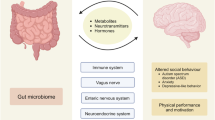
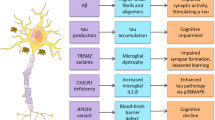
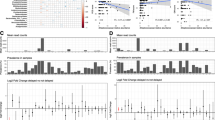
Abstract
Neurodevelopment is governed by precisely timed biological processes that are sensitive to environmental influences across generations. Among these, the gut microbiota (GM) has emerged as a key regulator of neurodevelopmental trajectories, not only within individuals but also through intergenerational transmission. This review highlights the emerging significance of the GM in shaping offspring brain and behavior, emphasizing its capacity to mediate maternal influences across generations. We first summarize the temporal and intergenerational effects of GM on host physiology and neurobehavioral outcomes. We then explore the mechanistic basis of neuro-microbial-immunometabolic interactions including epigenetic regulation, neurotransmitter modulation, neuroinflammation and intestinal barrier function in the context of the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Particular attention is given to how these mechanisms mediate the long-term impact of maternal states—such as stress, diet and inflammation—on offspring neurodevelopment. We further highlight the translational gap from animal models to humans and propose integrating multi-omics, computational modeling, and clinical approaches to define developmental windows and guide precision microbiota-based interventions for neurodevelopmental disorders. By elucidating how microbiota influence neurodevelopment across generations, this review aims to inform the development of novel microbial and pharmacological therapies to promote brain health from the maternal period through early offspring life.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silbereis JC, Pochareddy S, Zhu Y, Li M, Sestan N. The cellular and molecular landscapes of the developing human central nervous system. Neuron. 2016;89:248–68.
Roswall J, Olsson LM, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Nilsson S, Tremaroli V, Simon MC, et al. Developmental trajectory of the healthy human gut microbiota during the first 5 years of life. Cell Host Microbe. 2021;29:765–776 e3.
Grech A, Collins CE, Holmes A, Lal R, Duncanson K, Taylor R, et al. Maternal exposures and the infant gut microbiome: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Gut Microbes. 2021;13:1–30.
Hsiao CC, Tsai ML, Chen CC, Lin HC. Early optimal nutrition improves neurodevelopmental outcomes for very preterm infants. Nutr Rev. 2014;72:532–40.
de Weerth C. Do bacteria shape our development? Crosstalk between intestinal microbiota and HPA axis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017;83:458–71.
Dominguez-Bello MG, Costello EK, Contreras M, Magris M, Hidalgo G, Fierer N, et al. Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:11971–5.
Zoubovsky SP, Williams MT, Hoseus S, Tumukuntala S, Riesenberg A, Schulkin J, et al. Neurobehavioral abnormalities following prenatal psychosocial stress are differentially modulated by maternal environment. Transl Psychiatry. 2022;12:22.
Muhammad F, Fan B, Wang R, Ren J, Jia S, Wang L, et al. The molecular gut-brain axis in early brain development. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:15389.
Poon SSB, Hung LY, Wu Q, Parathan P, Yalcinkaya N, Haag A, et al. Neonatal antibiotics have long term sex-dependent effects on the enteric nervous system. J Physiol. 2022;600:4303–23.
Al Nabhani Z, Dulauroy S, Lecuyer E, Polomack B, Campagne P, Berard M, et al. Excess calorie intake early in life increases susceptibility to colitis in adulthood. Nat Metab. 2019;1:1101–9.
Ahrens AP, Hyotylainen T, Petrone JR, Igelstrom K, George CD, Garrett TJ, et al. Infant microbes and metabolites point to childhood neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell. 2024;187:1853–1873.e15.
Parnanen K, Karkman A, Hultman J, Lyra C, Bengtsson-Palme J, Larsson DGJ, et al. Maternal gut and breast milk microbiota affect infant gut antibiotic resistome and mobile genetic elements. Nat Commun. 2018;9:3891.
Prado EL, Dewey KG. Nutrition and brain development in early life. Nutr Rev. 2014;72:267–84.
Smith BL, Reyes TM. Offspring neuroimmune consequences of maternal malnutrition: potential mechanism for behavioral impairments that underlie metabolic and neurodevelopmental disorders. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2017;47:109–22.
Edlow AG. Maternal obesity and neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders in offspring. Prenat Diagn. 2017;37:95–110.
Sonnenburg ED, Smits SA, Tikhonov M, Higginbottom SK, Wingreen NS, Sonnenburg JL. Diet-induced extinctions in the gut microbiota compound over generations. Nature. 2016;529:212–5.
Buffington SA, Di Prisco GV, Auchtung TA, Ajami NJ, Petrosino JF, Costa-Mattioli M. Microbial reconstitution reverses maternal diet-induced social and synaptic deficits in offspring. Cell. 2016;165:1762–75.
Sohrabi R, Mousavi SN, Shapouri R, Nasiri Z, Heidarzadeh S, Shokri R. The gut dysbiosis of mothers with gestational diabetes and its correlation with diet. Sci Rep. 2025;15:18566.
Dearden L, Furigo IC, Pantaleao LC, Wong LWP, Fernandez-Twinn DS, de Almeida-Faria J, et al. Maternal obesity increases hypothalamic miR-505-5p expression in mouse offspring leading to altered fatty acid sensing and increased intake of high-fat food. PLoS Biol. 2024;22:e3002641.
Sgritta M, Dooling SW, Buffington SA, Momin EN, Francis MB, Britton RA, et al. Mechanisms underlying microbial-mediated changes in social behavior in mouse models of autism spectrum disorder. Neuron. 2019;101:246–259 e6.
