Abstract
Stroke is the second leading cause of mortality and the leading cause of adult disability worldwide. Neuroinflammation is a crucial mechanism that regulates the pathogenesis and prognosis of stroke and involves both peripheral and intracerebral immune cells. Neutrophils and microglia are the primary immune cells that mediate neuroinflammation and play bidirectional roles after stroke. Significant interactions between neutrophils and microglia exist. Microglia regulate the activation, infiltration, as well as formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), whereas neutrophils regulate the polarization and phagocytic activity of microglia. In this review, we summarize the bidirectional roles of neutrophils and microglia in stroke with an emphasis on the interactions between neutrophils and microglia, as well as the associated signaling pathways and targets involved. We further introduce potential stroke treatment drugs that regulate the interactions between neutrophils and microglia, including anti-inflammatory drugs and natural products. We propose that, according to the different ischemic times and cell activation states, regulating the interactions between neutrophils and microglia through relevant targets and signaling pathways may be an ideal strategy for the anti-inflammatory treatment of stroke, potentially improving treatment and prognosis of stroke.

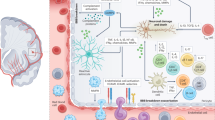
This review summarizes the bidirectional roles of neutrophils and microglia in stroke, respectively, focusing on the interactions and signaling pathways between neutrophils and microglia, as well as potential therapeutic targets and drugs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananth CV, Brandt JS, Keyes KM, Graham HL, Kostis JB, Kostis WJ. Epidemiology and trends in stroke mortality in the USA, 1975–2019. Int J Epidemiol. 2023;52:858–66.
Campbell BCV, De Silva DA, Macleod MR, Coutts SB, Schwamm LH, Davis SM, et al. Ischaemic stroke. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2019;5:70.
Sochocka M, Diniz BS, Leszek J. Inflammatory response in the CNS: friend or foe?. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54:8071–89.
Shi K, Tian DC, Li ZG, Ducruet AF, Lawton MT, Shi FD. Global brain inflammation in stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:1058–66.
Russo MV, McGavern DB. Immune surveillance of the CNS following infection and injury. Trends Immunol. 2015;36:637–50.
Bernhardt J, Hayward KS, Kwakkel G, Ward NS, Wolf SL, Borschmann K, et al. Agreed definitions and a shared vision for new standards in stroke recovery research: the stroke recovery and rehabilitation roundtable taskforce. Neurorehabilit Neural Repair. 2017;31:793–9.
Chen GY, Nunez G. Sterile inflammation: sensing and reacting to damage. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:826–37.
Qiu YM, Zhang CL, Chen AQ, Wang HL, Zhou YF, Li YN, et al. Immune cells in the BBB disruption after acute ischemic stroke: targets for immune therapy?. Front Immunol. 2021;12:678744.
Pan Z, Ma G, Kong L, Du G. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1: regulatory mechanisms and drug development in stroke. Pharmacol Res. 2021;170:105742.
Mastropietro A, Rizzo G, Fontana L, Figini M, Bernardini B, Straffi L, et al. Microstructural characterization of corticospinal tract in subacute and chronic stroke patients with distal lesions by means of advanced diffusion MRI. Neuroradiology. 2019;61:1033–45.
Xie W, Huang T, Guo Y, Zhang Y, Chen W, Li Y, et al. Neutrophil-derived cathelicidin promotes cerebral angiogenesis after ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2023;43:1503–18.
Ng MSF, Tan L, Wang Q, Mackay CR, Ng LG. Neutrophils in cancer-unresolved questions. Sci China Life Sci. 2021;64:1829–41.
Doring Y, Soehnlein O, Weber C. Neutrophil extracellular traps in atherosclerosis and atherothrombosis. Circ Res. 2017;120:736–43.
Liew PX, Kubes P. The neutrophil’s role during health and disease. Physiol Rev. 2019;99:1223–48.
Mantovani A, Cassatella MA, Costantini C, Jaillon S. Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:519–31.
Ma Y, Yang S, He Q, Zhang D, Chang J. The role of immune cells in post-stroke angiogenesis and neuronal remodeling: the known and the unknown. Front Immunol. 2021;12:784098.
Hottz ED, Azevedo-Quintanilha IG, Palhinha L, Teixeira L, Barreto EA, Pão CRR, et al. Platelet activation and platelet-monocyte aggregate formation trigger tissue factor expression in patients with severe COVID-19. Blood. 2020;136:1330–41.
Benakis C, Garcia-Bonilla L, Iadecola C, Anrather J. The role of microglia and myeloid immune cells in acute cerebral ischemia. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:461.
Dhanesha N, Jain M, Tripathi AK, Doddapattar P, Chorawala M, Bathla G, et al. Targeting myeloid-specific integrin alpha9beta1 improves short- and long-term stroke outcomes in murine models with preexisting comorbidities by limiting thrombosis and inflammation. Circ Res. 2020;126:1779–94.
Ehlers R, Ustinov V, Chen Z, Zhang X, Rao R, Luscinskas FW, et al. Targeting platelet-leukocyte interactions: identification of the integrin Mac-1 binding site for the platelet counter receptor glycoprotein Ibalpha. J Exp Med. 2003;198:1077–88.
