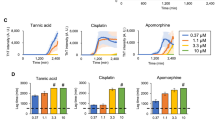
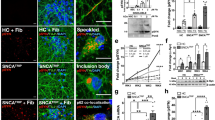
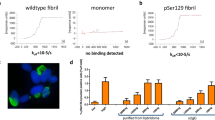
Abstract
Aggregation of α-synuclein, a component of Lewy bodies (LBs) or Lewy neurites in Parkinson’s disease (PD), is strongly linked with disease development, making it an attractive therapeutic target. Inhibiting aggregation can slow or prevent the neurodegenerative process. However, the bottleneck towards achieving this goal is the lack of such inhibitors. In the current study, we established a high-throughput screening platform to identify candidate compounds for preventing the aggregation of α-synuclein among the natural products in our in-house compound library. We found that a small molecule, 03A10, i.e., (+)-desdimethylpinoresinol, which is present in the fruits of Vernicia fordii (Euphorbiaceae), modulated aggregated α-synuclein, but not monomeric α-synuclein, to prevent further elongation of α-synuclein fibrils. In α-synuclein-overexpressing cell lines, 03A10 (10 μM) efficiently prevented α-synuclein aggregation and markedly ameliorated the cellular toxicity of α-synuclein fibril seeds. In the MPTP/probenecid (MPTP/p) mouse model, oral administration of 03A10 (0.3 mg· kg−1 ·d−1, 1 mg ·kg−1 ·d−1, for 35 days) significantly alleviated behavioral deficits, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) neuron degeneration and p-α-synuclein aggregation in the substantia nigra (SN). As the Braak hypothesis postulates that the prevailing site of early PD pathology is the gastrointestinal tract, we inoculated α-synuclein preformed fibrils (PFFs) into the mouse colon. We demonstrated that α-synuclein PFF inoculation promoted α-synuclein pathology and neuroinflammation in the gut and brain; oral administration of 03A10 (5 mg· kg−1 ·d−1, for 4 months) significantly attenuated olfactory deficits, α-synuclein accumulation and neuroinflammation in the olfactory bulb and SN. We conclude that 03A10 might be a promising drug candidate for the treatment of PD.

03A10 might be a novel drug candidate for PD treatment, as it inhibits α-synuclein aggregation by modulating aggregated α-synuclein rather than monomeric α-synuclein to prevent further elongation of α-synuclein fibrils and prevent α-synuclein toxicity in vitro, in an MPTP/p mouse model, and PFF-inoculated mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bloem BR, Okun MS, Klein C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 2021;397:2284–303.
Schapira AHV, Chaudhuri KR, Jenner P. Non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18:435–50.
Ganguly U, Chakrabarti SS, Kaur U, Mukherjee A, Chakrabarti S. Alpha-synuclein, Proteotoxicity and Parkinson’s disease: search for neuroprotective therapy. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16:1086–97.
Bengoa-Vergniory N, Roberts RF, Wade-Martins R, Alegre-Abarrategui J. Alpha-synuclein oligomers: a new hope. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;134:819–38.
Braak H, Ghebremedhin E, Rub U, Bratzke H, Del Tredici K. Stages in the development of Parkinson’s disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res. 2004;318:121–34.
Klingelhoefer L, Reichmann H. Pathogenesis of Parkinson disease–the gut-brain axis and environmental factors. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11:625–36.
Baumgartner AJ, Press DZ, Simon DK. The relationship between olfactory dysfunction and constipation in early Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2021;36:781–2.
Kim S, Kwon SH, Kam TI, Panicker N, Karuppagounder SS, Lee S, et al. Transneuronal propagation of pathologic alpha-synuclein from the gut to the brain models Parkinson’s disease. Neuron. 2019;103:627–41.
Uemura N, Yagi H, Uemura MT, Hatanaka Y, Yamakado H, Takahashi R. Inoculation of alpha-synuclein preformed fibrils into the mouse gastrointestinal tract induces Lewy body-like aggregates in the brainstem via the vagus nerve. Mol Neurodegener. 2018;13:21.
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Quinn SM, Zhang B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM, Neuronal α-synucleinopathy with severe movement disorder in mice expressing A53T Human α-Synuclein. Neuron 2002;34:521–33.
Wu Q, Yang X, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Feng L. Chronic mild stress accelerates the progression of Parkinson’s disease in A53T alpha-synuclein transgenic mice. Exp Neurol. 2016;285:61–71.
Hu H, Wang Q, Du J, Liu Z, Ding Y, Xue H, et al. Aha1 exhibits distinctive dynamics behavior and chaperone-like activity. Molecules 2021;26:1943.
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Luk KC, Lee VM. Addition of exogenous alpha-synuclein preformed fibrils to primary neuronal cultures to seed recruitment of endogenous alpha-synuclein to Lewy body and Lewy neurite-like aggregates. Nat Protoc. 2014;9:2135–46.