Zhang P, Jiang G, Wang Y, Yan E, He L, Guo J, et al. Maternal consumption of l-malic acid enriched diets improves antioxidant capacity and glucose metabolism in offspring by regulating the gut microbiota. Redox Biol. 2023;67:102889.
Ryan DP, Henzel KS, Pearson BL, Siwek ME, Papazoglou A, Guo L, et al. A paternal methyl donor-rich diet altered cognitive and neural functions in offspring mice. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23:1345–55.
Oh J, Riek AE, Bauerle KT, Dusso A, McNerney KP, Barve RA, et al. Embryonic vitamin D deficiency programs hematopoietic stem cells to induce type 2 diabetes. Nat Commun. 2023;14:3278.
Peter CJ, Fischer LK, Kundakovic M, Garg P, Jakovcevski M, Dincer A, et al. DNA methylation signatures of early childhood malnutrition associated with impairments in attention and cognition. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;80:765–74.
Victora CG, Adair L, Fall C, Hallal PC, Martorell R, Richter L, et al. Maternal and child undernutrition: consequences for adult health and human capital. Lancet. 2008;371:340–57.
Yajnik CS, Deshmukh US. Fetal programming: maternal nutrition and role of one-carbon metabolism. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2012;13:121–7.
Sucksdorff M, Brown AS, Chudal R, Surcel HM, Hinkka-Yli-Salomaki S, Cheslack-Postava K, et al. Maternal vitamin D levels and the risk of offspring attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2021;60:142–151 e2.
Vuong HE, Pronovost GN, Williams DW, Coley EJL, Siegler EL, Qiu A, et al. The maternal microbiome modulates fetal neurodevelopment in mice. Nature. 2020;586:281–6.
Jasarevic E, Rodgers AB, Bale TL. A novel role for maternal stress and microbial transmission in early life programming and neurodevelopment. Neurobiol Stress. 2015;1:81–8.
Fasano A, Chassaing B, Haller D, Flores Ventura E, Carmen-Collado M, Pastor N, et al. Microbiota during pregnancy and early life: role in maternal-neonatal outcomes based on human evidence. Gut Microbes. 2024;16:2392009.
Gonzalez A, Stombaugh J, Lozupone C, Turnbaugh PJ, Gordon JI, Knight R. The mind-body-microbial continuum. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2011;13:55–62.
Xue H, Liang B, Wang Y, Gao H, Fang S, Xie K, et al. The regulatory effect of polysaccharides on the gut microbiota and their effect on human health: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;270:132170.
Tremaroli V, Backhed F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature. 2012;489:242–9.
Aagaard K, Ma J, Antony KM, Ganu R, Petrosino J, Versalovic J. The placenta harbors a unique microbiome. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:237ra65–237ra65.
Lopez-Tello J, Schofield Z, Kiu R, Dalby MJ, van Sinderen D, Le Gall G, et al. Maternal gut microbiota Bifidobacterium promotes placental morphogenesis, nutrient transport and fetal growth in mice. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79:386.
Pronovost GN, Yu KB, Coley-O’Rourke EJL, Telang SS, Chen AS, Vuong HE, et al. The maternal microbiome promotes placental development in mice. Sci Adv. 2023;9:eadk1887.
Xiao L, Zhao F. Microbial transmission, colonisation and succession: from pregnancy to infancy. Gut. 2023;72:772–86.
Bokulich NA, Chung J, Battaglia T, Henderson N, Jay M, Li H, et al. Antibiotics, birth mode, and diet shape microbiome maturation during early life. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8:343ra82.
Wang S, Egan M, Ryan CA, Boyaval P, Dempsey EM, Ross RP, et al. A good start in life is important-perinatal factors dictate early microbiota development and longer term maturation. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2020;44:763–81.
Jasarevic E, Howard CD, Morrison K, Misic A, Weinkopff T, Scott P, et al. The maternal vaginal microbiome partially mediates the effects of prenatal stress on offspring gut and hypothalamus. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21:1061–71.
Gilbert NM, Foster LR, Cao B, Yin Y, Mysorekar IU, Lewis AL. Gardnerella vaginalis promotes group B Streptococcus vaginal colonization, enabling ascending uteroplacental infection in pregnant mice. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224:530 e1–530 e17.
Fischer LA, Demerath E, Bittner-Eddy P, Costalonga M. Placental colonization with periodontal pathogens: the potential missing link. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:383–392 e3.
Xu B, Han YW. Oral bacteria, oral health, and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Periodontol 2000. 2022;89:181–9.
Iheozor-Ejiofor Z, Middleton P, Esposito M, Glenny AM. Treating periodontal disease for preventing adverse birth outcomes in pregnant women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;6:CD005297.
Ren H, Du M. Role of maternal periodontitis in preterm birth. Front Immunol. 2017;8:139.
Lithgow KV, Buchholz VCH, Ku E, Konschuh S, D’Aubeterre A, Sycuro LK. Protease activities of vaginal Porphyromonas species disrupt coagulation and extracellular matrix in the cervicovaginal niche. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2022;8:8.
Keelan JA, Wong PM, Bird PS, Mitchell MD. Innate inflammatory responses of human decidual cells to periodontopathic bacteria. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;202:471 e1–11.
Thapar A, Cooper M, Rutter M. Neurodevelopmental disorders. Lancet Psychiatry. 2017;4:339–46.
Muhle RA, Reed HE, Stratigos KA, Veenstra-VanderWeele J. The emerging clinical neuroscience of autism spectrum disorder: a review. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75:514–23.
Polanczyk G, de Lima MS, Horta BL, Biederman J, Rohde LA. The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: a systematic review and metaregression analysis. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164:942–8.
Parenti I, Rabaneda LG, Schoen H, Novarino G. Neurodevelopmental disorders: from genetics to functional pathways. Trends Neurosci. 2020;43:608–21.