Chen C, Chu SF, Liu DD, Zhang Z, Kong LL, Zhou X, et al. Chemokines play complex roles in cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Int. 2018;112:146–58.
Kong LL, Wang ZY, Hu JF, Yuan YH, Han N, Li H, et al. Inhibition of chemokine-like factor 1 protects against focal cerebral ischemia through the promotion of energy metabolism and anti-apoptotic effect. Neurochem Int. 2014;76:91–8.
Kong LL, Wang ZY, Han N, Zhuang XM, Wang ZZ, Li H, et al. Neutralization of chemokine-like factor 1, a novel C-C chemokine, protects against focal cerebral ischemia by inhibiting neutrophil infiltration via MAPK pathways in rats. J Neuroinflamm. 2014;11:112.
Weisenburger-Lile D, Dong Y, Yger M, Weisenburger G, Polara GF, Chaigneau T, et al. Harmful neutrophil subsets in patients with ischemic stroke: association with disease severity. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2019;6:e571.
Ouk T, Potey C, Maestrini I, Petrault M, Mendyk AM, Leys D, et al. Neutrophils in tPA-induced hemorrhagic transformations: main culprit, accomplice or innocent bystander?. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;194:73–83.
Stowe AM, Adair-Kirk TL, Gonzales ER, Perez RS, Shah AR, Park TS, et al. Neutrophil elastase and neurovascular injury following focal stroke and reperfusion. Neurobiol Dis. 2009;35:82–90.
Zhao Z, Pan Z, Zhang S, Ma G, Zhang W, Song J, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps: A novel target for the treatment of stroke. Pharmacol Ther. 2023;241:108328.
Folco EJ, Mawson TL, Vromman A, Bernardes-Souza B, Franck G, Persson O, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps induce endothelial cell activation and tissue factor production through interleukin-1alpha and cathepsin G. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38:1901–12.
Vaibhav K, Braun M, Alverson K, Khodadadi H, Kutiyanawalla A, Ward A, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps exacerbate neurological deficits after traumatic brain injury. Sci Adv. 2020;6:eaax8847.
Li C, Xing Y, Zhang Y, Hua Y, Hu J, Bai Y. Neutrophil extracellular traps exacerbate ischemic brain damage. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59:643–56.
Planas AM. Role of immune cells migrating to the ischemic brain. Stroke. 2018;49:2261–7.
Zeng H, Fu X, Cai J, Sun C, Yu M, Peng Y, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps may be a potential target for treating early brain injury in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res. 2022;13:112–31.
Xie M, Hao Y, Feng L, Wang T, Yao M, Li H, et al. Neutrophil heterogeneity and its roles in the inflammatory network after ischemic stroke. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21:621–50.
Garcia-Culebras A, Duran-Laforet V, Pena-Martinez C, Moraga A, Ballesteros I, Cuartero MI, et al. Role of TLR4 (toll-like receptor 4) in N1/N2 neutrophil programming after stroke. Stroke. 2019;50:2922–32.
Serhan CN, Savill J. Resolution of inflammation: the beginning programs the end. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1191–7.
Cai W, Liu S, Hu M, Huang F, Zhu Q, Qiu W, et al. Functional dynamics of neutrophils after ischemic stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;11:108–21.
Vermeren S, Elks PM, Ellett F. Editorial: neutrophil functions in host immunity, inflammation and tissue repair. Front Immunol. 2021;12:810346.
Shim HB, Deniset JF, Kubes P. Neutrophils in homeostasis and tissue repair. Int Immunol. 2022;34:399–407.
Sas AR, Carbajal KS, Jerome AD, Menon R, Yoon C, Kalinski AL, et al. A new neutrophil subset promotes CNS neuron survival and axon regeneration. Nat Immunol. 2020;21:1496–505.
Fukushima K, Nabeshima H, Kida H. Revealing the diversity of neutrophil functions and subsets. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18:781–3.
Jerome AD, Atkinson JR, McVey Moffatt AL, Sepeda JA, Segal BM, Sas AR. Characterization of zymosan-modulated neutrophils with neuroregenerative properties. Front Immunol. 2022;13:912193.
Dalli J, Montero-Melendez T, Norling LV, Yin X, Hinds C, Haskard D, et al. Heterogeneity in neutrophil microparticles reveals distinct proteome and functional properties. Mol Cell Proteom. 2013;12:2205–19.
Wang J. Neutrophils in tissue injury and repair. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;371:531–9.
Eldahshan W, Fagan SC, Ergul A. Inflammation within the neurovascular unit: Focus on microglia for stroke injury and recovery. Pharmacol Res. 2019;147:104349.
Mason HD, McGavern DB. How the immune system shapes neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci. 2022;45:733–48.
Kim YR, Kim YM, Lee J, Park J, Lee JE, Hyun YM. Neutrophils return to bloodstream through the brain blood vessel after crosstalk with microglia during LPS-induced neuroinflammation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:613733.
Haley MJ, Lawrence CB. The blood-brain barrier after stroke: structural studies and the role of transcytotic vesicles. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37:456–70.
Pons V, Rivest S. Targeting systemic innate immune cells as a therapeutic avenue for Alzheimer disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2022;74:1–17.
Franco R, Fernandez-Suarez D. Alternatively activated microglia and macrophages in the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 2015;131:65–86.
Ma Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Yang GY. The biphasic function of microglia in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2017;157:247–72.