Volpicelli-Daley LA, Luk KC, Patel TP, Tanik SA, Riddle DM, Stieber A, et al. Exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils induce Lewy body pathology leading to synaptic dysfunction and neuron death. Neuron. 2011;72:57–71.
Luk KC, Song C, O'Brien P, Stieber A, Branch JR, Brunden KR, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM. Exogenous α-synuclein fibrils seed the formation of Lewy body-like intracellular inclusions in cultured cells. PNAS. 2009;106:20051–6.
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A, NMRPipe: A multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 1995;6:277–93.
Remy I, Michnick SW. A highly sensitive protein-protein interaction assay based on Gaussia luciferase. Nat Methods. 2006;3:977–9.
Kerppola TK. Visualization of molecular interactions by fluorescence complementation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:449–56.
Zhang Y, Wu Q, Zhang L, Wang Q, Yang Z, Liu J, et al. Caffeic acid reduces A53T alpha-synuclein by activating JNK/Bcl-2-mediated autophagy in vitro and improves behaviour and protects dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Pharm Res. 2019;150:104538.
Hu CD, Chinenov Y, Kerppola TK. Visualization of interactions among bZIP and Rel family proteins in living cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Mol Cell. 2002;9:789–98.
McAllister BB, Lacoursiere SG, Sutherland RJ, Mohajerani MH. Intracerebral seeding of amyloid-beta and tau pathology in mice: Factors underlying prion-like spreading and comparisons with alpha-synuclein. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020;112:1–27.
Tuttle MD, Comellas G, Nieuwkoop AJ, Covell DJ, Berthold DA, Kloepper KD, et al. Solid-state NMR structure of a pathogenic fibril of full-length human alpha-synuclein. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016;23:409–15.
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24:197–211.
Doty RL. Olfactory dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2012;8:329–39.
Keshavarzian A, Green SJ, Engen PA, Voigt RM, Naqib A, Forsyth CB, et al. Colonic bacterial composition in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2015;30:1351–60.
Zhang Q, Hu J, Feng JW, Hu XT, Wang T, Gong WX, et al. Influenza infection elicits an expansion of gut population of endogenous Bifidobacterium animalis which protects mice against infection. Genome Biol. 2020;21:99.
Hawkes CH, Del Tredici K, Braak H. A timeline for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2010;16:79–84.
Challis C, Hori A, Sampson TR, Yoo BB, Challis RC, Hamilton AM, et al. Gut-seeded alpha-synuclein fibrils promote gut dysfunction and brain pathology specifically in aged mice. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23:327–36.
Bartels T, Choi JG, Selkoe DJ. alpha-Synuclein occurs physiologically as a helically folded tetramer that resists aggregation. Nature. 2011;477:107–10.
Fusco G, Chen SW, Williamson PTF, Cascella R, Perni M, Jarvis JA, et al. Structural basis of membrane disruption and cellular toxicity by alpha-synuclein oligomers. Science. 2017;358:1440–3.
Li Y, Zhao C, Luo F, Liu Z, Gui X, Luo Z, et al. Amyloid fibril structure of alpha-synuclein determined by cryo-electron microscopy. Cell Res. 2018;28:897–903.
Zhao TT, Shin KS, Kim KS, Park HJ, Kim HJ, Lee KE, et al. Effects of (-)-sesamin on motor and memory deficits in an MPTP-lesioned mouse model of Parkinson’s disease treated with l-DOPA. Neuroscience. 2016;339:644–54.
Acknowledgements
The research reported in this publication was supported by grants from the National Science & Technology Major Project “Key New Drug Creation and Manufacturing Program”, China (2018ZX09711002-003-013), and the Scientific Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA12040304 and XDA12040216). This project was supported by the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology, China (18DZ2290200), and the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (2020B0303070002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LYF conceived and designed the experiments; QW, ZXY, Yu Zhang, Ye Zhang, and LZ performed most experiments; SY and YY synthesized 03A10; CZ and NXZ performed NMR and ITC; JTL, ZJX, and WLZ performed the molecular docking experiment; and QW and LYF wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Yao, S., Yang, Zx. et al. Pharmacological characterization of the small molecule 03A10 as an inhibitor of α-synuclein aggregation for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Acta Pharmacol Sin 44, 1122–1134 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-01039-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-022-01039-6
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Emerging targets of α-synuclein spreading in α-synucleinopathies: a review of mechanistic pathways and interventions
Molecular Neurodegeneration (2025)
-
Alternate-day fasting ameliorates α-synuclein pathology and suppresses inflammation via the gut-brain axis in an MPTP-induced subacute mouse model of Parkinson’s disease
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes (2025)
-
Exploring α-Syn’s Functions Through Ablation Models: Physiological and Pathological Implications
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2025)
-
Alpha-synuclein pathology and Parkinson’s disease-related olfactory dysfunctions: an update on preclinical models and therapeutic approaches
Mammalian Genome (2025)