Abstract
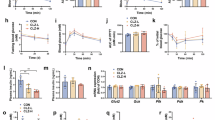
Atypical antipsychotics often cause hyperglycemia, with clozapine showing the highest risk. Metformin is a first-line medication for managing diabetes or prediabetes and is often used to control clozapine-induced hyperglycemia. Clinical studies, however, have reported metformin resistance in some clozapine-treated patients, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the mechanism by which clozapine impaired the hypoglycemic effect of metformin and developed a mechanism-based semi-PBPK-PD model to predict the effect of clozapine on the pharmacokinetics and hypoglycemic effect of metformin in rats. Rats received clozapine (50 mg·kg−1·d−1, i.g.) for 7 days. The rats received metformin (200 mg/kg, i.g.) at 0.5 h after the last dose on D7. IPGTT or pharmacokinetics study was performed at 0.5 h after the administration of metformin. We showed that clozapine impaired the hypoglycemic effect of metformin during the glucose tolerance test without altering the plasma exposure of metformin in the rats. The liver is the main target for the hypoglycemic effect of metformin. We showed that clozapine significantly reduced the hepatic distribution of metformin, inhibited metformin uptake in rat livers and rat primary hepatocytes, and inhibited the glucose consumption enhanced by metformin in rat primary hepatocytes. OCT1 mediates the hepatic uptake of metformin. We demonstrated that clozapine dose-dependently inhibited metformin uptake in HEK293-OCT1 cells with the IC50 value of 8.9 μM. Silencing OCT1 in rat primary hepatocytes impaired metformin uptake and attenuated the enhanced glucose consumption by metformin, suggesting that clozapine impaired the hypoglycemic effect of metformin by inhibiting OCT1-mediated hepatic uptake. Subsequently, a semi-PBPK-PD model was constructed based on this mechanism. The model well predicted the decreased hepatic exposure and hypoglycemic effect of metformin in the rat co-administered with clozapine.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yuen JWY, Kim DD, Procyshyn RM, Panenka WJ, Honer WG, Barr AM. A focused review of the metabolic side-effects of clozapine. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:609240.
Henderson DC, Nguyen DD, Copeland PM, Hayden DL, Borba CP, Louie PM, et al. Clozapine, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and cardiovascular risks and mortality: results of a 10-year naturalistic study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66:1116–21.
LaMoia TE, Shulman GI. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin action. Endocr Rev. 2021;42:77–96.
Siskind DJ, Leung J, Russell AW, Wysoczanski D, Kisely S. Metformin for clozapine associated obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0156208.
Zhuo C, Xu Y, Wang H, Zhou C, Liu J, Yu X, et al. Clozapine induces metformin-resistant prediabetes/diabetes that is associated with poor clinical efficacy in patients with early treatment-resistant schizophrenia. J Affect Disord. 2021;295:163–72.
Porras-Segovia A, Krivoy A, Horowitz M, Thomas G, Bolstridge M, Ion D, et al. Rapid-onset clozapine-induced loss of glycaemic control: case report. BJPsych Open. 2017;3:138–40.
Hendrick V, Dasher R, Gitlin M, Parsi M. Minimizing weight gain for patients taking antipsychotic medications: the potential role for early use of metformin. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2017;29:120–4.
Carrizo E, Fernández V, Connell L, Sandia I, Prieto D, Mogollón J, et al. Extended release metformin for metabolic control assistance during prolonged clozapine administration: a 14-week, double-blind, parallel group, placebo-controlled study. Schizophr Res. 2009;113:19–26.
Ehret M, Goethe J, Lanosa M, Coleman CI. The effect of metformin on anthropometrics and insulin resistance in patients receiving atypical antipsychotic agents: a meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;71:1286–92.
Zimbron J, Khandaker GM, Toschi C, Jones PB, Fernandez-Egea E. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of treatments for clozapine-induced obesity and metabolic syndrome. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016;26:1353–65.
Koepsell H. Organic cation transporters in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2020;72:253–319.
Cho SK, Kim CO, Park ES, Chung JY. Verapamil decreases the glucose-lowering effect of metformin in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;78:1426–32.
Shu Y, Sheardown SA, Brown C, Owen RP, Zhang S, Castro RA, et al. Effect of genetic variation in the organic cation transporter 1 (OCT1) on metformin action. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:1422–31.
Oh J, Chung H, Park SI, Yi SJ, Jang K, Kim AH, et al. Inhibition of the multidrug and toxin extrusion (MATE) transporter by pyrimethamine increases the plasma concentration of metformin but does not increase antihyperglycaemic activity in humans. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;18:104–8.
Yang Y, Zhang Z, Li P, Kong W, Liu X, Liu L. A whole-body physiologically based pharmacokinetic model characterizing interplay of OCTs and MATEs in intestine, liver and kidney to predict drug-drug interactions of metformin with perpetrators. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:698.
Cho SK, Yoon JS, Lee MG, Lee DH, Lim LA, Park K, et al. Rifampin enhances the glucose-lowering effect of metformin and increases OCT1 mRNA levels in healthy participants. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011;89:416–21.
Wang W, Bai M, Jiang T, Li C, Li P, Zhou H, et al. Clozapine-induced reduction of l-carnitine reabsorption via inhibition/down-regulation of renal carnitine/organic cation transporter 2 contributes to liver lipid metabolic disorder in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019;363:47–56.
Nair AB, Jacob S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2016;7:27–31.
Hong S, Li S, Meng X, Li P, Wang X, Su M, et al. Bile duct ligation differently regulates protein expressions of organic cation transporters in intestine, liver and kidney of rats through activation of farnesoid X receptor by cholate and bilirubin. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13:227–45.