Saijo K, Glass CK. Microglial cell origin and phenotypes in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:775–87.
Dejonckheere E, Vandenbroucke RE, Libert C. Matrix metalloproteinases as drug targets in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Drug Discov Today. 2011;16:762–78.
Levard D, Buendia I, Lanquetin A, Glavan M, Vivien D, Rubio M. Filling the gaps on stroke research: focus on inflammation and immunity. Brain Behav Immun. 2021;91:649–67.
Jassam YN, Izzy S, Whalen M, McGavern DB, El Khoury J. Neuroimmunology of traumatic brain injury: time for a paradigm shift. Neuron. 2017;95:1246–65.
Dokalis N, Prinz M. Resolution of neuroinflammation: mechanisms and potential therapeutic option. Semin Immunopathol. 2019;41:699–709.
Li Z, Song Y, He T, Wen R, Li Y, Chen T, et al. M2 microglial small extracellular vesicles reduce glial scar formation via the miR-124/STAT3 pathway after ischemic stroke in mice. Theranostics. 2021;11:1232–48.
Zhang Y, Lian L, Fu R, Liu J, Shan X, Jin Y, et al. Microglia: the hub of intercellular communication in ischemic stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:889442.
Amantea D, Micieli G, Tassorelli C, Cuartero MI, Ballesteros I, Certo M, et al. Rational modulation of the innate immune system for neuroprotection in ischemic stroke. Front Neurosci. 2015;9:147.
Shao A, Zhu Z, Li L, Zhang S, Zhang J. Emerging therapeutic targets associated with the immune system in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH): From mechanisms to translation. EBioMedicine. 2019;45:615–23.
Pan Z, Liu N, Ma G, Zhang S, Liu C, Zhao Z, et al. Xiaoshuan Tongluo recipe alleviated acute hyperglycemia-enhanced hemorrhagic transformation by regulating microglia polarization in thromboembolic stroke rats. Pharmacol Res Mod Chin Med. 2023;9:100315.
Brown GC. Neuronal loss after stroke due to microglial phagocytosis of stressed neurons. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:13442.
Neumann J, Henneberg S, von Kenne S, Nolte N, Muller AJ, Schraven B, et al. Beware the intruder: real time observation of infiltrated neutrophils and neutrophil-microglia interaction during stroke in vivo. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0193970.
Ortega-Velázquez R, Díez-Marqués ML, Ruiz-Torres MP, González-Rubio M, Rodríguez-Puyol M, Rodríguez Puyol D. Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (RGDS) peptide stimulates transforming growth factor beta1 transcription and secretion through integrin activation. FASEB J. 2003;17:1529–31.
Gardner JK, Swaims-Kohlmeier A, Herbst-Kralovetz MM. IL-36gamma Is a key regulator of neutrophil infiltration in the vaginal microenvironment and limits neuroinvasion in genital HSV-2 infection. J Immunol. 2019;203:2655–64.
Bozoyan L, Dumas A, Patenaude A, Vallieres L. Interleukin-36gamma is expressed by neutrophils and can activate microglia, but has no role in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflamm. 2015;12:173.
Hu Z, Deng N, Liu K, Zhou N, Sun Y, Zeng W. CNTF-STAT3-IL-6 axis mediates neuroinflammatory cascade across Schwann cell-neuron-microglia. Cell Rep. 2020;31:107657.
Wang X, Xuan W, Zhu ZY, Li Y, Zhu H, Zhu L, et al. The evolving role of neuro-immune interaction in brain repair after cerebral ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018;24:1100–14.
Cuartero MI, Ballesteros I, Moraga A, Nombela F, Vivancos J, Hamilton JA, et al. N2 neutrophils, novel players in brain inflammation after stroke: modulation by the PPARgamma agonist rosiglitazone. Stroke. 2013;44:3498–508.
Stark MA, Huo Y, Burcin TL, Morris MA, Olson TS, Ley K. Phagocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils regulates granulopoiesis via IL-23 and IL-17. Immunity. 2005;22:285–94.
Yin N, Wang W, Pei F, Zhao Y, Liu C, Guo M, et al. A neutrophil hijacking nanoplatform reprograming netosis for targeted microglia polarizing mediated ischemic stroke treatment. Adv Sci. 2024;11:e2305877.
Hanhai Z, Bin Q, Shengjun Z, Jingbo L, Yinghan G, Lingxin C, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps, released from neutrophil, promote microglia inflammation and contribute to poor outcome in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Aging. 2021;13:13108–23.
Moxon-Emre I, Schlichter LC. Neutrophil depletion reduces blood-brain barrier breakdown, axon injury, and inflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2011;70:218–35.
Kenne E, Erlandsson A, Lindbom L, Hillered L, Clausen F. Neutrophil depletion reduces edema formation and tissue loss following traumatic brain injury in mice. J Neuroinflamm. 2012;9:17.
Chen H, Ni L, Zhang J, Zheng X, Chen Y, Jin X, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote AIM2-dependent microglial pyroptosis following stroke. Aging Dis. 2025; https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2024.1733.
Atangana E, Schneider UC, Blecharz K, Magrini S, Wagner J, Nieminen-Kelha M, et al. Intravascular inflammation triggers intracerebral activated microglia and contributes to secondary brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage (eSAH). Transl Stroke Res. 2017;8:144–56.
