Abstract
The incidence of digestive system diseases is increasing, with liver diseases, obesity, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and hepatoenteric cancers being prominent contributors to global morbidity and mortality. Targeting farnesoid X receptor (FXR) has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy for various digestive disorders. FXR is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily, is expressed primarily in the liver and small intestine, and is activated by bile acids (BAs). Beyond classical ligand-dependent activation, FXR activity is precisely modulated by epigenetic regulation and posttranslational modifications (PTMs), such as DNA methylation, histone methylation and acetylation, noncoding RNA regulation, phosphorylation, acetylation, SUMOylation, ubiquitination, O-glycosylation, methylation, sulfhydration, and poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. Growing evidence reveals disease-associated alterations in FXR modification patterns, offering novel therapeutic perspectives for digestive pathologies. In this review, we comprehensively summarize the structure of FXR, its regulatory mechanisms through epigenetic modifications and PTMs, and its potential application in the treatment of digestive diseases.

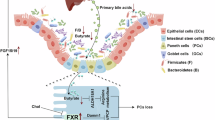
The structure of FXR, its regulatory mechanisms through epigenetic modifications and PTMs, and its potential application in the treatment of digestive diseases. Upper: epigenetic regulation of FXR. Below: posttranslational modifications of FXR. OG O-glycosylation, P phosphorylation, SUMO SUMOylation, SSH sulfhydration, Ac acetylation, Me methylation, Ub ubiquitination.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng Z, Wang T, Jiao Y, Qi J, Zhang X, Zhou S, et al. Burden of digestive system diseases in China and its provinces during 1990-2019: Results of the 2019 Global Disease Burden Study. Chin Med J. 2024;137:2182–9.
Peery AF, Murphy CC, Anderson C, Jensen ET, Deutsch-Link S, Egberg MD, et al. Burden and cost of gastrointestinal, liver, and pancreatic diseases in the United States: Update 2024. Gastroenterology. 2025;168:1000–24.
Devarbhavi H, Asrani SK, Arab JP, Nartey YA, Pose E, Kamath PS. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J Hepatol. 2023;79:516–37.
Wang C, Zhang X, Wang P, Yang X, Yu H, Xu W, et al. The role of obesity in mortality from digestive diseases in UK Biobank. Sci Rep. 2024;14:27126.
Ogbuji V, Gomez D’M, Paster IC, Irizarry VMT, McCormick K, Dennis LK, et al. Global burden of penile cancer: a review of health disparities for a rare disease. Urology. 2024;194:280–8.
Ding L, Yang L, Wang Z, Huang W. Bile acid nuclear receptor FXR and digestive system diseases. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015;5:135–44.
Jiang L, Zhang H, Xiao D, Wei H, Chen Y. Farnesoid X receptor (FXR): structures and ligands. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:2148–59.
Adorini L, Trauner M. FXR agonists in NASH treatment. J Hepatol. 2023;79:1317–31.
Liu Y, Chen K, Li F, Gu Z, Liu Q, He L, et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG prevents liver fibrosis through inhibiting hepatic bile acid synthesis and enhancing bile acid excretion in mice. Hepatology. 2020;71:2050–66.
Anderson KM, Gayer CP. The Pathophysiology of Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) in the GI tract: inflammation, barrier function and innate immunity. Cells. 2021;10:3206.
Lin S, Wang S, Wang P, Tang C, Wang Z, Chen L, et al. Bile acids and their receptors in regulation of gut health and diseases. Prog Lipid Res. 2023;89:101210.
Yu D, Lu Z, Wang R, Xiang Y, Li H, Lu J, et al. FXR agonists for colorectal and liver cancers, as a stand-alone or in combination therapy. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;212:115570.
Cheung KCP, Ma J, Loiola RA, Chen X, Jia W. Bile acid-activated receptors in innate and adaptive immunity: targeted drugs and biological agents. Eur J Immunol. 2023;53:e2250299.