Joffe JM. Genotype and prenatal and premating stress interact to affect adult behavior in rats. Science. 1965;150:1844–5.
Walsh K, McCormack CA, Webster R, Pinto A, Lee S, Feng T, et al. Maternal prenatal stress phenotypes associate with fetal neurodevelopment and birth outcomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:23996–4005.
Galley JD, Mashburn-Warren L, Blalock LC, Lauber CL, Carroll JE, Ross KM, et al. Maternal anxiety, depression and stress affects offspring gut microbiome diversity and bifidobacterial abundances. Brain Behav Immun. 2023;107:253–64.
Gomez de Aguero M, Ganal-Vonarburg SC, Fuhrer T, Rupp S, Uchimura Y, Li H, et al. The maternal microbiota drives early postnatal innate immune development. Science. 2016;351:1296–302.
Xu Z, Zhang X, Chang H, Kong Y, Ni Y, Liu R, et al. Rescue of maternal immune activation-induced behavioral abnormalities in adult mouse offspring by pathogen-activated maternal T(reg) cells. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24:818–30.
Hantsoo L, Kornfield S, Anguera MC, Epperson CN. Inflammation: a proposed intermediary between maternal stress and offspring neuropsychiatric risk. Biol Psychiatry. 2019;85:97–106.
Seki D, Mayer M, Hausmann B, Pjevac P, Giordano V, Goeral K, et al. Aberrant gut-microbiota-immune-brain axis development in premature neonates with brain damage. Cell Host Microbe. 2021;29:1558–1572 e6.
Argaw-Denboba A, Schmidt TSB, Di Giacomo M, Ranjan B, Devendran S, Mastrorilli E, et al. Paternal microbiome perturbations impact offspring fitness. Nature. 2024;629:652–9.
Sun Y, Xie R, Li L, Jin G, Zhou B, Huang H, et al. Prenatal maternal stress exacerbates experimental colitis of offspring in adulthood. Front Immunol. 2021;12:700995.
Malkova NV, Yu CZ, Hsiao EY, Moore MJ, Patterson PH. Maternal immune activation yields offspring displaying mouse versions of the three core symptoms of autism. Brain Behav Immun. 2012;26:607–16.
Estes ML, McAllister AK. Maternal immune activation: implications for neuropsychiatric disorders. Science. 2016;353:772–7.
Koren O, Konnikova L, Brodin P, Mysorekar IU, Collado MC. The maternal gut microbiome in pregnancy: implications for the developing immune system. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;21:35–45.
Foster JA. Modulating brain function with microbiota. Science. 2022;376:936–7.
Blacher E, Bashiardes S, Shapiro H, Rothschild D, Mor U, Dori-Bachash M, et al. Potential roles of gut microbiome and metabolites in modulating ALS in mice. Nature. 2019;572:474–80.
Hsiao EY, McBride SW, Hsien S, Sharon G, Hyde ER, McCue T, et al. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell. 2013;155:1451–63.
Needham BD, Funabashi M, Adame MD, Wang Z, Boktor JC, Haney J, et al. A gut-derived metabolite alters brain activity and anxiety behaviour in mice. Nature. 2022;602:647–53.
Stewart Campbell A, Needham BD, Meyer CR, Tan J, Conrad M, Preston GM, et al. Safety and target engagement of an oral small-molecule sequestrant in adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: an open-label phase 1b/2a trial. Nat Med. 2022;28:528–34.
Tan JK, Macia L, Mackay CR. Dietary fiber and SCFAs in the regulation of mucosal immunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023;151:361–70.
Martin-Gallausiaux C, Marinelli L, Blottière HM, Larraufie P, Lapaque N. SCFA: mechanisms and functional importance in the gut. Proc Nutr Soc. 2021;80:37–49.
Krautkramer KA, Fan J, Bäckhed F. Gut microbial metabolites as multi-kingdom intermediates. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19:77–94.
de Theije CG, Wopereis H, Ramadan M, van Eijndthoven T, Lambert J, Knol J, et al. Altered gut microbiota and activity in a murine model of autism spectrum disorders. Brain Behav Immun. 2014;37:197–206.
Osman A, Mervosh NL, Strat AN, Euston TJ, Zipursky G, Pollak RM, et al. Acetate supplementation rescues social deficits and alters transcriptional regulation in prefrontal cortex of Shank3 deficient mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2023;114:311–24.
Lee YM, Mu A, Wallace M, Gengatharan JM, Furst AJ, Bode L, et al. Microbiota control of maternal behavior regulates early postnatal growth of offspring. Sci Adv. 2021;7:eabe6563.
Morais LH, Schreiber HLT, Mazmanian SK. The gut microbiota-brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19:241–55.
Sharon G, Sampson TR, Geschwind DH, Mazmanian SK. The central nervous system and the gut microbiome. Cell. 2016;167:915–32.
Leclercq S, Le Roy T, Furgiuele S, Coste V, Bindels LB, Leyrolle Q, et al. Gut microbiota-induced changes in beta-hydroxybutyrate metabolism are linked to altered sociability and depression in alcohol use disorder. Cell Rep. 2020;33:108238.
Vicentini FA, Keenan CM, Wallace LE, Woods C, Cavin JB, Flockton AR, et al. Intestinal microbiota shapes gut physiology and regulates enteric neurons and glia. Microbiome. 2021;9:210.
Shi H, Ge X, Ma X, Zheng M, Cui X, Pan W, et al. A fiber-deprived diet causes cognitive impairment and hippocampal microglia-mediated synaptic loss through the gut microbiota and metabolites. Microbiome. 2021;9:223.
