Abstract
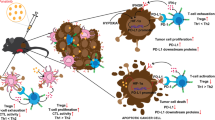
Histone deacetylases (HDAC) inhibition represents one of the few validated strategies in epigenetic cancer therapies, demonstrating significant clinical efficacy in T-cell lymphomas and multiple myeloma, yet exhibiting limited efficacy against solid tumors. GCJ-490A is a novel HDAC inhibitor discovered by medicinal chemists in our institute, which exhibits potent in vitro and in vivo anticancer activity. In this study, we investigated the effects of GCJ-490A on the tumor microenvironment and its potential in synergy with PD-1 antibody in anti-tumor therapy. In syngeneic murine models of breast (EMT6) and lung (LL/2) cancers, we demonstrated that GCJ-490A alone and in combination with PD-1 antibody inhibited tumor growth by regulating T cells and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). Specifically, GCJ-490A significantly enhanced T-cell proliferation and cytotoxicity, evidenced by the increased expression of Ki67, CD107a and Granzyme B, and modulated TAMs towards a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype, while reducing the M2 population. In addition, GCJ-490A upregulated PD-1 on T cells and PD-L1 on myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and TAMs, potentially enhancing PD-1 blockade efficacy. However, the anti-tumor efficacy was less pronounced in LL/2 tumors than in EMT6 tumors, which might be related to the increased infiltration of MDSCs in LL/2 tumors. GCJ-490A promoted MDSCs migration into the tumor by promoting the secretion of CXCL7 from LL/2 cells. In conclusion, GCJ-490A exerts its anti-tumor efficacy by reprogramming the tumor immune microenvironment in EMT6 and LL/2 tumor models, which is augmented when combined with anti-PD-1. However, CXCL7-mediated tumor-type-dependent recruitment of MDSCs by GCJ-490A may limit its therapeutic efficacy, and inhibition of the CXCL7/CXCR1/2 pathway might offer new strategies to address this challenge.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hogg SJ, Beavis PA, Dawson MA, Johnstone RW. Targeting the epigenetic regulation of antitumour immunity. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19:776–800.
Shvedunova M, Akhtar A. Modulation of cellular processes by histone and non-histone protein acetylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23:329–49.
Zhao S, Allis CD, Wang GG. The language of chromatin modification in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21:413–30.
Chun P. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in hematological malignancies and solid tumors. Arch Pharm Res. 2015;38:933–49.
Zhao A, Zhou H, Yang J, Li M, Niu T. Epigenetic regulation in hematopoiesis and its implications in the targeted therapy of hematologic malignancies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8:71.
McCaw TR, Li M, Starenki D, Liu M, Cooper SJ, Arend RC, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibition promotes intratumoral CD8+ T-cell responses, sensitizing murine breast tumors to anti-PD1. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019;68:2081–94.
Lisiero DN, Soto H, Everson RG, Liau LM, Prins RM. The histone deacetylase inhibitor, LBH589, promotes the systemic cytokine and effector responses of adoptively transferred CD8+ T cells. J Immunother Cancer. 2014;2:8.
Cao K, Wang G, Li W, Zhang L, Wang R, Huang Y, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors prevent activation-induced cell death and promote anti-tumor immunity. Oncogene. 2015;34:5960–70.
Guerriero JL, Sotayo A, Ponichtera HE, Castrillon JA, Pourzia AL, Schad S, et al. Class IIa HDAC inhibition reduces breast tumours and metastases through anti-tumour macrophages. Nature. 2017;543:428–32.
Huang J, Wang L, Dahiya S, Beier UH, Han R, Samanta A, et al. Histone/protein deacetylase 11 targeting promotes Foxp3+ Treg function. Sci Rep. 2017;7:8626.
Knox T, Sahakian E, Banik D, Hadley M, Palmer E, Noonepalle S, et al. Selective HDAC6 inhibitors improve anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade therapy by decreasing the anti-inflammatory phenotype of macrophages and down-regulation of immunosuppressive proteins in tumor cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9:6136.
Dahiya S, Beier UH, Wang L, Han R, Jiao J, Akimova T, et al. HDAC10 deletion promotes Foxp3+ T-regulatory cell function. Sci Rep. 2020;10:424.
Wang Y, Li X, Chen Q, Jiao F, Shi C, Pei M, et al. Histone deacetylase 6 regulates the activation of M1 macrophages by the glycolytic pathway during acute liver failure. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:1473–85.
Bejarano L, Jordāo MJC, Joyce JA. Therapeutic targeting of the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:933–59.
Vizioli MG, Liu T, Miller KN, Robertson NA, Gilroy K, Lagnado AB, et al. Mitochondria-to-nucleus retrograde signaling drives formation of cytoplasmic chromatin and inflammation in senescence. Genes Dev. 2020;34:428–45.
Oh DY, Fong L. Cytotoxic CD4+ T cells in cancer: expanding the immune effector toolbox. Immunity. 2021;54:2701–11.
Gracia-Hernandez M, Yende AS, Gajendran N, Alahmadi Z, Li X, Munoz Z, et al. Targeting HDAC6 improves anti-CD47 immunotherapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024;43:60.
Orillion A, Hashimoto A, Damayanti N, Shen L, Adelaiye-Ogala R, Arisa S, et al. Entinostat neutralizes myeloid-derived suppressor cells and enhances the antitumor effect of PD-1 inhibition in murine models of lung and renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:5187–201.
