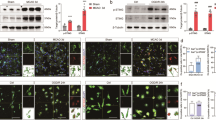
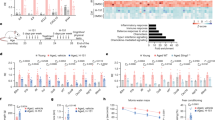
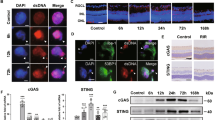
Abstract
Neuroinflammation, a significant contributor to secondary brain injury, plays a critical role in the pathological process and prognosis of intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH). Thus, developing interventions to mitigate secondary neuroimmune deterioration is of paramount importance. Currently, no effective immunomodulatory drugs are available for ICH. The cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)−stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway is a recently identified innate immune-sensing pathway primarily expressed in microglia within the central nervous system (CNS) that has been implicated in the pathophysiology of various neurological diseases. In this study we investigated the role of cGAS-STING pathway in ICH. A collagenase model of ICH was established in mice. Brain tissues were collected on D1 or D3 post-ICH. We observed a significant increase in double-stranded (dsDNA) levels and activation of the cGAS-STING pathway in the perihaematomal region of ICH mice. Administration of a blood brain barrier-permeable STING antagonist H151 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly decreased cell apoptosis, alleviated hematoma growth, and improved motor impairments in ICH mice, accompanied by inhibiting the STING pathway in microglia, reducing production/release of the cGAS-STING pathway downstream inflammatory factors, NLRP3 inflammasome activation and gasdermin D (GSDMD)-induced microglial pyroptosis. Microglial Sting conditional knockout significantly mitigated ICH-induced neuroinflammatory responses, pathological damage and motor dysfunction. These results suggest that the microglial STING pathway promotes brain pathological damage and behavioural defects in ICH mice by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome and microglial pyroptosis. The STING pathway may serve as a potential therapeutic target for ICH-induced secondary brain injury.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xi G, Keep RF, Hoff JT. Mechanisms of brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:53–63.
Broderick JP, Grotta JC, Naidech AM, Steiner T, Sprigg N, Toyoda K, et al. The story of intracerebral hemorrhage: from recalcitrant to treatable disease. Stroke. 2021;52:1905–14.
Cordonnier C, Demchuk A, Ziai W, Anderson CS. Intracerebral haemorrhage: current approaches to acute management. Lancet. 2018;392:1257–68.
Tschoe C, Bushnell CD, Duncan PW, Alexander-Miller MA, Wolfe SQ. Neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage and potential therapeutic targets. J Stroke. 2020;22:29–46.
Magid-Bernstein J, Girard R, Polster S, Srinath A, Romanos S, Awad IA, et al. Cerebral hemorrhage: pathophysiology, treatment, and future directions. Circ Res. 2022;130:1204–29.
Lan X, Han X, Li Q, Yang QW, Wang J. Modulators of microglial activation and polarization after intracerebral haemorrhage. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13:420–33.
Shao A, Zhu Z, Li L, Zhang S, Zhang J. Emerging therapeutic targets associated with the immune system in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH): from mechanisms to translation. EBioMedicine. 2019;45:615–23.
Heneka MT, McManus RM, Latz E. Inflammasome signalling in brain function and neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018;19:610–21.
Swanson KV, Deng M, Ting JP. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19:477–89.
Chen D, Dixon BJ, Doycheva DM, Li B, Zhang Y, Hu Q, et al. IRE1alpha inhibition decreased TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation through miR-17-5p after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rats. J Neuroinflamm. 2018;15:32.
Li W, Shen N, Kong L, Huang H, Wang X, Zhang Y, et al. STING mediates microglial pyroptosis via interaction with NLRP3 in cerebral ischaemic stroke. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2024;9:153–64.
Lei P, Li Z, Hua Q, Song P, Gao L, Zhou L, et al. Ursolic acid alleviates neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage by mediating microglial pyroptosis via the NF-kappaB/NLRP3/GSDMD pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:14771.
Toldo S, Abbate A. The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024;21:219–37.
Guo S, Wang R, Hu J, Sun L, Zhao X, Zhao Y, et al. Photobiomodulation promotes hippocampal CA1 NSC differentiation toward neurons and facilitates cognitive function recovery involving NLRP3 inflammasome mitigation following global cerebral ischemia. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021;15:731855.
Yu P, Zhang X, Liu N, Tang L, Peng C, Chen X. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:128.
Wei C, Jiang W, Wang R, Zhong H, He H, Gao X, et al. Brain endothelial GSDMD activation mediates inflammatory BBB breakdown. Nature. 2024;629:893–900.
