTM kinase assay. Furthermore, we showed that aiphanol (7.5−30 μM) dose-dependently counteracted VEGF-C-induced proliferation, migration and tubular formation of lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs), which was further verified in vivo. VEGFR3 knockdown markedly mitigated the inhibitory potency of aiphanol on lymphangiogenesis. In 4T1-luc breast tumor-bearing mice, oral administration of aiphanol (5 and 30 mg· kg−1 ·d−1) dose-dependently decreased lymphatic metastasis and prolonged survival time, which was associated with impaired lymphangiogenesis, angiogenesis and, interestingly, macrophage infiltration. In addition, we found that aiphanol decreased the COX2-dependent secretion of PGE2 and VEGF-C from tumor cells and macrophages. These results demonstrate that aiphanol is an appealing agent for preventing lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic dissemination by synergistically targeting VEGFR3 and inhibiting the COX2-PGE2-VEGF-C signaling axis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Steeg PS. Targeting metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:201–18.
Alitalo K. The lymphatic vasculature in disease. Nat Med. 2011;17:1371–80.
Dieterich LC, Seidel CD, Detmar M. Lymphatic vessels: new targets for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Angiogenesis. 2014;17:359–71.
Stacker SA, Williams SP, Karnezis T, Shayan R, Fox SB, Achen MG. Lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic vessel remodelling in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14:159–72.
Stacker SA, Achen MG, Jussila L, Baldwin ME, Alitalo K. Lymphangiogenesis and cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:573–83.
Wu H, Rahman H, Dong Y, Liu X, Lee Y, Wen A, et al. Epsin deficiency promotes lymphangiogenesis through regulation of VEGFR3 degradation in diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2018;128:4025–43.
Burton JB, Priceman SJ, Sung JL, Brakenhielm E, An DS, Pytowski B, et al. Suppression of prostate cancer nodal and systemic metastasis by blockade of the lymphangiogenic axis. Cancer Res. 2008;68:7828–37.
Alam A, Blanc I, Gueguen-Dorbes G, Duclos O, Bonnin J, Barron P, et al. SAR, a potent and selective VEGFR-3-TK inhibitor with antilymphangiogenic, antitumoral, and antimetastatic activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11:1637–49.
Lee D, Cuendet M, Vigo JS, Graham JG, Cabieses F, Fong HH, et al. A novel cyclooxygenase-inhibitory stilbenolignan from the seeds of Aiphanes aculeata. Org Lett. 2001;3:2169–71.
Chen S, Feng J, Zhao C, Wang L, Meng L, Liu C, et al. Aiphanol, a native compound, suppresses angiogenesis via dual-targeting VEGFR2 and COX2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:413.
Lala PK, Nandi P, Majumder M. Roles of prostaglandins in tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis with special reference to breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018;37:369–84.
Su JL, Shih JY, Yen ML, Jeng YM, Chang CC, Hsieh CY, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 induces EP1- and HER-2/Neu-dependent vascular endothelial growth factor-C up-regulation: a novel mechanism of lymphangiogenesis in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2004;64:554–64.
Chen C, He W, Huang J, Wang B, Li H, Cai Q, et al. LNMAT1 promotes lymphatic metastasis of bladder cancer via CCL2 dependent macrophage recruitment. Nat Commun. 2018;9:3826.
Ji H, Cao R, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Iwamoto H, Lim S, et al. TNFR1 mediates TNF-α-induced tumour lymphangiogenesis and metastasis by modulating VEGF-C-VEGFR3 signalling. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4944.
Cao Y. Opinion: emerging mechanisms of tumour lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:735–43.
Lohela M, Saaristo A, Veikkola T, Alitalo K. Lymphangiogenic growth factors, receptors and therapies. Thromb Haemost. 2003;90:167–84.
Chang J, Kim Y, Kwon HJ. Advances in identification and validation of protein targets of natural products without chemical modification. Nat Prod Rep. 2016;33:719–30.