Xie Z, Ago Y, Okada N, Tachibana M. Valproic acid attenuates immunosuppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 2018;137:359–65.
Liang R, Ding D, Li Y, Lan T, Ryabtseva S, Huang S, et al. HDACi combination therapy with IDO1i remodels the tumor microenvironment and boosts antitumor efficacy in colorectal cancer with microsatellite stability. J Nanobiotechnol. 2024;22:753.
McCaw TR, Li M, Starenki D, Cooper SJ, Liu M, Meza-Perez S, et al. The expression of MHC class II molecules on murine breast tumors delays T-cell exhaustion, expands the T-cell repertoire, and slows tumor growth. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019;68:175–88.
Li X, Dai H, Wang H. Low-dose HDACi potentiates anti-tumor activity of macrophages in immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology. 2021;10:1935668.
Hellmann MD, Jänne PA, Opyrchal M, Hafez N, Raez LE, Gabrilovich DI, et al. Entinostat plus pembrolizumab in patients with metastatic NSCLC previously treated with anti-PD-(L)1 therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27:1019–28.
Li Y, Seto E. HDACs and HDAC inhibitors in cancer development and therapy. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016;6:a026831.
Shi MQ, Xu Y, Fu X, Pan DS, Lu XP, Xiao Y, et al. Advances in targeting histone deacetylase for treatment of solid tumors. J Hematol Oncol. 2024;17:37.
Zhang SW, Gong CJ, Su MB, Chen F, He T, Zhang YM, et al. Synthesis and in vitro and in vivo biological evaluation of tissue-specific bisthiazole histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2020;63:804–15.
He T, Gao Y, Fang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Nan F, et al. The HDAC inhibitor GCJ-490A suppresses c-Met expression through IKKα and overcomes gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Med. 2022;19:1172–92.
Shen X, Zhou S, Yang Y, Hong T, Xiang Z, Zhao J, et al. TAM-targeted reeducation for enhanced cancer immunotherapy: mechanism and recent progress. Front Oncol. 2022;12:1034842.
Tafuri A, Shahinian A, Bladt F, Yoshinaga SK, Jordana M, Wakeham A, et al. ICOS is essential for effective T-helper-cell responses. Nature. 2001;409:105–9.
Im SJ, Hashimoto M, Gerner MY, Lee J, Kissick HT, Burger MC, et al. Defining CD8+ T cells that provide the proliferative burst after PD-1 therapy. Nature. 2016;537:417–21.
Barry ST, Gabrilovich DI, Sansom OJ, Campbell AD, Morton JP. Therapeutic targeting of tumour myeloid cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2023;23:216–37.
Jaillon S, Ponzetta A, Di Mitri D, Santoni A, Bonecchi R, Mantovani A. Neutrophil diversity and plasticity in tumour progression and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20:485–503.
Zebley CC, Zehn D, Gottschalk S, Chi H. T cell dysfunction and therapeutic intervention in cancer. Nat Immunol. 2024;25:1344–54.
Georgiev P, Muise ES, Linn DE, Hinton MC, Wang Y, Cai M, et al. Reverse translating molecular determinants of anti-programmed death 1 immunotherapy response in mouse syngeneic tumor models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2022;21:427–39.
Rivera LB, Meyronet D, Hervieu V, Frederick MJ, Bergsland E, Bergers G. Intratumoral myeloid cells regulate responsiveness and resistance to antiangiogenic therapy. Cell Rep. 2015;11:577–91.
Kumar V, Donthireddy L, Marvel D, Condamine T, Wang F, Lavilla-Alonso S, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts neutralize the anti-tumor effect of CSF1 receptor blockade by inducing PMN-MDSC infiltration of tumors. Cancer Cell. 2017;32:654–668.e5.
Loeuillard E, Yang J, Buckarma E, Wang J, Liu Y, Conboy C, et al. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages and granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells augments PD-1 blockade in cholangiocarcinoma. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:5380–96.
Unver N. Identification of the dominant angiogenic CXCL class chemokines associated with non-small cell lung cancer via bioinformatics tools. Med Oncol. 2021;38:68.
Johnson ML, Strauss J, Patel MR, Garon EB, Eaton KD, Neskorik T, et al. Mocetinostat in combination with durvalumab for patients with advanced NSCLC: results from a phase I/II study. Clin Lung Cancer. 2023;24:218–27.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission “Shanghai Action Plan for Science, Technology and Innovation” in the field of experimental animal research project (21140902000, China), Program of Shanghai Academic/Technology Research Leader under the Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan (22XD1404400, China), Shandong Laboratory Program (SYS202205) and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Science (XDB1060401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WXZ, YFF and YC designed the experiments. WXZ, TH, KF, YLG, YMS, FJN, JD, YFF and YC acquired the data. WXZ, YFF and YC drafted the manuscript. WXZ, TH, KF, YLG, YS, FJN, JD, YFF and YC and JD revised the manuscript. JD, YFF and YC obtained funding and supervised the study. All authors approved the final version of the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Jian Ding is the editor-in-chief of the journal and was not involved in the peer review or the decision making of the article. The authors declare no other competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Wx., He, T., Fang, K. et al. HDAC inhibitor GCJ-490A modulates tumor microenvironment and synergizes with PD-1 antibody against breast and lung cancers in syngeneic murine models. Acta Pharmacol Sin (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01646-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01646-z