Liu X, Zhang Z, Ruan J, Pan Y, Magupalli VG, Wu H, et al. Inflammasome-activated gasdermin D causes pyroptosis by forming membrane pores. Nature. 2016;535:153–8.
Wu J, Sun L, Chen X, Du F, Shi H, Chen C, et al. Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA. Science. 2013;339:826–30.
Gulen MF, Samson N, Keller A, Schwabenland M, Liu C, Gluck S, et al. cGAS-STING drives ageing-related inflammation and neurodegeneration. Nature. 2023;620:374–80.
Zhang X, Bai XC, Chen ZJ. Structures and mechanisms in the cGAS-STING innate immunity pathway. Immunity. 2020;53:43–53.
Balka KR, Louis C, Saunders TL, Smith AM, Calleja DJ, D’Silva DB, et al. TBK1 and IKKepsilon act redundantly to mediate STING-Induced NF-kappaB responses in myeloid cells. Cell Rep. 2020;31:107492.
Ding R, Li H, Liu Y, Ou W, Zhang X, Chai H, et al. Activating cGAS-STING axis contributes to neuroinflammation in CVST mouse model and induces inflammasome activation and microglia pyroptosis. J Neuroinflamm. 2022;19:137.
Li Y, Li J, Yu Q, Ji L, Peng B. METTL14 regulates microglia/macrophage polarization and NLRP3 inflammasome activation after ischemic stroke by the KAT3B-STING axis. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;185:106253.
Gaidt MM, Ebert TS, Chauhan D, Ramshorn K, Pinci F, Zuber S, et al. The DNA inflammasome in human myeloid cells is initiated by a STING-cell death program upstream of NLRP3. Cell. 2017;171:1110–24.e18.
Wang W, Hu D, Wu C, Feng Y, Li A, Liu W, et al. STING promotes NLRP3 localization in ER and facilitates NLRP3 deubiquitination to activate the inflammasome upon HSV-1 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2020;16:e1008335.
Gamdzyk M, Doycheva DM, Araujo C, Ocak U, Luo Y, Tang J, et al. cGAS/STING pathway activation contributes to delayed neurodegeneration in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model: possible involvement of LINE-1. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57:2600–19.
Shao J, Meng Y, Yuan K, Wu Q, Zhu S, Li Y, et al. RU.521 mitigates subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced brain injury via regulating microglial polarization and neuroinflammation mediated by the cGAS/STING/NF-kappaB pathway. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21:264.
Xu C, Pan Y, Zhang H, Sun Y, Cao Y, Qi P, et al. Platelet-membrane-coated polydopamine nanoparticles for neuroprotection by reducing oxidative stress and repairing damaged vessels in intracerebral hemorrhage. Adv Health Mater. 2023;12:e2300797.
Kobritz M, Borjas T, Patel V, Coppa G, Aziz M, Wang P. H151, a small molecule inhibitor of sting as a novel therapeutic in intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Shock. 2022;58:241–50.
Xu C, Jiang F, Mao Y, Wei W, Song J, Jia F, et al. Disulfiram attenuates cell and tissue damage and blood‒brain barrier dysfunction after intracranial haemorrhage by inhibiting the classical pyroptosis pathway. Sci Rep. 2024;14:21860.
Ren H, Kong Y, Liu Z, Zang D, Yang X, Wood K, et al. Selective NLRP3 (pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome inhibitor reduces brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2018;49:184–92.
Fan H, Ding R, Liu W, Zhang X, Li R, Wei B, et al. Heat shock protein 22 modulates NRF1/TFAM-dependent mitochondrial biogenesis and DRP1-sparked mitochondrial apoptosis through AMPK-PGC1alpha signaling pathway to alleviate the early brain injury of subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Redox Biol. 2021;40:101856.
Yang J, Li Q, Wang Z, Qi C, Han X, Lan X, et al. Multimodality MRI assessment of grey and white matter injury and blood-brain barrier disruption after intracerebral haemorrhage in mice. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40358.
Liu Y, Cui F, Xu A, Wang B, Ma Y, Zhang Q, et al. Interaction between the PERK/ATF4 branch of the endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial one-carbon metabolism regulates neuronal survival after intracerebral hemorrhage. Int J Biol Sci. 2024;20:4277–96.
