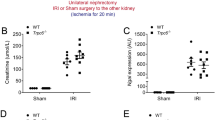
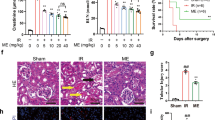
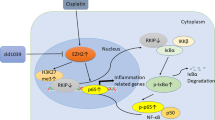
Abstract
Methotrexate (MTX) is frequently administered with the proton pump inhibitor omeprazole (OPZ) to relieve gastrointestinal adverse reactions of MTX, but the coadministration increases the risk of kidney injury. In this study, we investigated the mechanisms of combined OPZ and MTX-induced acute kidney injury (OPZ + MTX-AKI), which was induced in rats or mice by administration of OPZ plus MTX for 14 days. Analysis of the FAERS database revealed that AKI was the principal form of kidney injury when OPZ was administered with MTX. We showed that coadministration of OPZ and MTX to rats resulted in the development of AKI. We found that OPZ and MTX, by inhibiting the expression and activity of SERCA2 and IP3R, respectively, jointly disrupted Ca2+ homeostasis, thereby causing cell damage. Transcriptomic analysis of clinical samples revealed that G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) served as a key protein in OPZ + MTX-AKI. In Grk2+/− mice and in mice with renal tubular epithelial cell (RTEC)-specific Grk2 knockdown, the manifestations of kidney injury, along with the levels of oxidative stress and apoptosis in the context of OPZ + MTX-AKI, were notably ameliorated. Conversely, in mice with RTEC-specific Grk2 overexpression, the kidney injury was markedly aggravated. Administration of GRK2 inhibitor CP-25 (17.5, 35, 70 mg/kg/d, i.g.) for 14 days dose-dependently alleviated OPZ + MTX-AKI in mice with RTEC-specific Grk2 overexpression. This study elucidates a novel mechanism of AKI induced by the combination of OPZ and MTX and identifies potential therapeutic targets. We provide an essential theoretical foundation for the rational clinical application of OPZ and MTX, as well as for prevention and treatment of the related kidney injury.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levey AS, Eckardt KU, Dorman NM, Christiansen SL, Hoorn EJ, Ingelfinger JR, et al. Nomenclature for kidney function and disease: report of a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Consensus Conference. Kidney Int. 2020;97:1117–29.
Chen C, Xie D, Gewirtz DA, Li N. Nephrotoxicity in cancer treatment: an update. Adv Cancer Res. 2022;155:77–129.
Chan ES, Cronstein BN. Methotrexate-how does it really work? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6:175–8.
Yu J, Zhou P. The advances of methotrexate resistance in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammopharmacology. 2020;28:1183–93.
Bitoun S, Nocturne G, Ly B, Krzysiek R, Roques P, Pruvost A, et al. Methotrexate and BAFF interaction prevents immunization against TNF inhibitors. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:1463–70.
Ramsey LB, Balis FM, O’Brien MM, Schmiegelow K, Pauley JL, Bleyer A, et al. Consensus guideline for use of glucarpidase in patients with high-dose methotrexate induced acute kidney injury and delayed methotrexate clearance. Oncologist. 2018;23:52–61.
Widemann BC, Adamson PC. Understanding and managing methotrexate nephrotoxicity. Oncologist. 2006;11:694–703.
Jones B, Hewson E, Price A. Acute interstitial nephritis due to omeprazole. Lancet. 1994;344:1017–8.
Tun KM, Laeeq T, Mohammed S, Naik K, Ohning G. A rare case of methotrexate-induced gastric ulcer. Cureus. 2023;15:e36321.
Kumar C, Kuhn M, Herrmann K, Leuchten N, Aringer M. Severe methotrexate toxicity in elderly patients under diuretics. RMD Open. 2024;10:e003827.
Jafari F, Arasteh O, Hosseinjani H, Allahyari A, Ataei Azimi S, Askari VR. A critical review of methotrexate clinical interactions: role of transporters. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2023;19:91–107.
Joerger M, Huitema AD, van den Bongard HJ, Baas P, Schornagel JH, Schellens JH, et al. Determinants of the elimination of methotrexate and 7-hydroxy-methotrexate following high-dose infusional therapy to cancer patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006;62:71–80.
