Abstract
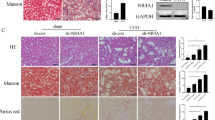
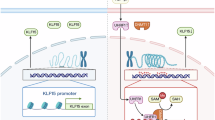
The pyroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells leads to tubular loss and inflammation and then promotes renal fibrosis. The transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) can bidirectionally regulate the transcription of target genes. Our previous study revealed that sustained elevation of KLF4 is responsible for the transition of acute kidney injury (AKI) into chronic kidney disease (CKD) and renal fibrosis. In this study, we explored the upstream mechanisms of renal tubular epithelial cell pyroptosis from the perspective of posttranslational regulation and focused on the transcription factor KLF4. Mice were subjected to unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) surgery and euthanized on D7 or D14 for renal tissue harvesting. We showed that the pyroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells mediated by both the Caspase-1/GSDMD and Caspase-3/GSDME pathways was time-dependently increased in UUO mouse kidneys. Furthermore, we found that the expression of the transcription factor KLF4 was also upregulated in a time-dependent manner in UUO mouse kidneys. Tubular epithelial cell-specific Klf4 knockout alleviated UUO-induced pyroptosis and renal fibrosis. In Ang II-treated mouse renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (MTECs), we demonstrated that KLF4 bound to the promoter regions of Caspase-3 and Caspase-1 and directly increased their transcription. In addition, we found that ubiquitin-specific protease 11 (USP11) was increased in UUO mouse kidneys. USP11 deubiquitinated KLF4. Knockout of Usp11 or pretreatment with the USP11 inhibitor mitoxantrone (3 mg/kg, i.p., twice a week for two weeks before UUO surgery) significantly alleviated the increases in KLF4 expression, pyroptosis and renal fibrosis. These results demonstrated that the increased expression of USP11 in renal tubular cells prevents the ubiquitin degradation of KLF4 and that elevated KLF4 promotes inflammation and renal fibrosis by initiating tubular cell pyroptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Zhang L, Long J, Jiang W, Shi Y, He X, Zhou Z, et al. Trends in chronic kidney disease in China. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:905–6.
Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, Bragg-Gresham J, Chen X, Gipson D, et al. US renal data system 2019 annual data report: epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;75:A6–A7.
Ni JY, Wang X, Xie HY, Yang NH, Li JY, Sun XA, et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme USP11 promotes renal tubular cell senescence and fibrosis via inhibiting the ubiquitin degradation of TGF-β receptor II. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023;44:584–95.
Nastase MV, Zeng-Brouwers J, Wygrecka M, Schaefer L. Targeting renal fibrosis: mechanisms and drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;129:295–307.
Humphreys BD. Mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2018;80:309–26.
Liu BC, Tang TT, Lv LL, Lan HY. Renal tubule injury: a driving force toward chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2018;93:568–79.
Maremonti F, Meyer C, Linkermann A. Mechanisms and models of kidney tubular necrosis and nephron loss. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022;33:472–86.
Ferenbach DA, Bonventre JV. Mechanisms of maladaptive repair after AKI leading to accelerated kidney ageing and CKD. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015;11:264–76.
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, Agostinis P, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:486–541.
Tang D, Kang R, Berghe TV, Vandenabeele P, Kroemer G. The molecular machinery of regulated cell death. Cell Res. 2019;29:347–64.
Bergsbaken T, Fink SL, Cookson BT. Pyroptosis: host cell death and inflammation. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009;7:99–109.
Li Y, Yuan Y, Huang ZX, Chen H, Lan R, Wang Z, et al. GSDME-mediated pyroptosis promotes inflammation and fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28:2333–50.
Liu X, Zhang Z, Ruan J, Pan Y, Magupalli VG, Wu H, et al. Inflammasome-activated gasdermin D causes pyroptosis by forming membrane pores. Nature. 2016;535:153–8.
He WT, Wan H, Hu L, Chen P, Wang X, Huang Z, et al. Gasdermin D is an executor of pyroptosis and required for interleukin-1β secretion. Cell Res. 2015;25:1285–98.
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Gao W, Ding J, Li P, et al. Inflammatory caspases are innate immune receptors for intracellular LPS. Nature. 2014;514:187–92.
Wang Y, Gao W, Shi X, Ding J, Liu W, He H, et al. Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature. 2017;547:99–103.
Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Xia S, Kong Q, Li S, Liu X, et al. Gasdermin E suppresses tumour growth by activating anti-tumour immunity. Nature. 2020;579:415–20.
Hu L, Chen M, Chen X, Zhao C, Fang Z, Wang H, et al. Chemotherapy-induced pyroptosis is mediated by BAK/BAX-caspase-3-GSDME pathway and inhibited by 2-bromopalmitate. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:281.
Ghaleb AM, Yang VW. Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4): what we currently know. Gene. 2017;611:27–37.