Jafari R, Almqvist H, Axelsson H, Ignatushchenko M, Lundbäck T, Nordlund P, et al. The cellular thermal shift assay for evaluating drug target interactions in cells. Nat Protoc. 2014;9:2100–22.
Arroyo-Crespo JJ, Armiñán A, Charbonnier D, Deladriere C, Palomino-Schätzlein M, Lamas-Domingo R, et al. Characterization of triple-negative breast cancer preclinical models provides functional evidence of metastatic progression. Int J Cancer. 2019;145:2267–81.
Dinicola S, Masiello MG, Proietti S, Coluccia P, Fabrizi G, Catizone A, et al. Nicotine increases colon cancer cell migration and invasion through epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT): COX-2 involvement. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:4935–48.
Hosono K, Isonaka R, Kawakami T, Narumiya S, Majima M. Signaling of prostaglandin E receptors, EP3 and EP4 facilitates wound healing and lymphangiogenesis with enhanced recruitment of M2 macrophages in mice. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0162532.
Dieterich LC, Detmar M. Tumor lymphangiogenesis and new drug development. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;99:148–60.
Yang C, Ma C, Li Y, Mo P, Yang Y. High Tiam1 expression predicts positive lymphatic metastasis and worse survival in patients with malignant solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:5925–36.
Biaoxue R, Xiling J, Shuanying Y, Wei Z, Xiguang C, Jinsui W, et al. Upregulation of Hsp90-beta and annexin A1 correlates with poor survival and lymphatic metastasis in lung cancer patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012;31:70.
Dixelius J, Makinen T, Wirzenius M, Karkkainen MJ, Wernstedt C, Alitalo K, et al. Ligand-induced vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR-3) heterodimerization with VEGFR-2 in primary lymphatic endothelial cells regulates tyrosine phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:40973–9.
Salameh A, Galvagni F, Bardelli M, Bussolino F, Oliviero S. Direct recruitment of CRK and GRB2 to VEGFR-3 induces proliferation, migration, and survival of endothelial cells through the activation of ERK, AKT, and JNK pathways. Blood. 2005;106:3423–31.
Lyons TR, O'brien J, Borges VF, Conklin MW, Keely PJ, Eliceiri KW, et al. Postpartum mammary gland involution drives progression of ductal carcinoma in situ through collagen and COX-2. Nat Med. 2011;17:1109–15.
Lyons TR, Borges VF, Betts CB, Guo Q, Kapoor P, Martinson HA, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent lymphangiogenesis promotes nodal metastasis of postpartum breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:3901–12.
Tammela T, Alitalo K. Lymphangiogenesis: molecular mechanisms and future promise. Cell. 2010;140:460–76.
Matias M, Le Teuff G, Albiges L, Guida A, Brard C, Bacciarelo G, et al. Real world prospective experience of axitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma in a large comprehensive cancer centre. Eur J Cancer. 2017;79:185–92.
Duerinck J, Du Four S, Bouttens F, Andre C, Verschaeve V, Van Fraeyenhove F, et al. Randomized phase II trial comparing axitinib with the combination of axitinib and lomustine in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 2018;136:115–25.
Kanwar SS, Yu Y, Nautiyal J, Patel BB, Padhye S, Sarkar FH, et al. Difluorinated-curcumin (CDF): a novel curcumin analog is a potent inhibitor of colon cancer stem-like cells. Pharmacol Res. 2011;28:827–38.
Matsuo M, Sakurai H, Koizumi K, Saiki I. Curcumin inhibits the formation of capillary-like tubes by rat lymphatic endothelial cells. Cancer Lett. 2007;251:288–95.
Astin JW, Jamieson SM, Eng TC, Flores MV, Misa JP, Chien A, et al. An in vivo antilymphatic screen in zebrafish identifies novel inhibitors of mammalian lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic-mediated metastasis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13:2450–62.
Tai HC, Lee TH, Tang CH, Chen LP, Chen WC, Lee MS, et al. Phomaketide A inhibits lymphangiogenesis in human lymphatic endothelial cells. Mar Drugs. 2019;17:215.