Endres M, Moro MA, Nolte CH, Dames C, Buckwalter MS, Meisel A. Immune pathways in etiology, acute phase, and chronic sequelae of ischemic stroke. Circ Res. 2022;130:1167–86.
Dordoe C, Huang W, Bwalya C, Wang X, Shen B, Wang H, et al. The role of microglial activation on ischemic stroke: modulation by fibroblast growth factors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023;74:122–33.
Chen J, Jin J, Zhang X, Yu H, Zhu X, Yu L, et al. Microglial lnc-U90926 facilitates neutrophil infiltration in ischemic stroke via MDH2/CXCL2 axis. Mol Ther. 2021;29:2873–85.
D’Mello C, Le T, Swain MG. Cerebral microglia recruit monocytes into the brain in response to tumor necrosis factor alpha signaling during peripheral organ inflammation. J Neurosci. 2009;29:2089–102.
Cao K, Liao X, Lu J, Yao S, Wu F, Zhu X, et al. IL-33/ST2 plays a critical role in endothelial cell activation and microglia-mediated neuroinflammation modulation. J Neuroinflamm. 2018;15:136.
Wu F, Chen X, Zhai L, Wang H, Sun M, Song C, et al. CXCR2 antagonist attenuates neutrophil transmigration into brain in a murine model of LPS induced neuroinflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;529:839–45.
Hijioka M, Futokoro R, Ohto-Nakanishi T, Nakanishi H, Katsuki H, Kitamura Y. Microglia-released leukotriene B(4) promotes neutrophil infiltration and microglial activation following intracerebral hemorrhage. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;85:106678.
Boyce M, Xin Y, Chowdhury O, Shang P, Liu H, Koontz V, et al. Microglia-neutrophil interactions drive dry AMD-like pathology in a mouse model. Cells. 2022;11:3535.
Ghosh S, Padmanabhan A, Vaidya T, Watson AM, Bhutto IA, Hose S, et al. Neutrophils homing into the retina trigger pathology in early age-related macular degeneration. Commun Biol. 2019;2:348.
Wanrooy BJ, Wen SW, Wong CH. Dynamic roles of neutrophils in post-stroke neuroinflammation. Immunol Cell Biol. 2021;99:924–35.
Otxoa-de-Amezaga A, Miro-Mur F, Pedragosa J, Gallizioli M, Justicia C, Gaja-Capdevila N, et al. Microglial cell loss after ischemic stroke favors brain neutrophil accumulation. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;137:321–41.
Qin C, Fan WH, Liu Q, Shang K, Murugan M, Wu LJ, et al. Fingolimod protects against ischemic white matter damage by modulating microglia toward M2 polarization via STAT3 pathway. Stroke. 2017;48:3336–46.
Luo L, Liu M, Fan Y, Zhang J, Liu L, Li Y, et al. Intermittent theta-burst stimulation improves motor function by inhibiting neuronal pyroptosis and regulating microglial polarization via TLR4/NFkappaB/NLRP3 signaling pathway in cerebral ischemic mice. J Neuroinflamm. 2022;19:141.
Zhang YJ, Song JR, Zhao MJ. NR4A1 regulates cerebral ischemia-induced brain injury by regulating neuroinflammation through interaction with NF-kappaB/p65. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;518:59–65.
Neumann J, Riek-Burchardt M, Herz J, Doeppner TR, Konig R, Hutten H, et al. Very-late-antigen-4 (VLA-4)-mediated brain invasion by neutrophils leads to interactions with microglia, increased ischemic injury and impaired behavior in experimental stroke. Acta Neuropathol. 2015;129:259–77.
Yan Z, Gibson SA, Buckley JA, Qin H, Benveniste EN. Role of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in regulation of innate immunity in neuroinflammatory diseases. Clin Immunol. 2018;189:4–13.
Jain M, Singh MK, Shyam H, Mishra A, Kumar S, Kumar A, et al. Role of JAK/STAT in the neuroinflammation and its association with neurological disorders. Ann Neurosci. 2021;28:191–200.
Gong P, Zhang Z, Zou Y, Tian Q, Han S, Xu Z, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption in ischemia/reperfusion injury through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;854:289–97.
Maes M, Nikiforov NG, Plaimas K, Suratanee A, Alfieri DF, Vissoci Reiche EM. New drug targets to prevent death due to stroke: a review based on results of protein-protein interaction network, enrichment, and annotation analyses. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:12108.
Lyu J, Xie D, Bhatia TN, Leak RK, Hu X, Jiang X. Microglial/Macrophage polarization and function in brain injury and repair after stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021;27:515–27.
Hu X, Leak RK, Shi Y, Suenaga J, Gao Y, Zheng P, et al. Microglial and macrophage polarization-new prospects for brain repair. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11:56–64.
Meier AB, Basheer F, Sertori R, Laird M, Liongue C, Ward AC. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor mediated regulation of early myeloid cells in zebrafish. Front Biosci. 2022;27:110.
Ye L, Schnepf D, Staeheli P. Interferon-lambda orchestrates innate and adaptive mucosal immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19:614–25.
Futosi K, Fodor S, Mocsai A. Neutrophil cell surface receptors and their intracellular signal transduction pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013;17:638–50.