Ahmed H, Leyrolle Q, Koistinen V, Karkkainen O, Laye S, Delzenne N, et al. Microbiota-derived metabolites as drivers of gut-brain communication. Gut Microbes. 2022;14:2102878.
Sun W, Xie G, Jiang X, Khaitovich P, Han D, Liu X. Epigenetic regulation of human-specific gene expression in the prefrontal cortex. BMC Biol. 2023;21:123.
Gomes TM, Dias da Silva D, Carmo H, Carvalho F, Silva JP. Epigenetics and the endocannabinoid system signaling: an intricate interplay modulating neurodevelopment. Pharmacol Res. 2020;162:105237.
Jeong S, Chokkalla AK, Davis CK, Vemuganti R. Post-stroke depression: epigenetic and epitranscriptomic modifications and their interplay with gut microbiota. Mol Psychiatry. 2023;28:4044–55.
De Rubeis S, He X, Goldberg AP, Poultney CS, Samocha K, Cicek AE, et al. Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism. Nature. 2014;515:209–15.
Pan W-H, Sommer F, Falk-Paulsen M, Ulas T, Best L, Fazio A, et al. Exposure to the gut microbiota drives distinct methylome and transcriptome changes in intestinal epithelial cells during postnatal development. Genome Med. 2018;10:27.
Takeuchi T, Kubota T, Nakanishi Y, Tsugawa H, Suda W, Kwon AT, et al. Gut microbial carbohydrate metabolism contributes to insulin resistance. Nature. 2023;621:389–95.
Li Y, Luo ZY, Hu YY, Bi YW, Yang JM, Zou WJ, et al. The gut microbiota regulates autism-like behavior by mediating vitamin B(6) homeostasis in EphB6-deficient mice. Microbiome. 2020;8:120.
Rosario D, Bidkhori G, Lee S, Bedarf J, Hildebrand F, Le Chatelier E, et al. Systematic analysis of gut microbiome reveals the role of bacterial folate and homocysteine metabolism in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Rep. 2021;34:108807.
Wang X, Li Y, Chen W, Shi H, Eren AM, Morozov A, et al. Transcriptome-wide reprogramming of N6-methyladenosine modification by the mouse microbiome. Cell Res. 2019;29:167–70.
Sun Z, Lee-Sarwar K, Kelly RS, Lasky-Su JA, Litonjua AA, Weiss ST, et al. Revealing the importance of prenatal gut microbiome in offspring neurodevelopment in humans. eBioMedicine. 2023;90:104491.
Wang T, Kong S, Tao M, Ju S. The potential role of RNA N6-methyladenosine in cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:88.
Chen S, Zhang L, Li M, Zhang Y, Sun M, Wang L, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum reduces METTL3-mediated m6A modification and contributes to colorectal cancer metastasis. Nat Commun. 2022;13:1248.
Yshii L, Pasciuto E, Bielefeld P, Mascali L, Lemaitre P, Marino M, et al. Astrocyte-targeted gene delivery of interleukin 2 specifically increases brain-resident regulatory T cell numbers and protects against pathological neuroinflammation. Nat Immunol. 2022;23:878–91.
Brown EM, Kenny DJ, Xavier RJ. Gut microbiota regulation of T cells during inflammation and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2019;37:599–624.
Round JL, Mazmanian SK. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:313–23.
Fujimura KE, Sitarik AR, Havstad S, Lin DL, Levan S, Fadrosh D, et al. Neonatal gut microbiota associates with childhood multisensitized atopy and T cell differentiation. Nat Med. 2016;22:1187–91.
Bostick JW, Schonhoff AM, Mazmanian SK. Gut microbiome-mediated regulation of neuroinflammation. Curr Opin Immunol. 2022;76:102177.
Xie K, Wang C, Scifo E, Pearson B, Ryan D, Henzel K, et al. Intermittent fasting boosts sexual behavior by limiting the central availability of tryptophan and serotonin. Cell Metab. 2025;37:1189–205.e7.
O’Donnell MP, Fox BW, Chao PH, Schroeder FC, Sengupta P. A neurotransmitter produced by gut bacteria modulates host sensory behaviour. Nature. 2020;583:415–20.
Miyauchi E, Kim SW, Suda W, Kawasumi M, Onawa S, Taguchi-Atarashi N, et al. Gut microorganisms act together to exacerbate inflammation in spinal cords. Nature. 2020;585:102–6.
Mishra A, Lai GC, Yao LJ, Aung TT, Shental N, Rotter-Maskowitz A, et al. Microbial exposure during early human development primes fetal immune cells. Cell. 2021;184:3394–3409 e20.
Kim JE, Li B, Fei L, Horne R, Lee D, Loe AKH, et al. Gut microbiota promotes stem cell differentiation through macrophage and mesenchymal niches in early postnatal development. Immunity. 2023;56:2175.
Renz H, Skevaki C. Early life microbial exposures and allergy risks: opportunities for prevention. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21:177–91.
Wang T, Chen B, Luo M, Xie L, Lu M, Lu X, et al. Microbiota-indole 3-propionic acid-brain axis mediates abnormal synaptic pruning of hippocampal microglia and susceptibility to ASD in IUGR offspring. Microbiome. 2023;11:245.
Thomas RH, Meeking MM, Mepham JR, Tichenoff L, Possmayer F, Liu S, et al. The enteric bacterial metabolite propionic acid alters brain and plasma phospholipid molecular species: further development of a rodent model of autism spectrum disorders. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9:153.
Berger S, Ronovsky M, Horvath O, Berger A, Pollak DD. Impact of maternal immune activation on maternal care behavior, offspring emotionality and intergenerational transmission in C3H/He mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2018;70:131–40.
Braniste V, Al-Asmakh M, Kowal C, Anuar F, Abbaspour A, Toth M, et al. The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:263ra158.