Fiorucci S, Zampella A, Ricci P, Distrutti E, Biagioli M. Immunomodulatory functions of FXR. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2022;551:111650.
Panzitt K, Wagner M. FXR in liver physiology: multiple faces to regulate liver metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021;1867:166133.
Appelman MD, van der Veen SW, van Mil SWC. Post-translational modifications of FXR; implications for cholestasis and obesity-related disorders. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:729828.
Zhou M, Wang D, Li X, Cao Y, Yi C, Wiredu Ocansey DK, et al. Farnesoid-X receptor as a therapeutic target for inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1016836.
Xiang D, Yang J, Liu L, Yu H, Gong X, Liu D. The regulation of tissue-specific farnesoid X receptor on genes and diseases involved in bile acid homeostasis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;168:115606.
Tian SY, Chen SM, Pan CX, Li Y. FXR: structures, biology, and drug development for NASH and fibrosis diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43:1120–32.
Devarakonda S, Harp JM, Kim Y, Ozyhar A, Rastinejad F. Structure of the heterodimeric ecdysone receptor DNA-binding complex. EMBO J. 2003;22:5827–40.
Otte K, Kranz H, Kober I, Thompson P, Hoefer M, Haubold B, et al. Identification of farnesoid X receptor beta as a novel mammalian nuclear receptor sensing lanosterol. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:864–72.
Panzitt K, Zollner G, Marschall HU, Wagner M. Recent advances on FXR-targeting therapeutics. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2022;552:111678.
Vaquero J, Monte MJ, Dominguez M, Muntané J, Marin JJ. Differential activation of the human farnesoid X receptor depends on the pattern of expressed isoforms and the bile acid pool composition. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;86:926–39.
Garcia M, Holota H, De Haze A, Saru JP, Sanchez P, Battistelli E, et al. Alternative splicing is an FXRα loss-of-function mechanism and impacts energy metabolism in hepatocarcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2025;301:108022.
Anakk S, Dean AE. Fxr-alpha skips alternatively in liver metabolism. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1655–7.
Chen X, Xu H, Shu X, Song CX. Mapping epigenetic modifications by sequencing technologies. Cell Death Differ. 2025;32:56–65.
Huang X, Zhu J, Wei T, Luo L, Li C, Zhao M. Epigenetic modifications in vitiligo. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025;68:39.
Lee AV, Nestler KA, Chiappinelli KB. Therapeutic targeting of DNA methylation alterations in cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2024;258:108640.
Oliva M, Demanelis K, Lu Y, Chernoff M, Jasmine F, Ahsan H, et al. DNA methylation QTL mapping across diverse human tissues provides molecular links between genetic variation and complex traits. Nat Genet. 2023;55:112–22.
Huang W, Li H, Yu Q, Xiao W, Wang DO, LncRNA-mediated DNA. methylation: an emerging mechanism in cancer and beyond. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41:100.
Wang K, He Z, Jin G, Jin S, Du Y, Yuan S, et al. Targeting DNA methyltransferases for cancer therapy. Bioorg Chem. 2024;151:107652.
Yang J, Xu J, Wang W, Zhang B, Yu X, Shi S. Epigenetic regulation in the tumor microenvironment: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8:210.
Wang S, Zha L, Cui X, Yeh YT, Liu R, Jing J, et al. Epigenetic regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism by DNA methylation. Adv Sci. 2023;10:e2206068.
Cabrerizo R, Castaño GO, Burgueño AL, Fernández Gianotti T, Gonzalez Lopez Ledesma MM, Flichman D, et al. Promoter DNA methylation of farnesoid X receptor and pregnane X receptor modulates the intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy phenotype. PLoS One. 2014;9:e87697.
Zaffaroni G, Mannucci A, Koskenvuo L, de Lacy B, Maffioli A, Bisseling T, et al. Updated European guidelines for clinical management of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), MUTYH-associated polyposis (MAP), gastric adenocarcinoma, proximal polyposis of the stomach (GAPPS) and other rare adenomatous polyposis syndromes: a joint EHTG-ESCP revision. Br J Surg. 2024;111:znae070.
