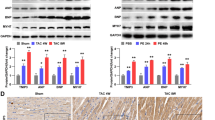
Abstract
Tax1 banding protein 1 (Tax1bp1) was originally identified as an NF-κB regulatory protein that participated in inflammatory, antiviral and innate immune processes. Tax1bp1 also functions as an autophagy receptor that plays a role in autophagy. Our previous study shows that Tax1bp1 protects against cardiomyopathy in STZ-induced diabetic mice. In this study we investigated the role of Tax1bp1 in heart failure. Pressure overload-induced heart failure model was established in mice by aortic banding (AB) surgery, and angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced heart failure model was established by infusion of Ang II through osmotic minipump for 4 weeks. We showed that the expression levels of Tax1bp1 in the heart were markedly increased 2 and 4 weeks after AB surgery. Knockdown of Tax1bp1 in mouse hearts significantly ameliorated both AB- and Ang II infusion-induced heart failure parameters. On the contrary, AB-induced heart failure was aggravated in cardiac-specific Tax1bp1 transgenic mice. Similar results were observed in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCMs) under Ang II insult. We demonstrated that the pro-heart failure effect of Tax1bp1 resulted from its interaction with the E3 ligase ITCH to promote the transcription factor P73 ubiquitination and degradation, causing enhanced BCL2 interacting protein 3 (BNIP3)-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Knockdown ITCH or BNIP3 in NRCMs significantly reduced Ang II-induced apoptosis in vitro. Similarly, BNIP3 knockdown attenuated heart failure in cardiac-specific Tax1bp1 transgenic mice. In the left ventricles of heart failure patients, Tax1bp1 expression level was significantly increased; Tax1bp1 gene expression was negatively correlated with left ventricular ejection fraction in heart failure patients. Collectively, the Tax1bp1 increase in heart failure enhances ITCH-P73-BNIP3-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis and induced cardiac injury. Tax1bp1 may serve as a potent therapeutic target for the treatment of heart failure.
• Cardiac Tax1bp1 transgene mice were more vulnerable to cardiac dysfunction under stress.
• Cardiac Tax1bp1 transgene mice were more vulnerable to cardiac dysfunction under stress.
• Knockout of Tax1bp1 in mouse hearts ameliorated heart failure induced by pressure overload.
• Tax1bp1 interacts with the E3 ligase Itch to promote P73 ubiquitination and degradation, causing enhanced BNIP3-mediated apoptosis.
• Tax1bp1 may become a target of new therapeutic methods for treating heart failure.

Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Di Palo KE, Barone NJ. Hypertension and heart failure: prevention, targets, and treatment. Heart Fail Clin. 2020;16:99–106.
Groenewegen A, Rutten FH, Mosterd A, Hoes AW. Epidemiology of heart failure. Eur J Heart Failure. 2020;22:1342–56.
Braunwald E. Heart failure. Jacc Heart Fail. 2013;1:1–20.
Wu QQ, Xiao Y, Yuan Y, Ma ZG, Liao HH, Liu C, et al. Mechanisms contributing to cardiac remodelling. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017;131:2319–45.
Jones NR, Roalfe AK, Adoki I, Hobbs FDR, Taylor CJ. Survival of patients with chronic heart failure in the community: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019;21:1306–25.
Vasagiri N, Kutala VK. Structure, function, and epigenetic regulation of BNIP3: a pathophysiological relevance. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41:7705–14.
Webster KA, Graham RM, Bishopric NH. BNip3 and signal-specific programmed death in the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2005;38:35–45.
Zhang J, Ney PA. Role of BNIP3 and NIX in cell death, autophagy, and mitophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2009;16:939–46.
Dhingra A, Jayas R, Afshar P, Guberman M, Maddaford G, Gerstein J, et al. Ellagic acid antagonizes Bnip3-mediated mitochondrial injury and necrotic cell death of cardiac myocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;112:411–22.
Fordjour PA, Wang L, Gao H, Li L, Wang Y, Nyagblordzro M, et al. Targeting BNIP3 in inflammation-mediated heart failure: a novel concept in heart failure therapy. Heart Fail Rev. 2016;21:489–97.
Choi YB, Shembade N, Parvatiyar K, Balachandran S, Harhaj EW. TAX1BP1 restrains virus-induced apoptosis by facilitating Itch-mediated degradation of the mitochondrial adaptor MAVS. Mol Cell Biol. 2016;37:e00422–16.
Matsushita N, Suzuki M, Ikebe E, Nagashima S, Inatome R, Asano K, et al. Regulation of B cell differentiation by the ubiquitin-binding protein TAX1BP1. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31266.
Nakano S, Ikebe E, Tsukamoto Y, Wang Y, Matsumoto T, Mitsui T, et al. Commensal microbiota contributes to chronic endocarditis in TAX1BP1 deficient mice. PLoS One. 2013;8:e73205.
Tumbarello DA, Manna PT, Allen M, Bycroft M, Arden SD, Kendrick-Jones J, et al. The autophagy receptor TAX1BP1 and the molecular motor Myosin VI are required for clearance of salmonella typhimurium by autophagy. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1005174.
Xiao Y, Wu QQ, Duan MX, Liu C, Yuan Y, Yang Z, et al. TAX1BP1 overexpression attenuates cardiac dysfunction and remodeling in STZ-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy in mice by regulating autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2018;1864:1728–43.