Hoyles L, Pontifex MG, Rodriguez-Ramiro I, Anis-Alavi MA, Jelane KS, Snelling T, et al. Regulation of blood-brain barrier integrity by microbiome-associated methylamines and cognition by trimethylamine N-oxide. Microbiome. 2021;9:235.
Danhof HA, Lee J, Thapa A, Britton RA, Di Rienzi SC. Microbial stimulation of oxytocin release from the intestinal epithelium via secretin signaling. Gut Microbes. 2023;15:2256043.
Guzzardi MA, Ederveen THA, Rizzo F, Weisz A, Collado MC, Muratori F, et al. Maternal pre-pregnancy overweight and neonatal gut bacterial colonization are associated with cognitive development and gut microbiota composition in pre-school-age offspring. Brain Behav Immun. 2022;100:311–20.
Xu M, Zu P, Ma SS, Wang HX, Jiang N, Bian JF, et al. Variations in executive function in toddlers after exposure to pre-pregnancy overweight and obesity and the mediating role of inflammation in a longitudinal pregnancy cohort study. Brain Behav Immun. 2025;130:106075.
Tabouy L, Getselter D, Ziv O, Karpuj M, Tabouy T, Lukic I, et al. Dysbiosis of microbiome and probiotic treatment in a genetic model of autism spectrum disorders. Brain Behav Immun. 2018;73:310–9.
Schulfer AF, Battaglia T, Alvarez Y, Bijnens L, Ruiz VE, Ho M, et al. Intergenerational transfer of antibiotic-perturbed microbiota enhances colitis in susceptible mice. Nat Microbiol. 2018;3:234–42.
Yang S, Li W, Challis JR, Reid G, Kim SO, Bocking AD. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 supernatant prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced preterm birth and reduces inflammation in pregnant CD-1 mice. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014;211:44.e1–44.e12.
Kong XJ, Liu J, Liu K, Koh M, Sherman H, Liu S, et al. Probiotic and oxytocin combination therapy in patients with autism spectrum disorder: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled pilot trial. Nutrients. 2021;13:1552.
He Z, Li W, Yuan W, He Y, Xu J, Yuan C, et al. Lactobacillus reuteri inhibits Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis by regulating oxytocin releasing and gut microbiota in mice. FASEB J. 2024;38:e23383.
Carson KE, Alvarez J, Mackley JQ, Travagli RA, Browning KN. Perinatal high-fat diet exposure alters oxytocin and corticotropin releasing factor inputs onto vagal neurocircuits controlling gastric motility. J Physiol. 2023;601:2853–75.
Yuan L, Liu S, Bai X, Gao Y, Liu G, Wang X, et al. Oxytocin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in microglial cells and attenuates microglial activation in lipopolysaccharide-treated mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2016;13:77.
Jiang J, Zou Y, Xie C, Yang M, Tong Q, Yuan M, et al. Oxytocin alleviates cognitive and memory impairments by decreasing hippocampal microglial activation and synaptic defects via OXTR/ERK/STAT3 pathway in a mouse model of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Brain Behav Immun. 2023;114:195–213.
Lindsay KL, Brennan L, Kennelly MA, Maguire OC, Smith T, Curran S, et al. Impact of probiotics in women with gestational diabetes mellitus on metabolic health: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212:496 e1–11.
Wu Y, Zhang G, Wang Y, Wei X, Liu H, Zhang L, et al. A review on maternal and infant microbiota and their implications for the prevention and treatment of allergic diseases. Nutrients. 2023;15:2483.
Xiang Q, Yan X, Shi W, Li H, Zhou K. Early gut microbiota intervention in premature infants: application perspectives. J Adv Res. 2023;51:59–72.
Hudobenko J, Di Gesu CM, Mooz PR, Petrosino J, Putluri N, Ganesh BP, et al. Maternal dysbiosis produces long-lasting behavioral changes in offspring. Mol Psychiatry. 2024;30:1847–58.
Taylor BL, Woodfall GE, Sheedy KE, O’Riley ML, Rainbow KA, Bramwell EL, et al. Effect of probiotics on metabolic outcomes in pregnant women with gestational diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients. 2017;9:461.
Chao J, Tan Z, Li Z, Xu C. The role of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in perinatal depression: novel insights for treatment. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025 https://doi.org/10.2174/011570159X380460250710061340.
Zuccotti G, Meneghin F, Aceti A, Barone G, Callegari ML, Di Mauro A, et al. Probiotics for prevention of atopic diseases in infants: systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy. 2015;70:1356–71.
Brosseau C, Selle A, Duval A, Misme-Aucouturier B, Chesneau M, Brouard S, et al. Prebiotic supplementation during pregnancy modifies the gut microbiota and increases metabolites in amniotic fluid, driving a tolerogenic environment in utero. Front Immunol. 2021;12:712614.
Jones JM, Reinke SN, Mousavi-Derazmahalleh M, Garssen J, Jenmalm MC, Srinivasjois R, et al. Maternal prebiotic supplementation during pregnancy and lactation modifies the microbiome and short chain fatty acid profile of both mother and infant. Clin Nutr. 2024;43:969–80.
Paul HA, Collins KH, Nicolucci AC, Urbanski SJ, Hart DA, Vogel HJ, et al. Maternal prebiotic supplementation reduces fatty liver development in offspring through altered microbial and metabolomic profiles in rats. FASEB J. 2019;33:5153–67.
Renz H, Adkins BD, Bartfeld S, Blumberg RS, Farber DL, Garssen J, et al. The neonatal window of opportunity-early priming for life. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:1212–4.
Mu J, Guo X, Zhou Y, Cao G. The effects of probiotics/synbiotics on glucose and lipid metabolism in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients. 2023;15:1375.