Selmin OI, Fang C, Lyon AM, Doetschman TC, Thompson PA, Martinez JD, et al. Inactivation of adenomatous polyposis coli reduces bile acid/farnesoid X receptor expression through Fxr gene CpG methylation in mouse colon tumors and human colon cancer cells. J Nutr. 2016;146:236–42.
Bailey AM, Zhan L, Maru D, Shureiqi I, Pickering CR, Kiriakova G, et al. FXR silencing in human colon cancer by DNA methylation and KRAS signaling. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014;306:G48–58.
Romagnolo DF, Donovan MG, Doetschman TC, Selmin OI. n-6 linoleic acid induces epigenetics alterations associated with colonic inflammation and cancer. Nutrients. 2019;11:171.
Ching T, Ha J, Song MA, Tiirikainen M, Molnar J, Berry MJ, et al. Genome-scale hypomethylation in the cord blood DNAs associated with early onset preeclampsia. Clin Epigenetics. 2015;7:21.
Zaib S, Rana N, Khan I. Histone modifications and their role in epigenetics of cancer. Curr Med Chem. 2022;29:2399–411.
Du Y, He Z, Jin S, Jin G, Wang K, Yang F, et al. Targeting histone methylation and demethylation for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Bioorg Chem. 2024;151:107698.
Charidemou E, Kirmizis A. A two-way relationship between histone acetylation and metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci. 2024;49:1046–62.
Pathikonda S, Amirmahani F, Mathew D, Muthukrishnan SD. Histone acetyltransferases as promising therapeutic targets in glioblastoma resistance. Cancer Lett. 2024;604:217269.
Ma L, Lv J, Zhang A. Depletion of S-adenosylmethionine induced by arsenic exposure is involved in liver injury of rat through perturbing histone H3K36 trimethylation dependent bile acid metabolism. Environ Pollut. 2023;334:122228.
Yu J, Yang K, Zheng J, Zhao P, Xia J, Sun X, et al. Activation of FXR and inhibition of EZH2 synergistically inhibit colorectal cancer through cooperatively accelerating FXR nuclear location and upregulating CDX2 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:388.
Wan QL, Meng X, Dai W, Luo Z, Wang C, Fu X, et al. N6-methyldeoxyadenine and histone methylation mediate transgenerational survival advantages induced by hormetic heat stress. Sci Adv. 2021;7:eabc3026.
Farias-Pereira R, Kim E, Park Y. Cafestol increases fat oxidation and energy expenditure in Caenorhabditis elegans via DAF-12-dependent pathway. Food Chem. 2020;307:125537.
García-Rodríguez JL, Barbier-Torres L, Fernández-Álvarez S, Gutiérrez-de Juan V, Monte MJ, Halilbasic E, et al. SIRT1 controls liver regeneration by regulating bile acid metabolism through farnesoid X receptor and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling. Hepatology. 2014;59:1972–83.
Gong J, Cong M, Wu H, Wang M, Bai H, Wang J, et al. P53/miR-34a/SIRT1 positive feedback loop regulates the termination of liver regeneration. Aging. 2023;15:1859–77.
Li M, Zhang X, Lu Y, Meng S, Quan H, Hou P, et al. The nuclear translocation of transketolase inhibits the farnesoid receptor expression by promoting the binding of HDAC3 to FXR promoter in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:31.
Martino MTD, Tagliaferri P, Tassone P. MicroRNA in cancer therapy: breakthroughs and challenges in early clinical applications. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025;44:126.
Ho PTB, Clark IM, Le LTT. MicroRNA-based diagnosis and therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:7167.
Dong R, Wang X, Wang L, Wang C, Huang K, Fu T, et al. Yangonin inhibits ethanol-induced hepatocyte senescence via miR-194/FXR axis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;890:173653.