Wu WH, Zhi H, Feng WK, Jiang L, Yang L, Qian LQ, et al. Clozapine impaired glucose-stimulated insulin secretion partly by increasing plasma 5-HT levels due to the inhibition of OCT1-mediated hepatic 5-HT uptake in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025;46:687–701.
Inoue Y, Kurihara R, Tsuchida A, Hasegawa M, Nagashima T, Mori T, et al. Efficient delivery of siRNA using dendritic poly(l-lysine) for loss-of-function analysis. J Control Release. 2008;126:59–66.
Ling Z, Shu N, Xu P, Wang F, Zhong Z, Sun B, et al. Involvement of pregnane X receptor in the impaired glucose utilization induced by atorvastatin in hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016;100:98–111.
Wang Z-J, Ma P, Xu C-Y, Xu T-S, Zhang L, He P, et al. Identification of a novel hypoglycemic small molecule, trans-2, 4-dimethoxystilbene by rectifying gut microbiota and activating hepatic AMPKα-PPARγ pathway through gut-liver axis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;176:116760.
Zhang S, Li X. Hypoglycemic activity in vitro of polysaccharides from Camellia oleifera Abel. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;115:811–9.
Duan JY, Chen W, Zhao YQ, He LL, Li EC, Bai ZH, et al. Flavonoids from Hypericum patulum enhance glucose consumption and attenuate lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. J Food Biochem. 2021;45:e13898.
Yin J, Hu R, Chen M, Tang J, Li F, Yang Y, et al. Effects of berberine on glucose metabolism in vitro. Metabolism. 2002;51:1439–43.
Ganci D, Bellistrì F, Mauro M, Chiarelli R, Longo F, Indelicato S, et al. Valorization of winemaking by-products: white and red grape seed oils improve glucose consumption and uptake in vitro. Molecules. 2025;30:1933.
Wang G, Xu J, Ma H, Mu Y, Xu W, Yan N, et al. Phenolipid JE improves metabolic profile and inhibits gluconeogenesis via modulating AKT-mediated insulin signaling in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Pharmacol Res. 2023;187:106569.
Liu P, Jiang L, Kong W, Xie Q, Li P, Liu X, et al. PXR activation impairs hepatic glucose metabolism partly via inhibiting the HNF4alpha-GLUT2 pathway. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12:2391–405.
Yang H, Su M, Liu M, Sheng Y, Zhu L, Yang L, et al. Hepatic retinaldehyde deficiency is involved in diabetes deterioration by enhancing PCK1- and G6PC-mediated gluconeogenesis. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13:3728–43.
Stepensky D, Friedman M, Raz I, Hoffman A. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis of the glucose-lowering effect of metformin in diabetic rats reveals first-pass pharmacodynamic effect. Drug Metab Dispos. 2002;30:861–8.
Sasaki N, Iwase M, Uchizono Y, Nakamura U, Imoto H, Abe S, et al. The atypical antipsychotic clozapine impairs insulin secretion by inhibiting glucose metabolism and distal steps in rat pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 2006;49:2930–8.
Melkersson K, Jansson E. Effects of the atypical antipsychotic clozapine on insulin release in vitro. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2007;28:854–60.
Liu X, Wu Z, Lian J, Hu CH, Huang XF, Deng C. Time-dependent changes and potential mechanisms of glucose-lipid metabolic disorders associated with chronic clozapine or olanzapine treatment in rats. Sci Rep. 2017;7:2762.
Haenisch B, Drescher E, Thiemer L, Xin H, Giros B, Gautron S, et al. Interaction of antidepressant and antipsychotic drugs with the human organic cation transporters hOCT1, hOCT2 and hOCT3. Naunyn Schmiedeb Arch Pharmacol. 2012;385:1017–23.
Zhu JB, Yang JX, Nian YQ, Liu GQ, Duan YB, Bai X, et al. Pharmacokinetics of acetaminophen and metformin hydrochloride in rats after exposure to simulated high altitude hypoxia. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:692349.
Choi YH, Lee I, Lee MG. Effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharide on the pharmacokinetics of metformin in rats. Int J Pharm. 2007;337:194–201.
Manjunath K, Venkateswarlu V. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and bioavailability of clozapine solid lipid nanoparticles after intravenous and intraduodenal administration. J Control Release. 2005;107:215–28.
Li Z, Lee SH, Jeong HJ, Kang HE. Pharmacokinetic changes of clozapine and norclozapine in a rat model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by orotic acid. Xenobiotica. 2020;51:324–34.
Ortega‑Ayala A, De Andrés F, Llerena A, Bartolo‑Montiel C, Molina‑Guarneros JA. Impact of slc22a1 variants rs622342 and rs72552763 on HbA1c and metformin plasmatic concentration levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomed Rep. 2024;21:117.
Naem Alaa Abd AH, Al-Terehi Mona N, Ghafil Fadhaa A, Ataya Farid S, Batiha Gaber ES, Alexiou A, et al. The influence of OCT3 and MATE2 genetic polymorphisms in poor response to metformin in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2024;7:e486.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82173884).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WHW was responsible for conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, validation, and writing-original draft. LL and XDL were responsible for conceptualization, methodology, writing-reviewing, editing, supervision, and funding acquisition. LJ was responsible for methodology, writing-reviewing, and editing. YDD was responsible for investigation, validation, and data curation. WKF, HRC, and XYZ were responsible for investigation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Wh., Dai, Yd., Feng, Wk. et al. Clozapine impaired the hypoglycemic effect of metformin by inhibiting hepatic organic cation transporter 1 (OCT1). Acta Pharmacol Sin (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01707-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01707-3