Whang MI, Tavares RM, Benjamin DI, Kattah MG, Advincula R, Nomura DK, et al. The ubiquitin binding protein TAX1BP1 mediates autophagasome induction and the metabolic transition of activated T Cells. Immunity. 2017;46:405–20.
De Valck D, Jin DY, Heyninck K, Van de Craen M, Contreras R, Fiers W, et al. The zinc finger protein A20 interacts with a novel anti-apoptotic protein which is cleaved by specific caspases. Oncogene. 1999;18:4182–90.
Wu QQ, Xiao Y, Duan MX, Yuan Y, Jiang XH, Yang Z, et al. Aucubin protects against pressure overload-induced cardiac remodelling via the beta3 -adrenoceptor-neuronal NOS cascades. Br J Pharmacol. 2018;175:1548–66.
Wu QQ, Xu M, Yuan Y, Li FF, Yang Z, Liu Y, et al. Cathepsin B deficiency attenuates cardiac remodeling in response to pressure overload via TNF-alpha/ASK1/JNK pathway. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;308:H1143–54.
Wu QQ, Liu C, Cai Z, Xie Q, Hu T, Duan M, et al. High-mobility group AT-hook 1 promotes cardiac dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy via autophagy inhibition. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:160.
Bienko M, Green CM, Crosetto N, Rudolf F, Zapart G, Coull B, et al. Ubiquitin-binding domains in Y-family polymerases regulate translesion synthesis. Science. 2005;310:1821–4.
Levy D, Adamovich Y, Reuven N, Shaul Y. The Yes-associated protein 1 stabilizes p73 by preventing Itch-mediated ubiquitination of p73. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:743–51.
Parvatiyar K, Barber GN, Harhaj EW. TAX1BP1 and A20 inhibit antiviral signaling by targeting TBK1-IKKi kinases. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:14999–5009.
Sarraf SA, Shah HV, Kanfer G, Pickrell AM, Holtzclaw LA, Ward ME, et al. Loss of TAX1BP1-directed autophagy results in protein aggregate accumulation in the brain. Mol Cell. 2020;80:779–95 e10.
Verstrepen L, Verhelst K, Carpentier I, Beyaert R. TAX1BP1, a ubiquitin-binding adaptor protein in innate immunity and beyond. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011;36:347–54.
Yang Q, Liu TT, Lin H, Zhang M, Wei J, Luo WW, et al. TRIM32-TAX1BP1-dependent selective autophagic degradation of TRIF negatively regulates TLR3/4-mediated innate immune responses. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006600.
Iha H, Peloponese JM, Verstrepen L, Zapart G, Ikeda F, Smith CD, et al. Inflammatory cardiac valvulitis in TAX1BP1-deficient mice through selective NF-kappaB activation. EMBO J. 2008;27:629–41.
Jia G, Whaley-Connell A, Sowers JR. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: a hyperglycaemia- and insulin-resistance-induced heart disease. Diabetologia. 2018;61:21–8.
Du J, Liu Y, Fu J. Autophagy and heart failure. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1207:223–7.
Del Re DP, Amgalan D, Linkermann A, Liu Q, Kitsis RN. Fundamental mechanisms of regulated cell death and implications for heart disease. Physiol Rev. 2019;99:1765–817.
Petrova V, Mancini M, Agostini M, Knight RA, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Barlev NA, et al. TAp73 transcriptionally represses BNIP3 expression. Cell Cycle. 2015;14:2484–93.
Levy D, Reuven N, Shaul Y. A regulatory circuit controlling Itch-mediated p73 degradation by Runx. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:27462–8.
Rossi M, De Laurenzi V, Munarriz E, Green DR, Liu YC, Vousden KH, et al. The ubiquitin-protein ligase Itch regulates p73 stability. EMBO J. 2005;24:836–48.
Corsetti G, Pasini E, Romano C, Chen-Scarabelli C, Scarabelli TM, Flati V, et al. How can malnutrition affect autophagy in chronic heart failure? Focus and Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22.
Corsetti G, Chen-Scarabelli C, Romano C, Pasini E, Dioguardi FS, Onorati F, et al. Autophagy and oncosis/necroptosis are enhanced in cardiomyocytes from heart failure patients. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2019;25:33–44.
Gao A, Jiang J, Xie F, Chen L. Bnip3 in mitophagy: novel insights and potential therapeutic target for diseases of secondary mitochondrial dysfunction. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;506:72–83.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82170382 and 81700353), Hubei Province’s Outstanding Medical Academic Leader Program, National Key R&D Program of China(2018YFC1311300)and the Fundamental Research Funds of the Central Universities (2042017kf0060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QQW and QZT: conceived and designed the experiments; YY, QY, TTH, and YW: performed the experiments; QWX and JHZ: analyzed the data; QQW: wrote and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Qq., Yao, Q., Hu, Tt. et al. Tax1 banding protein 1 exacerbates heart failure in mice by activating ITCH-P73-BNIP3-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43, 2562–2572 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00950-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-00950-2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Piezo1 in heart failure: A new perspective from cytomechanical sensing to diverse cellular pathways
Molecular Biology Reports (2025)
-
FTO-targeted siRNA delivery by MSC-derived exosomes synergistically alleviates dopaminergic neuronal death in Parkinson's disease via m6A-dependent regulation of ATM mRNA
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)