Yu H, Lin L, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Hu H. Targeting NF-kappaB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:209.
Park BS, Lee JO. Recognition of lipopolysaccharide pattern by TLR4 complexes. Exp Mol Med. 2013;45:e66.
Zusso M, Lunardi V, Franceschini D, Pagetta A, Lo R, Stifani S, et al. Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin attenuate microglia inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-κB pathway. J Neuroinflamm. 2019;16:148.
Gordon JW, Shaw JA, Kirshenbaum LA. Multiple facets of NF-kappaB in the heart: to be or not to NF-kappaB. Circ Res. 2011;108:1122–32.
Li XH, Yin FT, Zhou XH, Zhang AH, Sun H, Yan GL, et al. The signaling pathways and targets of natural compounds from traditional Chinese medicine in treating ischemic stroke. Molecules. 2022;27:3099.
Mussbacher M, Salzmann M, Brostjan C, Hoesel B, Schoergenhofer C, Datler H, et al. Cell type-specific roles of NF-kappaB linking inflammation and thrombosis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:85.
Steffen BJ, Breier G, Butcher EC, Schulz M, Engelhardt B. ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and MAdCAM-1 are expressed on choroid plexus epithelium but not endothelium and mediate binding of lymphocytes in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1996;148:1819–38.
Ri MH, Xing Y, Zuo HX, Li MY, Jin HL, Ma J, et al. Regulatory mechanisms of natural compounds from traditional Chinese herbal medicines on the microglial response in ischemic stroke. Phytomedicine. 2023;116:154889.
Zhang W, Mi Y, Jiao K, Xu J, Guo T, Zhou D, et al. Kellerin alleviates cognitive impairment in mice after ischemic stroke by multiple mechanisms. Phytother Res. 2020;34:2258–74.
von Vietinghoff S, Asagiri M, Azar D, Hoffmann A, Ley K. Defective regulation of CXCR2 facilitates neutrophil release from bone marrow causing spontaneous inflammation in severely NF-kappa B-deficient mice. J Immunol. 2010;185:670–8.
He R, Chen Y, Cai Q. The role of the LTB4-BLT1 axis in health and disease. Pharmacol Res. 2020;158:104857.
Saiwai H, Ohkawa Y, Yamada H, Kumamaru H, Harada A, Okano H, et al. The LTB4-BLT1 axis mediates neutrophil infiltration and secondary injury in experimental spinal cord injury. Am J Pathol. 2010;176:2352–66.
Gong M, Duan H, Wu F, Ren Y, Gong J, Xu L, et al. Berberine alleviates insulin resistance and inflammation via inhibiting the LTB4-BLT1 axis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:722360.
Afonso Philippe V, Janka-Junttila M, Lee Young J, McCann Colin P, Oliver Charlotte M, Aamer Khaled A, et al. LTB4 is a signal-relay molecule during neutrophil chemotaxis. Dev Cell. 2012;22:1079–91.
Brandt SL, Serezani CH. Too much of a good thing: How modulating LTB(4) actions restore host defense in homeostasis or disease. Semin Immunol. 2017;33:37–43.
Serezani CH, Lewis C, Jancar S, Peters-Golden M. Leukotriene B4 amplifies NF-kappaB activation in mouse macrophages by reducing SOCS1 inhibition of MyD88 expression. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:671–82.
Rao NL, Kotian GB, Shetty JK, Shelley BP, Dmello MK, Lobo EC, et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end product, organ crosstalk, and pathomechanism targets for comprehensive molecular therapeutics in diabetic ischemic stroke. Biomolecules. 2022;12:1712.
Hijioka M, Anan J, Ishibashi H, Kurauchi Y, Hisatsune A, Seki T, et al. Inhibition of leukotriene B4 action mitigates intracerebral hemorrhage-associated pathological events in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017;360:399–408.
Pietronigro E, Zenaro E, Bianca VD, Dusi S, Terrabuio E, Iannoto G, et al. Blockade of alpha4 integrins reduces leukocyte-endothelial interactions in cerebral vessels and improves memory in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep. 2019;9:12055.
Katsuki H. Exploring neuroprotective drug therapies for intracerebral hemorrhage. J Pharm Sci. 2010;114:366–78.
Carmichael ST, Vespa PM, Saver JL, Coppola G, Geschwind DH, Starkman S, et al. Genomic profiles of damage and protection in human intracerebral hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2008;28:1860–75.
Pan J, Fei CJ, Hu Y, Wu XY, Nie L, Chen J. Current understanding of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway: structure, regulatory mechanisms, and related diseases. Zool Res. 2023;44:183–218.
Schmitz CRR, Maurmann RM, Guma F, Bauer ME, Barbe-Tuana FM. cGAS-STING pathway as a potential trigger of immunosenescence and inflammaging. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1132653.
Song JX, Villagomes D, Zhao H, Zhu M. cGAS in nucleus: the link between immune response and DNA damage repair. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1076784.
Decout A, Katz JD, Venkatraman S, Ablasser A. The cGAS-STING pathway as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21:548–69.
Chauhan C, Kaundal RK. Understanding the role of cGAS-STING signaling in ischemic stroke: a new avenue for drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2023:18:1133–49.