Xu J, Chen Z, Yu F, Liu H, Ma C, Xie D, et al. IL-4/STAT6 signaling facilitates innate hematoma resolution and neurological recovery after hemorrhagic stroke in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:32679–90.
Xiao Y, Zhao C, Tai Y, Li B, Lan T, Lai E, et al. STING mediates hepatocyte pyroptosis in liver fibrosis by epigenetically activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Redox Biol. 2023;62:102691.
Haag SM, Gulen MF, Reymond L, Gibelin A, Abrami L, Decout A, et al. Targeting STING with covalent small-molecule inhibitors. Nature. 2018;559:269–73.
Wu C, Zhang S, Sun H, Li A, Hou F, Qi L, et al. STING inhibition suppresses microglia-mediated synapses engulfment and alleviates motor functional deficits after stroke. J Neuroinflamm. 2024;21:86.
Xie X, Ma G, Li X, Zhao J, Zhao Z, Zeng J. Activation of innate immune cGAS-STING pathway contributes to Alzheimer’s pathogenesis in 5xFAD mice. Nat Aging. 2023;3:202–12.
Li Y, Liu C, Wang G, Wang H, Liu X, Huang C, et al. HDAC3 inhibitor (BRD3308) modulates microglial pyroptosis and neuroinflammation through PPARgamma/NLRP3/GSDMD to improve neurological function after intraventricular hemorrhage in mice. Neuropharmacology. 2023;237:109633.
Karmakar M, Minns M, Greenberg EN, Diaz-Aponte J, Pestonjamasp K, Johnson JL, et al. N-GSDMD trafficking to neutrophil organelles facilitates IL-1beta release independently of plasma membrane pores and pyroptosis. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2212.
Hayman TJ, Baro M, MacNeil T, Phoomak C, Aung TN, Cui W, et al. STING enhances cell death through regulation of reactive oxygen species and DNA damage. Nat Commun. 2021;12:2327.
Li N, Zhou H, Wu H, Wu Q, Duan M, Deng W, et al. STING-IRF3 contributes to lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction, inflammation, apoptosis and pyroptosis by activating NLRP3. Redox Biol. 2019;24:101215.
Wang C, Yang T, Xiao J, Xu C, Alippe Y, Sun K, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation triggers gasdermin D-independent inflammation. Sci Immunol. 2021;6:eabj3859.
Coll RC, Robertson AA, Chae JJ, Higgins SC, Munoz-Planillo R, Inserra MC, et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat Med. 2015;21:248–55.
Tapia-Abellan A, Angosto-Bazarra D, Martinez-Banaclocha H, de Torre-Minguela C, Ceron-Carrasco JP, Perez-Sanchez H, et al. MCC950 closes the active conformation of NLRP3 to an inactive state. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15:560–4.
Hu JJ, Liu X, Xia S, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Zhao J, et al. FDA-approved disulfiram inhibits pyroptosis by blocking gasdermin D pore formation. Nat Immunol. 2020;21:736–45.
Aglietti RA, Estevez A, Gupta A, Ramirez MG, Liu PS, Kayagaki N, et al. GsdmD p30 elicited by caspase-11 during pyroptosis forms pores in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:7858–63.
Ding J, Wang K, Liu W, She Y, Sun Q, Shi J, et al. Pore-forming activity and structural autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature. 2016;535:111–6.
Devant P, Kagan JC. Molecular mechanisms of gasdermin D pore-forming activity. Nat Immunol. 2023;24:1064–75.
Zhao Q, Wei Y, Pandol SJ, Li L, Habtezion A. STING signaling promotes inflammation in experimental acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:1822–35 e2.
Abdullah A, Zhang M, Frugier T, Bedoui S, Taylor JM, Crack PJ. STING-mediated type-I interferons contribute to the neuroinflammatory process and detrimental effects following traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflamm. 2018;15:323.
Woo MS, Mayer C, Binkle-Ladisch L, Sonner JK, Rosenkranz SC, Shaposhnykov A, et al. STING orchestrates the neuronal inflammatory stress response in multiple sclerosis. Cell. 2024;187:4043–60.e30.
Hou Y, Wei Y, Lautrup S, Yang B, Wang Y, Cordonnier S, et al. NAD+ supplementation reduces neuroinflammation and cell senescence in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease via cGAS-STING. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118:e2011226118.
Hinkle JT, Patel J, Panicker N, Karuppagounder SS, Biswas D, Belingon B, et al. STING mediates neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation in nigrostriatal alpha-synucleinopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2022;119:e2118819119.