Rane MJ, Zhao Y, Cai L. Krϋppel-like factors (KLFs) in renal physiology and disease. EBioMedicine. 2019;40:743–50.
Shields JM, Christy RJ, Yang VW. Identification and characterization of a gene encoding a gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor expressed during growth arrest. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20009–17.
Ghaleb AM, Katz JP, Kaestner KH, Du JX, Yang VW. Krüppel-like factor 4 exhibits antiapoptotic activity following gamma-radiation-induced DNA damage. Oncogene. 2007;26:2365–73.
Li Z, Zhao J, Li Q, Yang W, Song Q, Li W, et al. KLF4 promotes hydrogen-peroxide-induced apoptosis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells involving the Bcl-2/Bax pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2010;15:905–12.
Saha B, Bala S, Hosseini N, Kodys K, Szabo G. Krüppel-like factor 4 is a transcriptional regulator of M1/M2 macrophage polarization in alcoholic liver disease. J Leukoc Biol. 2015;97:963–73.
Hamik A, Lin Z, Kumar A, Balcells M, Sinha S, Katz J, et al. Kruppel-like factor 4 regulates endothelial inflammation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:13769–79.
Ke B, Zhang A, Wu X, Fang X. The role of Krüppel-like factor 4 in renal fibrosis. Front Physiol. 2015;6:327.
Xu D, Chen PP, Zheng PQ, Yin F, Cheng Q, Zhou ZL, et al. KLF4 initiates sustained YAP activation to promote renal fibrosis in mice after ischemia-reperfusion kidney injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021;42:436–50.
Chen ZY, Wang X, Zhou Y, Offner G, Tseng CC. Destabilization of Krüppel-like factor 4 protein in response to serum stimulation involves the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Cancer Res. 2005;65:10394–400.
Park J, Cho J, Song EJ. Ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) as a target for anticancer treatment. Arch Pharm Res. 2020;43:1144–61.
Çetin G, Klafack S, Studencka-Turski M, Krüger E, Ebstein F. The ubiquitin-proteasome system in immune cells. Biomolecules. 2021;11:60.
Harper S, Gratton HE, Cornaciu I, Oberer M, Scott DJ, Emsley J, et al. Structure and catalytic regulatory function of ubiquitin specific protease 11 N-terminal and ubiquitin-like domains. Biochemistry. 2014;53:2966–78.
Miao NJ, Xie HY, Xu D, Yin JY, Wang YZ, Wang B, et al. Caspase-11 promotes renal fibrosis by stimulating IL-1β maturation via activating caspase-1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40:790–800.
Reis-Mendes A, Dores-Sousa JL, Padrão AI, Duarte-Araújo M, Duarte JA, Seabra V, et al. Inflammation as a possible trigger for mitoxantrone-induced cardiotoxicity: an in vivo study in adult and infant mice. Pharmaceuticals. 2021;14:510.
Subramaniam V, Chuang G, Xia H, Burn B, Bradley J, Maderdrut JL, et al. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) protects against mitoxantrone-induced cardiac injury in mice. Peptides. 2017;95:25–32.
Brandão SR, Reis-Mendes A, Domingues P, Duarte JA, Bastos ML, Carvalho F, et al. Exploring the aging effect of the anticancer drugs doxorubicin and mitoxantrone on cardiac mitochondrial proteome using a murine model. Toxicology. 2021;459:152852.
Huang M, Zhu S, Huang H, He J, Tsuji K, Jin WW, et al. Integrin-linked kinase deficiency in collecting duct principal cell promotes necroptosis of principal cell and contributes to kidney inflammation and fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;30:2073–90.
He W, Dai C, Li Y, Zeng G, Monga SP, Liu Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes renal interstitial fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:765–76.
Jiang M, Qi L, Li L, Li Y. The caspase-3/GSDME signal pathway as a switch between apoptosis and pyroptosis in cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2020;6:112.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82370695, 82070712) to L Lu and (81900623, 82270728) to Y Wen. Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (21ZR1409000) to W Zhang. National Clinical Research Center for Aging and Medicine, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University (2024KF2004) to L Lu. Special Basic Cooperative Research Programs of Yunnan Provincial Undergraduate Universities’ Association (202301BA070001-047) to L Lu. We are grateful to Pro. Bicheng Liu (Southeast University, Nanjing) and Hui-juan Wu (Fudan University, Shanghai) for research information and experimental materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LML, HX, and XW participated in the design of the study. LML and XW wrote the paper. XW and XX performed the experiments and analysed the results. XW, XX, JYN, JYL, XAS, HYX, NHY, HJG, LL, MN, LZ, JL, CX, WZ, YW, and QS revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Xie, X., Ni, Jy. et al. USP11 promotes renal tubular cell pyroptosis and fibrosis in UUO mice via inhibiting KLF4 ubiquitin degradation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 46, 159–170 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01363-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01363-z
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Gasdermin D regulates the activation of EGFR in colorectal cancer
Journal of Translational Medicine (2024)