Zhang Y, Sun L, Chen X, Zhao L, Wang X, Zhao Z, et al. A systematic review of population pharmacokinetic models of methotrexate. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2022;47:143–64.
Wang X, Song Y, Wang J, He J, Liu R, Li X, et al. Effect of proton pump inhibitors on high-dose methotrexate elimination: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pharm. 2020;42:23–30.
Wang W, Guan X, Wang S, Shi L, Zhu Y, Hua P, et al. Epirubicin and gait apraxia: a real-world data analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System database. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1249845.
Al-Shabanah OA, Aleisa AM, Al-Yahya AA, Al-Rejaie SS, Bakheet SA, Fatani AG, et al. Increased urinary losses of carnitine and decreased intramitochondrial coenzyme A in gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in rats. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2010;25:69–76.
Widemann BC, Balis FM, Kempf-Bielack B, Bielack S, Pratt CB, Ferrari S, et al. High-dose methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in patients with osteosarcoma. Cancer. 2004;100:2222–32.
Perazella MA, Moeckel GW. Nephrotoxicity from chemotherapeutic agents: clinical manifestations, pathobiology, and prevention/therapy. Semin Nephrol. 2010;30:570–81.
Torpey N, Barker T, Ross C. Drug-induced tubulo-interstitial nephritis secondary to proton pump inhibitors: experience from a single UK renal unit. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19:1441–6.
Geevasinga N, Coleman PL, Roger SD. Rabeprazole-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Nephrology. 2005;10:7–9.
Klassen S, Krepinsky JC, Prebtani AP. Pantoprazole-induced acute interstitial nephritis. CMAJ. 2013;185:56–9.
Geevasinga N, Kairaitis L, Rangan GK, Coleman PL. Acute interstitial nephritis secondary to esomeprazole. Med J Aust. 2005;182:235–6.
Nypaver J, Nair D, Deshpande S, Amin S, Wynn J, Shrestha M, et al. A case of omeprazole-associated acute interstitial nephritis. Cureus. 2024;16:e55035.
Blank ML, Parkin L, Paul C, Herbison P. A nationwide nested case-control study indicates an increased risk of acute interstitial nephritis with proton pump inhibitor use. Kidney Int. 2014;86:837–44.
Chioukh R, Noel-Hudson MS, Ribes S, Fournier N, Becquemont L, Verstuyft C. Proton pump inhibitors inhibit methotrexate transport by renal basolateral organic anion transporter hOAT3. Drug Metab Dispos. 2014;42:2041–8.
Suzuki K, Doki K, Homma M, Tamaki H, Hori S, Ohtani H, et al. Co-administration of proton pump inhibitors delays elimination of plasma methotrexate in high-dose methotrexate therapy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009;67:44–9.
Song N, Yang M, Zhang H, Yang SK. Intracellular calcium homeostasis and kidney disease. Curr Med Chem. 2021;28:3647–65.
Song Y, Liu L, Liu B, Liu R, Chen Y, Li C, et al. Interaction of nobiletin with methotrexate ameliorates 7-OH methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity through endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent PERK/CHOP signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res. 2021;165:105371.
Eisner DA, Caldwell JL, Kistamas K, Trafford AW. Calcium and excitation-contraction coupling in the heart. Circ Res. 2017;121:181–95.
Krasel C, Dammeier S, Winstel R, Brockmann J, Mischak H, Lohse MJ. Phosphorylation of GRK2 by protein kinase C abolishes its inhibition by calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:1911–5.
Geraldes P, King GL. Activation of protein kinase C isoforms and its impact on diabetic complications. Circ Res. 2010;106:1319–31.
Perez LM, Milkiewicz P, Ahmed-Choudhury J, Elias E, Ochoa JE, Sanchez Pozzi EJ, et al. Oxidative stress induces actin-cytoskeletal and tight-junctional alterations in hepatocytes by a Ca2+-dependent, PKC-mediated mechanism: protective effect of PKA. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006;40:2005–17.