Lawson MAE, O’Neill IJ, Kujawska M, Gowrinadh Javvadi S, Wijeyesekera A, Flegg Z, et al. Breast milk-derived human milk oligosaccharides promote Bifidobacterium interactions within a single ecosystem. ISME J. 2020;14:635–48.
Ferro LE, Crowley LN, Bittinger K, Friedman ES, Decker JE, Russel K, et al. Effects of prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics on the infant gut microbiota and other health outcomes: a systematic review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63:5620–42.
Catassi G, Aloi M, Giorgio V, Gasbarrini A, Cammarota G, Ianiro G. The role of diet and nutritional interventions for the infant gut microbiome. Nutrients. 2024;16:400.
Zhang W, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Li L, Zhang Z, Hettinga K, et al. A comprehensive review on dietary polysaccharides as prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics in infant formula and their influences on gut microbiota. Nutrients. 2024;16:4122.
He P, Yu L, Tian F, Chen W, Zhang H, Zhai Q. Effects of probiotics on preterm infant gut microbiota across populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv Nutr. 2024;15:100233.
Elhossiny RM, Elshahawy HH, Mohamed HM, Abdelmageed RI. Assessment of probiotic strain Lactobacillus acidophilus LB supplementation as adjunctive management of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a randomized controlled clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2023;23:823.
Colombo J, Zavaleta N, Kannass KN, Lazarte F, Albornoz C, Kapa LL, et al. Zinc supplementation sustained normative neurodevelopment in a randomized, controlled trial of Peruvian infants aged 6-18 months. J Nutr. 2014;144:1298–305.
Gharibeh N, Razaghi M, Vanstone CA, Sotunde OF, Glenn L, Mullahoo K, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on bone mass in infants with 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations less than 50 nmol/L: a prespecified secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2023;177:353–62.
Sharon G, Cruz NJ, Kang DW, Gandal MJ, Wang B, Kim YM, et al. Human gut microbiota from autism spectrum disorder promote behavioral symptoms in mice. Cell. 2019;177:1600–1618 e17.
Kang DW, Adams JB, Coleman DM, Pollard EL, Maldonado J, McDonough-Means S, et al. Long-term benefit of microbiota transfer therapy on autism symptoms and gut microbiota. Sci Rep. 2019;9:5821.
Dang H, Feng P, Zhang S, Peng L, Xing S, Li Y, et al. Maternal gut microbiota influence stem cell function in offspring. Cell Stem Cell. 2025;32:246–262 e8.
Wang Q, Yang Q, Liu X. The microbiota-gut-brain axis and neurodevelopmental disorders. Protein Cell. 2023;14:762–75.
Morton JT, Jin DM, Mills RH, Shao Y, Rahman G, McDonald D, et al. Multi-level analysis of the gut-brain axis shows autism spectrum disorder-associated molecular and microbial profiles. Nat Neurosci. 2023;26:1208–17.
Park JC, Chang L, Kwon HK, Im SH. Beyond the gut: decoding the gut-immune-brain axis in health and disease. Cell Mol Immunol. 2025;22:1287–312.
Saben JL, Boudoures AL, Asghar Z, Thompson A, Drury A, Zhang W, et al. Maternal metabolic syndrome programs mitochondrial dysfunction via germline changes across three generations. Cell Rep. 2016;16:1–8.
Jones HN, Woollett LA, Barbour N, Prasad PD, Powell TL, Jansson T. High-fat diet before and during pregnancy causes marked up-regulation of placental nutrient transport and fetal overgrowth in C57/BL6 mice. FASEB J. 2009;23:271–8.
Chen B, Du YR, Zhu H, Sun ML, Wang C, Cheng Y, et al. Maternal inheritance of glucose intolerance via oocyte TET3 insufficiency. Nature. 2022;605:761–6.
Liu X, Li X, Xia B, Jin X, Zou Q, Zeng Z, et al. High-fiber diet mitigates maternal obesity-induced cognitive and social dysfunction in the offspring via gut-brain axis. Cell Metab. 2021;33:923–938 e6.
Govindarajah V, Sakabe M, Good S, Solomon M, Arasu A, Chen N, et al. Gestational diabetes in mice induces hematopoietic memory that affects the long-term health of the offspring. J Clin Invest. 2024;134:e169730.
Ceasrine AM, Devlin BA, Bolton JL, Green LA, Jo YC, Huynh C, et al. Maternal diet disrupts the placenta-brain axis in a sex-specific manner. Nat Metab. 2022;4:1732–45.
Elgazzaz M, Berdasco C, Garai J, Baddoo M, Lu S, Daoud H, et al. Maternal Western diet programs cardiometabolic dysfunction and hypothalamic inflammation via epigenetic mechanisms predominantly in the male offspring. Mol Metab. 2024;80:101864.
Cerychova R, Bohuslavova R, Papousek F, Sedmera D, Abaffy P, Benes V, et al. Adverse effects of Hif1a mutation and maternal diabetes on the offspring heart. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17:68.
Fidilio A, Grasso M, Caruso G, Musso N, Begni V, Privitera A, et al. Prenatal stress induces a depressive-like phenotype in adolescent rats: the key role of TGF-beta1 pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1075746.
Bronson SL, Bale TL. Prenatal stress-induced increases in placental inflammation and offspring hyperactivity are male-specific and ameliorated by maternal antiinflammatory treatment. Endocrinology. 2014;155:2635–46.
Gumusoglu SB, Fine RS, Murray SJ, Bittle JL, Stevens HE. The role of IL-6 in neurodevelopment after prenatal stress. Brain Behav Immun. 2017;65:274–83.