Gamdzyk M, Doycheva DM, Araujo C, Ocak U, Luo Y, Tang J, et al. cGAS/STING pathway activation contributes to delayed neurodegeneration in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model: possible involvement of LINE-1. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57:2600–19.
Kong L, Li W, Chang E, Wang W, Shen N, Xu X, et al. mtDNA-STING axis mediates microglial polarization via IRF3/NF-kappaB signaling after ischemic stroke. Front Immunol. 2022;13:860977.
Yang Y, Huang Y, Zeng Z. Advances in cGAS-STING signaling pathway and diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:800393.
Kang L, Yu H, Yang X, Zhu Y, Bai X, Wang R, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps released by neutrophils impair revascularization and vascular remodeling after stroke. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2488.
Wang R, Zhu Y, Liu Z, Chang L, Bai X, Kang L, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote tPA-induced brain hemorrhage via cGAS in mice with stroke. Blood. 2021;138:91–103.
An C, Shi Y, Li P, Hu X, Gan Y, Stetler RA, et al. Molecular dialogs between the ischemic brain and the peripheral immune system: dualistic roles in injury and repair. Prog Neurobiol. 2014;115:6–24.
Kim SW, Lee H, Lee HK, Kim ID, Lee JK. Neutrophil extracellular trap induced by HMGB1 exacerbates damages in the ischemic brain. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7:94.
Kong L, Ma Y, Wang Z, Liu N, Ma G, Liu C, et al. Inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor 1 by YC-1 attenuates tissue plasminogen activator induced hemorrhagic transformation by suppressing HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kappaB mediated neutrophil infiltration in thromboembolic stroke rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;94:107507.
Liu N, Liu C, Yang Y, Ma G, Wei G, Liu S, et al. Xiao-Xu-Ming decoction prevented hemorrhagic transformation induced by acute hyperglycemia through inhibiting AGE-RAGE-mediated neuroinflammation. Pharmacol Res. 2021;169:105650.
Sun Y, Hei M, Fang Z, Tang Z, Wang B, Hu N. High-mobility group box 1 contributes to cerebral cortex injury in a neonatal hypoxic-ischemic rat model by regulating the phenotypic polarization of microglia. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:506.
Li J, Wang Z, Li J, Zhao H, Ma Q. HMGB1: a new target for ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic transformation. Transl Stroke Res. 2025;16:990–1015.
Gou X, Ying J, Yue Y, Qiu X, Hu P, Qu Y, et al. The roles of high mobility group box 1 in cerebral ischemic injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:600280.
Zhang W, Feng C, Jiang H. Novel target for treating Alzheimer’s diseases: crosstalk between the Nrf2 pathway and autophagy. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;65:101207.
Sun G, Zhao Z, Lang J, Sun B, Zhao Q. Nrf2 loss of function exacerbates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in TBI mice. Neurosci Lett. 2022;770:136400.
Wang L, He C. Nrf2-mediated anti-inflammatory polarization of macrophages as therapeutic targets for osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:967193.
Fadoul G, Ikonomovic M, Zhang F, Yang T. The cell-specific roles of Nrf2 in acute and chronic phases of ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024;30:e14462.
Wang N, Nie H, Zhang Y, Han H, Wang S, Liu W, et al. Dexmedetomidine exerts cerebral protective effects against cerebral ischemic injury by promoting the polarization of M2 microglia via the Nrf2/HO-1/NLRP3 pathway. Inflammation Res. 2021;71:93–106.
Liu L, Locascio LM, Dore S. Critical role of Nrf2 in experimental ischemic stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:153.
Zhao X, Sun G, Zhang J, Strong R, Dash PK, Kan YW, et al. Transcription factor Nrf2 protects the brain from damage produced by intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2007;38:3280–6.
Yu J, Wang WN, Matei N, Li X, Pang JW, Mo J, et al. Ezetimibe attenuates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation via the AMPK/Nrf2/TXNIP pathway after MCAO in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:4717258.
Lu Q, Liu R, Sherchan P, Ren R, He W, Fang Y, et al. TREM (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells)-1 inhibition attenuates neuroinflammation via PKC (protein kinase C) delta/CARD9 (caspase recruitment domain family member 9) signaling pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Stroke. 2021;52:2162–73.
Fu X, Zeng H, Zhao J, Zhou G, Zhou H, Zhuang J, et al. Inhibition of dectin-1 ameliorates neuroinflammation by regulating microglia/macrophage phenotype after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Transl Stroke Res. 2021;12:1018–34.
Wu X, Zeng H, Xu C, Chen H, Fan L, Zhou H, et al. TREM1 regulates neuroinflammatory injury by modulate proinflammatory subtype transition of microglia and formation of neutrophil extracellular traps via interaction with SYK in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front Immunol. 2021;12:766178.
Seo DH, Che X, Kim S, Kim DH, Ma HW, Kim JH, et al. Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 agonist regulates intestinal inflammation via Cd177+ neutrophils. Front Immunol. 2021;12:650864.
Murao A, Arif A, Brenner M, Denning NL, Jin H, Takizawa S, et al. Extracellular CIRP and TREM-1 axis promotes ICAM-1-Rho-mediated NETosis in sepsis. FASEB J. 2020;34:9771–86.
Xu P, Hong Y, Xie Y, Yuan K, Li J, Sun R, et al. TREM-1 exacerbates neuroinflammatory injury via NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;12:643–59.