Ribas C, Penela P, Murga C, Salcedo A, Garcia-Hoz C, Jurado-Pueyo M, et al. The G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) interactome: role of GRKs in GPCR regulation and signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1768:913–22.
Luo H, Chen C, Guo L, Xu Z, Peng X, Wang X, et al. Exposure to maternal diabetes mellitus causes renal dopamine D1 receptor dysfunction and hypertension in adult rat offspring. Hypertension. 2018;72:962–70.
Yousefipour Z, Oyekan A, Newaz M. Role of G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated modulation of blood pressure and renal vascular reactivity in SHR. Am J Nephrol. 2009;30:201–8.
Tutunea-Fatan E, Abd-Elrahman KS, Thibodeau JF, Holterman CE, Holleran BJ, Leduc R, et al. GRK2 knockdown in mice exacerbates kidney injury and alters renal mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Sci Rep. 2018;8:11415.
Rosales TO, Horewicz VV, Ferreira MA, Nardi GM, Assreuy J. Dynamics of GRK2 in the kidney: a putative mechanism for sepsis-associated kidney injury. Clin Sci. 2021;135:2341–56.
Zhang S, Li X, Liu S, Zhang W, Li M, Qiao C. Research progress on the role of ET-1 in diabetic kidney disease. J Cell Physiol. 2023;238:1183–92.
Ammon JC, Valls D, Eldemerdash M, Patel JR, Tran PD, Feng L, et al. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 modifies the cellular reaction to cisplatin through interactions with NADPH oxidase 4. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476:1505–16.
Theccanat T, Philip JL, Razzaque AM, Ludmer N, Li J, Xu X, et al. Regulation of cellular oxidative stress and apoptosis by G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2; The role of NADPH oxidase 4. Cell Signal. 2016;28:190–203.
Han C, Li Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Cui D, Luo T, et al. Targeted inhibition of GRK2 kinase domain by CP-25 to reverse fibroblast-like synoviocytes dysfunction and improve collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11:1835–52.
Wang C, Wei X, Wu Y, Tang H, Wang B, Wang Y, et al. CP-25 improves nephropathy in collagen-induced arthritis rats by inhibiting the renal inflammatory response. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;88:106997.
Sun W, Bin W, Hao T, Yong H, Asenso J, Jinzhang G, et al. The effect of CP-25 on the expression of uptake transporter. Acta Univ Med Anhui. 2021;56:1687–91.
Wei X, Wu Y, Tang H, Wang B, Wang Y, Sun W, et al. CP-25 ameliorates methotrexate induced nephrotoxicity via improving renal apoptosis and methotrexate excretion. J Pharmacol Sci. 2021;146:21–8.
Wang C, Tang H, Wang Y, Chang Y, Wu YJ, Wang B, et al. CP-25 enhances OAT1-mediated absorption of methotrexate in synoviocytes of collagen-induced arthritis rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023;44:81–91.
Wei X, Yu J, Xu Z, Wang C, Wu Y. Incidence, pathogenesis, and management of proton pump inhibitor-induced nephrotoxicity. Drug Saf. 2022;45:703–12.
Svanstrom H, Lund M, Melbye M, Pasternak B. Use of proton pump inhibitors and the risk of acute kidney injury among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: cohort study. Drug Saf. 2018;41:817–26.
Ikuta K, Nakagawa S, Momo K, Yonezawa A, Itohara K, Sato Y, et al. Association of proton pump inhibitors and concomitant drugs with risk of acute kidney injury: a nested case-control study. BMJ Open. 2021;11:e041543.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Key Research and Development Plan of Anhui Province (grant number 2023s07020003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XW: Writing - original draft, data curation, methodology. JY: Investigation, data curation, validation. JZG: Investigation, data curation, validation. ZKX: Data curation, validation. XJ, WWS: Investigation. CW: Writing - review & editing, resources, Funding acquisition, conceptualization. YGW: Writing - review & editing, resources, conceptualization.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, X., Yu, J., Gao, Jz. et al. GRK2 dysfunction mediates acute kidney injury in murine administered methotrexate combined with omeprazole. Acta Pharmacol Sin 47, 148–161 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01602-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01602-x