Zhou X, Wang J, Yu L, Qiao G, Qin D, Yuen-Kwan Law B, et al. Mitophagy and cGAS-STING crosstalk in neuroinflammation. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024;14:3327–61.
Maimaiti M, Li C, Cheng M, Zhong Z, Hu J, Yang L, et al. Blocking cGAS-STING pathway promotes post-stroke functional recovery in an extended treatment window via facilitating remyelination. Med. 2024;5:622–44.e8.
Li Q, Cao Y, Dang C, Han B, Han R, Ma H, et al. Inhibition of double-strand DNA-sensing cGAS ameliorates brain injury after ischemic stroke. EMBO Mol Med. 2020;12:e11002.
Bader ER, Pana TA, Barlas RS, Metcalf AK, Potter JF, Myint PK. Elevated inflammatory biomarkers and poor outcomes in intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurol. 2022;269:6330–41.
Gu T, Pan J, Chen L, Li K, Wang L, Zou Z, et al. Association of inflammatory cytokines expression in cerebrospinal fluid with the severity and prognosis of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. BMC Neurol. 2024;24:7.
Xue M, Yong VW. Neuroinflammation in intracerebral haemorrhage: immunotherapies with potential for translation. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:1023–32.
Pan Y, You Y, Sun L, Sui Q, Liu L, Yuan H, et al. The STING antagonist H-151 ameliorates psoriasis via suppression of STING/NF-kappaB-mediated inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 2021;178:4907–22.
Wu B, Xu MM, Fan C, Feng CL, Lu QK, Lu HM, et al. STING inhibitor ameliorates LPS-induced ALI by preventing vascular endothelial cells-mediated immune cells chemotaxis and adhesion. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43:2055–66.
Hu Z, Zhang F, Brenner M, Jacob A, Wang P. The protective effect of H151, a novel STING inhibitor, in renal ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2023;324:F558–F67.
Qiao H, Chiu Y, Liang X, Xia S, Ayrapetyan M, Liu S, et al. Microglia innate immune response contributes to the antiviral defense and blood-CSF barrier function in human choroid plexus organoids during HSV-1 infection. J Med Virol. 2023;95:e28472.
Zamiri K, Kesari S, Paul K, Hwang SH, Hammock B, Kaczor-Urbanowicz KE, et al. Therapy of autoimmune inflammation in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: dimethyl fumarate and H-151 downregulate inflammatory cytokines in the cGAS-STING pathway. FASEB J. 2023;37:e23068.
Ohashi SN, DeLong JH, Kozberg MG, Mazur-Hart DJ, van Veluw SJ, Alkayed NJ, et al. Role of inflammatory processes in hemorrhagic stroke. Stroke. 2023;54:605–19.
Sun L, Wu J, Du F, Chen X, Chen ZJ. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science. 2013;339:786–91.
Loan JJ, Kirby C, Emelianova K, Dando OR, Poon MT, Pimenova L, et al. Secondary injury and inflammation after intracerebral haemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis of molecular markers in patient brain tissue. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2022;93:126–32.
Gu F, Wang Z, Ding H, Tao X, Zhang J, Dai K, et al. Microglial mitochondrial DNA release contributes to neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage through activating AIM2 inflammasome. Exp Neurol. 2024;382:114950.
Yu CH, Davidson S, Harapas CR, Hilton JB, Mlodzianoski MJ, Laohamonthonkul P, et al. TDP-43 triggers mitochondrial DNA release via mPTP to activate cGAS/STING in ALS. Cell. 2020;183:636–49.e18.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFF1203005), the China National Science and Technology Innovation 2030 (2021ZD0204004), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 22177068, 22494694, 82171292), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (Grant 24ZR1491100, 22ZR1434700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YXX, YJC, MZQ, and FFS performed the experiments. YXX processed and analysed the data. YXX, YY, and CYD wrote the manuscript. YHS, AZ, LGB, YTL, and YY provided the critical reagents and participated in the discussions. CYD, YY, and AZ conceived and designed the study. All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Yx., Chen, Yj., Qin, Mz. et al. Microglial STING activation promotes neuroinflammation and pathological changes in experimental mice with intracerebral haemorrhage. Acta Pharmacol Sin 46, 2376–2392 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01540-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01540-8
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Renal denervation alleviates neuroinflammation by suppressing the microglial Ifi27l2a/cGAS-STING signaling axis
Inflammation Research (2025)