Chen HJ, Galley JD, Verosky BG, Yang FT, Rajasekera TA, Bailey MT, et al. Fetal CCL2 signaling mediates offspring social behavior and recapitulates effects of prenatal stress. Brain Behav Immun. 2024;115:308–18.
Zijlmans MA, Korpela K, Riksen-Walraven JM, de Vos WM, de Weerth C. Maternal prenatal stress is associated with the infant intestinal microbiota. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015;53:233–45.
Golubeva AV, Crampton S, Desbonnet L, Edge D, O’Sullivan O, Lomasney KW, et al. Prenatal stress-induced alterations in major physiological systems correlate with gut microbiota composition in adulthood. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015;60:58–74.
Gur TL, Shay L, Palkar AV, Fisher S, Varaljay VA, Dowd S, et al. Prenatal stress affects placental cytokines and neurotrophins, commensal microbes, and anxiety-like behavior in adult female offspring. Brain Behav Immun. 2017;64:50–58.
Garcia-Flores V, Romero R, Furcron AE, Levenson D, Galaz J, Zou C, et al. Prenatal maternal stress causes preterm birth and affects neonatal adaptive immunity in mice. Front Immunol. 2020;11:254.
Brawner KM, Yeramilli VA, Kennedy BA, Patel RK, Martin CA. Prenatal stress increases IgA coating of offspring microbiota and exacerbates necrotizing enterocolitis-like injury in a sex-dependent manner. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;89:291–9.
Liu MY, Wei LL, Zhu XH, Ding HC, Liu XH, Li H, et al. Prenatal stress modulates HPA axis homeostasis of offspring through dentate TERT independently of glucocorticoids receptor. Mol Psychiatry. 2023;28:1383–95.
Goldstein JM, Holsen L, Huang G, Hammond BD, James-Todd T, Cherkerzian S, et al. Prenatal stress-immune programming of sex differences in comorbidity of depression and obesity/metabolic syndrome. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2016;18:425–36.
Lian S, Li W, Wang D, Xu B, Guo X, Yang H, et al. Effects of prenatal cold stress on maternal serum metabolomics in rats. Life Sci. 2020;246:117432.
Tegethoff M, Greene N, Olsen J, Schaffner E, Meinlschmidt G. Stress during pregnancy and offspring pediatric disease: A National Cohort Study. Environ Health Perspect. 2011;119:1647–52.
Mughal MK, Giallo R, Arnold PD, Kehler H, Bright K, Benzies K, et al. Trajectories of maternal distress and risk of child developmental delays: findings from the All Our Families (AOF) pregnancy cohort. J Affect Disord. 2019;248:1–12.
Lin Y, Xu J, Huang J, Jia Y, Zhang J, Yan C, et al. Effects of prenatal and postnatal maternal emotional stress on toddlers’ cognitive and temperamental development. J Affect Disord. 2017;207:9–17.
Glynn LM, Howland MA, Sandman CA, Davis EP, Phelan M, Baram TZ, et al. Prenatal maternal mood patterns predict child temperament and adolescent mental health. J Affect Disord. 2018;228:83–90.
Furse S, Koulman A, Ozanne SE, Poston L, White SL, Meek CL. Altered lipid metabolism in obese women with gestational diabetes and associations with offspring adiposity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107:E2825–E2832.
Gillman MW, Oakey H, Baghurst PA, Volkmer RE, Robinson JS, Crowther CA. Effect of treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus on obesity in the next generation. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:964–8.
Wang S, Liu Y, Tam WH, Ching JYL, Xu W, Yan S, et al. Maternal gestational diabetes mellitus associates with altered gut microbiome composition and head circumference abnormalities in male offspring. Cell Host Microbe. 2024;32:1192–1206 e5.
Zhang C, Chen Y, Duan R, Zhang Y, Zheng H, Zhang J, et al. Preconception maternal gut dysbiosis affects enteric nervous system development and disease susceptibility in offspring via the GPR41-GDNF/RET/SOX10 signaling pathway. Imeta. 2025;4:e70012.
Coley-O’Rourke EJ, Lum GR, Pronovost GN, Yu LW, Ozcan E, Yu KB, et al. Murine maternal microbiome modifies adverse effects of protein undernutrition on offspring neurobehaviour. Nat Microbiol. 2025;10:1648–64.
Liu Z, Wu C, Sun Z, Lin Z, Sun Y, Amjad N, et al. Gut microbiota remodeling exacerbates neuroinflammation and cognitive dysfunction via the microbiota-gut-brain axis in prenatal VPA-exposed C57BL/6 mice offspring. Front Immunol. 2025;16:1633680.
Liu J, Liu C, Gao Z, Zhou L, Gao J, Luo Y, et al. GW4064 alters gut microbiota composition and counteracts autism-associated behaviors in BTBR T+tf/J Mice. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12:911259.
Wang C, Chen W, Jiang Y, Xiao X, Zou Q, Liang J, et al. A synbiotic formulation of Lactobacillus reuteri and inulin alleviates ASD-like behaviors in a mouse model: the mediating role of the gut-brain axis. Food Funct. 2024;15:387–400.
Chen CM, Wu CC, Kim Y, Hsu WY, Tsai YC, Chiu SL. Enhancing social behavior in an autism spectrum disorder mouse model: investigating the underlying mechanisms of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum intervention. Gut Microbes. 2024;16:2359501.
Fourie NH, Wang D, Abey SK, Creekmore AL, Hong S, Martin CG, et al. Structural and functional alterations in the colonic microbiome of the rat in a model of stress induced irritable bowel syndrome. Gut Microbes. 2017;8:33–45.