Kimura Y, Sumiyoshi M. Resveratrol prevents tumor growth and metastasis by inhibiting lymphangiogenesis and M2 macrophage activation and differentiation in tumor-associated macrophages. Nutr Cancer. 2016;68:667–78.
Kimura Y, Sumiyoshi M. Anti-tumor and anti-metastatic actions of wogonin isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis roots through anti-lymphangiogenesis. Phytomedicine. 2013;20:328–36.
Xu J, Yu Y, He X, Niu N, Li X, Zhang R, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages induce invasion and poor prognosis in human gastric cancer in a cyclooxygenase-2/MMP9-dependent manner. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11:6040–54.
Chen EP, Markosyan N, Connolly E, Lawson JA, Li X, Grant GR, et al. Myeloid cell COX-2 deletion reduces mammary tumor growth through enhanced cytotoxic T-lymphocyte function. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:1788–97.
Li J, Qin S, Xu RH, Shen L, Xu J, Bai Y, et al. Effect of fruquintinib vs placebo on overall survival in patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer: The FRESCO Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2018;319:2486–96.
Rini BI, Pal SK, Escudier BJ, Atkins MB, Hutson TE, Porta C, et al. Tivozanib versus sorafenib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (TIVO-3): a phase 3, multicentre, randomised, controlled, open-label study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:95–104.
Sharma P, Allison JP. Immune checkpoint targeting in cancer therapy: toward combination strategies with curative potential. Cell. 2015;161:205–14.
Melero I, Berman DM, Aznar MA, Korman AJ, Pérez Gracia JL, Haanen J. Evolving synergistic combinations of targeted immunotherapies to combat cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15:457–72.
Sunay MM, Foote JB, Leatherman JM, Edwards JP, Armstrong TD, Nirschl CJ, et al. Sorafenib combined with HER-2 targeted vaccination can promote effective T cell immunity in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;46:112–23.
Läubli H, Müller P, D’Amico L, Buchi M, Kashyap AS, Zippelius A. The multi-receptor inhibitor axitinib reverses tumor-induced immunosuppression and potentiates treatment with immune-modulatory antibodies in preclinical murine models. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2018;67:815–24.
Prima V, Kaliberova LN, Kaliberov S, Curiel DT, Kusmartsev S. COX2/mPGES1/PGE2 pathway regulates PD-L1 expression in tumor-associated macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:1117–22.
Tang H, Liu Y, Wang C, Zheng H, Chen Y, Liu W, et al. Inhibition of COX-2 and EGFR by melafolone improves anti-PD-1 therapy through vascular normalization and PD-L1 downregulation in lung cancer. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019;368:401–13.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81773219), National Basic Research Program of China (2015CB553906), the Digestive Medical Coordinated Development Center of Beijing Hospitals Authority (XXT21, China), Clinical Medicine Plus X - Young Scholars Project, Peking University, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (PKU2022LCXQ021) and the PKU-Baidu Fund (2019BD015, China). The author would like to thank Mrs. Hui Xu (Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, China) for help in animal studies, Dr. Bin Dong (Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, China) for assistance in frozen sections, and Mrs. Jing Wang (School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Peking University, Beijing, China) for assistance in SPR and BLI assays.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CCS, LKQ, CKZ and YXJ designed experiments; YXJ and LCY synthesized Aiphanol and biotin-Aiphanol. SMC, LXW, and YNM carried out experiments; SMC, CCS, LKQ and CKZ analyzed experimental results; CCS, LKQ, SMC and CKZ wrote the manuscript; LM and CYL provided laboratory assistance. SQC identified Aiphanol from Sarsaparilla.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Sm., Zhao, Ck., Yao, Lc. et al. Aiphanol, a multi-targeting stilbenolignan, potently suppresses mouse lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 44, 189–200 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00940-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00940-4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Synergistic effects of mTOR inhibitors with VEGFR3 inhibitors on the interaction between TSC2-mutated cells and lymphatic endothelial cells
Science China Life Sciences (2025)