Shen T, Cui G, Chen H, Huang L, Song W, Zu J, et al. TREM-1 mediates interaction between substantia nigra microglia and peripheral neutrophils. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19:1375–84.
Chitu V, Gokhan S, Nandi S, Mehler MF, Stanley ER. Emerging roles for CSF-1 receptor and its ligands in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 2016;39:378–93.
He J, Fu Y, Ge L, Dai J, Fang Y, Li Y, et al. Disease-associated microglial activation prevents photoreceptor degeneration by suppressing the accumulation of cell debris and neutrophils in degenerating rat retinas. Theranostics. 2022;12:2687–706.
Li Y, Ritzel RM, Khan N, Cao T, He J, Lei Z, et al. Delayed microglial depletion after spinal cord injury reduces chronic inflammation and neurodegeneration in the brain and improves neurological recovery in male mice. Theranostics. 2020;10:11376–403.
Tan Q, Guo P, Zhou J, Zhang J, Zhang B, Lan C, et al. Targeting neutrophil extracellular traps enhanced tPA fibrinolysis for experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Transl Res. 2019;211:139–46.
Zhu D, Lu Y, Wang Y, Wang Y. PAD4 and its inhibitors in cancer progression and prognosis. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14:2414.
Kong Y, He G, Zhang X, Li J. The role of neutrophil extracellular traps in lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behaviors in mice. Brain Sci. 2021;11:1514.
Wasserman JK, Schlichter LC. Minocycline protects the blood-brain barrier and reduces edema following intracerebral hemorrhage in the rat. Exp Neurol. 2007;207:227–37.
Liu Y, Li Z, Khan S, Zhang R, Wei R, Zhang Y, et al. Neuroprotection of minocycline by inhibition of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer expression following intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Neurosci Lett. 2021;764:136297.
Chen Y, Won SJ, Xu Y, Swanson RA. Targeting microglial activation in stroke therapy: pharmacological tools and gender effects. Curr Med Chem. 2014;21:2146–55.
Ma G, Pan Z, Kong L, Du G. Neuroinflammation in hemorrhagic transformation after tissue plasminogen activator thrombolysis: potential mechanisms, targets, therapeutic drugs and biomarkers. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;90:107216.
Beller E, Reuter L, Kluge A, Preibisch C, Lindauer U, Bogdanov A, et al. Pilot study to assess visualization and therapy of inflammatory mechanisms after vessel reopening in a mouse stroke model. Sci Rep. 2018;8:745.
Wakita H, Tomimoto H, Akiguchi I, Kimura J. Dose-dependent, protective effect of FK506 against white matter changes in the rat brain after chronic cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 1998;792:105–13.
Furuichi Y, Noto T, Li J-Y, Oku T, Ishiye M, Moriguchi A, et al. Multiple modes of action of tacrolimus (FK506) for neuroprotective action on ischemic damage after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2004;1014:120–30.
Zhao Y, Li Q, Niu J, Guo E, Zhao C, Zhang J, et al. Neutrophil membrane-camouflaged polyprodrug nanomedicine for inflammation suppression in ischemic stroke therapy. Adv Mater. 2024;36:e2311803.
Wei Y, Yemisci M, Kim HH, Yung LM, Shin HK, Hwang SK, et al. Fingolimod provides long-term protection in rodent models of cerebral ischemia. Ann Neurol. 2010;69:119–29.
Czech B, Pfeilschifter W, Mazaheri-Omrani N, Strobel MA, Kahles T, Neumann-Haefelin T, et al. The immunomodulatory sphingosine 1-phosphate analog FTY720 reduces lesion size and improves neurological outcome in a mouse model of cerebral ischemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;389:251–6.
Brattas MK, Reikvam H, Tvedt THA, Bruserud O. Dasatinib as an investigational drug for the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019;28:411–20.
Ryu KY, Lee HJ, Woo H, Kang RJ, Han KM, Park H, et al. Dasatinib regulates LPS-induced microglial and astrocytic neuroinflammatory responses by inhibiting AKT/STAT3 signaling. J Neuroinflamm. 2019;16:190.
Dhawan G, Combs CK. Inhibition of Src kinase activity attenuates amyloid associated microgliosis in a murine model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflamm. 2012;9:117.
Lawana V, Singh N, Sarkar S, Charli A, Jin H, Anantharam V, et al. Involvement of c-Abl kinase in microglial activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and impairment in autolysosomal system. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2017;12:624–60.
Gu L, Sun M, Li R, Zhang X, Tao Y, Yuan Y, et al. Didymin suppresses microglia pyroptosis and neuroinflammation through the Asc/Caspase-1/GSDMD pathway following experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Immunol. 2022;13:810582.
Liu Y, Dang W, Zhang S, Wang L, Zhang X. Artesunate attenuates inflammatory injury and inhibits the NF-kappaB pathway in a mouse model of cerebral ischemia. J Int Med Res. 2021;49:3000605211053549.
Chen Y, Wu J, Zhu J, Yang G, Tian J, Zhao Y, et al. Artesunate provides neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via the TLR-4/NF-kappaB pathway in rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2021;44:350–6.
Song Z, Feng J, Zhang Q, Deng S, Yu D, Zhang Y, et al. Tanshinone IIA protects against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury by regulating microglial activation and polarization via NF-kappaB pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:641848.