Chu DM, Ma J, Prince AL, Antony KM, Seferovic MD, Aagaard KM. Maturation of the infant microbiome community structure and function across multiple body sites and in relation to mode of delivery. Nat Med. 2017;23:314–26.
Chevalier G, Siopi E, Guenin-Mace L, Pascal M, Laval T, Rifflet A, et al. Effect of gut microbiota on depressive-like behaviors in mice is mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Nat Commun. 2020;11:6363.
Rautava S, Kainonen E, Salminen S, Isolauri E. Maternal probiotic supplementation during pregnancy and breast-feeding reduces the risk of eczema in the infant. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:1355–60.
Kallio S, Jian C, Korpela K, Kukkonen AK, Salonen A, Savilahti E, et al. Early-life gut microbiota associates with allergic rhinitis during 13-year follow-up in a Finnish probiotic intervention cohort. Microbiol Spectr. 2024;12:e0413523.
Sass L, Bjarnadottir E, Stokholm J, Chawes B, Vinding RK, Mora-Jensen AC, et al. Fish oil supplementation in pregnancy and neurodevelopment in childhood—a randomized clinical trial. Child Dev. 2021;92:1624–35.
Lyons-Reid J, Derraik JGB, Kenealy T, Albert BB, Ramos Nieves JM, Monnard CR, et al. Impact of preconception and antenatal supplementation with myo-inositol, probiotics, and micronutrients on offspring BMI and weight gain over the first 2 years. BMC Med. 2024;22:39.
Ma G, Chen Y, Liu X, Gao Y, Deavila JM, Zhu MJ, et al. Vitamin a supplementation during pregnancy in shaping child growth outcomes: a meta-analysis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63:12240–55.
Lee SR, Jeong SH, Mukae M, Kim SY, Ko JW, Kwun HJ, et al. Dietary supplementation with nicotinamide riboside improves fetal growth under hypoglycemia. J Nutr Biochem. 2023;116:109310.
Barbian ME, Owens JA, Naudin CR, Denning P, Patel RM, Jones RM. A high fiber diet or supplementation with Lactococcus lactis subspecies cremoris to pregnant mice confers protection against intestinal injury in adult offspring. Gut Microbes. 2024;16:2337317.
Gareau MG, Jury J, MacQueen G, Sherman PM, Perdue MH. Probiotic treatment of rat pups normalises corticosterone release and ameliorates colonic dysfunction induced by maternal separation. Gut. 2007;56:1522–8.
Samara J, Moossavi S, Alshaikh B, Ortega VA, Pettersen VK, Ferdous T, et al. Supplementation with a probiotic mixture accelerates gut microbiome maturation and reduces intestinal inflammation in extremely preterm infants. Cell Host Microbe. 2022;30:696–711 e5.
Van Rossum T, Haiss A, Knoll RL, Marissen J, Podlesny D, Pagel J, et al. Bifidobacterium and lactobacillus probiotics and gut dysbiosis in preterm infants: the PRIMAL randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2024;178:985–95.
Rojas MA, Lozano JM, Rojas MX, Rodriguez VA, Rondon MA, Bastidas JA, et al. Prophylactic probiotics to prevent death and nosocomial infection in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2012;130:e1113–20.
Chi C, Fan Y, Li C, Li Y, Guo S, Li T, et al. Early gut microbiota colonisation of premature infants fed with breastmilk or formula with or without probiotics: a cohort study. Nutrients. 2021;13:4068.
Lin HC, Hsu CH, Chen HL, Chung MY, Hsu JF, Lien RI, et al. Oral probiotics prevent necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight preterm infants: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2008;122:693–700.
Hop le T, Berger J. Multiple micronutrient supplementation improves anemia, micronutrient nutrient status, and growth of Vietnamese infants: double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Nutr. 2005;135:660S–665S.
Taneja S, Upadhyay RP, Chowdhury R, Kurpad AV, Bhardwaj H, Kumar T, et al. Impact of supplementation with milk-cereal mix during 6-12 months of age on growth at 12 months: a 3-arm randomized controlled trial in Delhi, India. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022;115:83–93.
Kalbermatter C, Fernandez Trigo N, Christensen S, Ganal-Vonarburg SC. Maternal microbiota, early life colonization and breast milk drive immune development in the newborn. Front Immunol. 2021;12:683022.
Evans LW, Stratton MS, Ferguson BS. Dietary natural products as epigenetic modifiers in aging-associated inflammation and disease. Nat Prod Rep. 2020;37:653–76.
Peng B, Wang R, Zuo W, Liu H, Deng C, Jing X, et al. Distinct correlation network of clinical characteristics in suicide attempters having adolescent major depressive disorder with non-suicidal self-injury. Transl Psychiatry. 2024;14:134.
Slavin J. Fiber and prebiotics: mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients. 2013;5:1417–35.
Shenhav L, Fehr K, Reyna ME, Petersen C, Dai DLY, Dai R, et al. Microbial colonization programs are structured by breastfeeding and guide healthy respiratory development. Cell. 2024;187:5431–5452.e20.
Acknowledgements
This review was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32371213, 31900728), the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2023A1515011743), the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (JCYJ20250604183013017, KCXFZ20211020163549011, JCYJ20250604182920028), the Basic research of Shenzhen science and technology plan project (JCYJ20210324135211030), the Guangdong High-Level Hospital Construction Fund (LCYJ2022094), the Shenzhen Medical Research Funds (D2301002). The Figure 2 and Figure 4 were drawn by Figdraw.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XAL conceived and designed the project. RXW, AA, and XYJ prepared the manuscript. XAL, DZC, YZ, JXF, and ZXC reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Rx., Afzal, A., Jing, Xy. et al. Intergenerational effects of the microbiota on neurodevelopment: mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Acta Pharmacol Sin (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01693-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01693-6