Xu L, Liu X, Zhang Y, Jia T, Li L, Du Y, et al. Tanshinone IIA improves acute gouty arthritis in rats through regulating neutrophil activation and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Dis Markers. 2022;2022:5851412.
Chen Y, Wu X, Yu S, Lin X, Wu J, Li L, et al. Neuroprotection of tanshinone IIA against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibition of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in rats. PLoS One. 2012;7:e40165.
Wang L, Xiong X, Zhang X, Ye Y, Jian Z, Gao W, et al. Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy and inflammation. Neuroscience. 2020;441:46–57.
Chen J, Zhang X, Zhang C, Wang W, Chen R, Jiao H, et al. Anti-inflammation of natural components from medicinal plants at low concentrations in brain via inhibiting neutrophil infiltration after stroke. Mediat Inflamm. 2016;2016:9537901.
Kim SW, Jin Y, Shin JH, Kim ID, Lee HK, Park S, et al. Glycyrrhizic acid affords robust neuroprotection in the postischemic brain via anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting HMGB1 phosphorylation and secretion. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;46:147–56.
Michaelis M, Geiler J, Naczk P, Sithisarn P, Leutz A, Doerr HW, et al. Glycyrrhizin exerts antioxidative effects in H5N1 influenza A virus-infected cells and inhibits virus replication and pro-inflammatory gene expression. PLoS One. 2011;6:e19705.
Pu Q, Guo XX, Hu JJ, Li AL, Li GG, Li XY. Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases cell viability and restores tight junctions in high-glucose-treated human corneal epithelial cells via the SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;147:112659.
Wei CC, Kong YY, Li GQ, Guan YF, Wang P, Miao CY. Nicotinamide mononucleotide attenuates brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage by activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 2017;7:717.
Wan S, Ding Y, Ji X, Meng R. The safety and efficacy of ezetimibe plus statins on ASVD and related diseases. Aging Dis. 2021;12:1857–71.
Wei R, Huimin L, Huadong Y, Bei Y, Jianjin Z, Jiuzheng D, et al. Ezetimibe attenuates functional impairment via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation in traumatic spinal cord injury. Cell Mol Biol. 2023;69:175–80.
Yan N, Xu Z, Qu C, Zhang J. Dimethyl fumarate improves cognitive deficits in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats by alleviating inflammation, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis via NRF2/ARE/NF-kappaB signal pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;98:107844.
Yao Y, Miao W, Liu Z, Han W, Shi K, Shen Y, et al. Dimethyl fumarate and monomethyl fumarate promote post-ischemic recovery in mice. Transl Stroke Res. 2016;7:535–47.
Dashdulam D, Kim ID, Lee H, Lee HK, Kim SW, Lee JK. Osteopontin heptamer peptide containing the RGD motif enhances the phagocytic function of microglia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;524:371–7.
Davaanyam D, Kim ID, Lee JK. Intranasal delivery of RGD-containing osteopontin heptamer peptide confers neuroprotection in the ischemic brain and augments microglia M2 polarization. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:9999.
Elphick GF, Sarangi PP, Hyun YM, Hollenbaugh JA, Ayala A, Biffl WL, et al. Recombinant human activated protein C inhibits integrin-mediated neutrophil migration. Blood. 2009;113:4078–85.
Jin Y-C, Lee H, Kim S-W, Kim I-D, Lee H-K, Lee Y, et al. Intranasal delivery of RGD motif-containing osteopontin icosamer confers neuroprotection in the postischemic brain via αvβ3 integrin binding. Mol Neurobiol. 2015;53:5652–63.
Moon C, Han JR, Park HJ, Hah JS, Kang JL. Synthetic RGDS peptide attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation by inhibiting integrin signaled MAP kinase pathways. Respir Res. 2009;10:18.
Matuleviciute R, Akinluyi ET, Muntslag TAO, Dewing JM, Long KR, Vernon AC, et al. Microglial contribution to the pathology of neurodevelopmental disorders in humans. Acta Neuropathol. 2023;146:663–83.
Nauseef WM. Human neutrophils not equal murine neutrophils: Does it matter?. Immunol Rev. 2023;314:442–56.
Allen LH. Closing the gap between murine neutrophils and neutrophil-like cell lines. J Leukoc Biol. 2023;114:199–201.
Yu F, Wang Y, Stetler AR, Leak RK, Hu X, Chen J. Phagocytic microglia and macrophages in brain injury and repair. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022;28:1279–93.
Lampl Y, Boaz M, Gilad R, Lorberboym M, Dabby R, Rapoport A, et al. Minocycline treatment in acute stroke. Neurology. 2007;69:1404–10.
Zhu Z, Fu Y, Tian D, Sun N, Han W, Chang G, et al. Combination of the immune modulator fingolimod with alteplase in acute ischemic stroke. Circulation. 2015;132:1104–12.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS) (2022-I2M-1-015); National Natural Science Foundation of China (82474112, 82360788); Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Neurology and Oncology Drug Development (SKLSIM-F-202456).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Lr., Zhao, Zy., Li, Zw. et al. Targeting the interactions between neutrophils and microglia: a novel strategy for anti-inflammatory treatment of stroke. Acta Pharmacol Sin (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01662-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01662-z