Jiang M, Li F, Liu Y, Gu Z, Zhang L, Lee J, et al. Probiotic-derived nanoparticles inhibit ALD through intestinal miR194 suppression and subsequent FXR activation. Hepatology. 2023;77:1164–80.
Nie X, Liu H, Wei X, Li L, Lan L, Fan L, et al. miRNA-382-5p Suppresses the expression of farnesoid X receptor to promote progression of liver cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2021;13:8025–35.
Diener C, Keller A, Meese E. The miRNA-target interactions: an underestimated intricacy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024;52:1544–57.
Roberts TC. The MicroRNA biology of the mammalian nucleus. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2014;3:e188.
Fan L, Lai R, Ma N, Dong Y, Li Y, Wu Q, et al. miR-552-3p modulates transcriptional activities of FXR and LXR to ameliorate hepatic glycolipid metabolism disorder. J Hepatol. 2021;74:8–19.
Herman AB, Tsitsipatis D, Gorospe M. Integrated lncRNA function upon genomic and epigenomic regulation. Mol Cell. 2022;82:2252–66.
Ferrer J, Dimitrova N. Transcription regulation by long non-coding RNAs: mechanisms and disease relevance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25:396–415.
Chen J, Wang R, Xiong F, Sun H, Kemper B, Li W, et al. Hammerhead-type FXR agonists induce an enhancer RNA Fincor that ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. eLife. 2024;13:RP91438.
Lee EB, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Gains or losses: molecular mechanisms of TDP43-mediated neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;13:38–50.
Ma Y, Harris J, Li P, Cao H. Long noncoding RNAs-a new dimension in the molecular architecture of the bile acid/FXR pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021;525:111191.
Salovska B, Liu Y. Post-translational modification and phenotype. Proteomics. 2023;23:e2200535.
Gineste R, Sirvent A, Paumelle R, Helleboid S, Aquilina A, Darteil R, et al. Phosphorylation of farnesoid X receptor by protein kinase C promotes its transcriptional activity. Mol Endocrinol. 2008;22:2433–47.
Kemper JK, Xiao Z, Ponugoti B, Miao J, Fang S, Kanamaluru D, et al. FXR acetylation is normally dynamically regulated by p300 and SIRT1 but constitutively elevated in metabolic disease states. Cell Metab. 2009;10:392–404.
Balasubramaniyan N, Luo Y, Sun AQ, Suchy FJ. SUMOylation of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) regulates the expression of FXR target genes. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:13850–62.
Shapiro H, Kolodziejczyk AA, Halstuch D, Elinav E. Bile acids in glucose metabolism in health and disease. J Exp Med. 2018;215:383–96.
Benhamed F, Filhoulaud G, Caron S, Lefebvre P, Staels B. Postic C. O-GlcNAcylation links ChREBP and FXR to glucose-sensing. Front Endocrinol. 2015;5:230.
Balasubramaniyan N, Ananthanarayanan M, Suchy FJ. Direct methylation of FXR by Set7/9, a lysine methyltransferase, regulates the expression of FXR target genes. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;302:G937–947.
Xu W, Cui C, Cui C, Chen Z, Zhang H, Cui Q, et al. Hepatocellular cystathionine γ lyase/hydrogen sulfide attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by activating farnesoid X receptor. Hepatology. 2022;76:1794–810.
Wang C, Zhang F, Wang L, Zhang Y, Li X, Huang K, et al. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 promotes oxidative-stress-induced liver cell death via suppressing farnesoid X receptor α. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33:4492–503.
Bilbrough T, Piemontese E, Seitz O. Dissecting the role of protein phosphorylation: a chemical biology toolbox. Chem Soc Rev. 2022;51:5691–730.
Morgan JAM, Singh A, Kurz L, Nadler-Holly M, Ruwolt M, Ganguli S, et al. Extensive protein pyrophosphorylation revealed in human cell lines. Nat Chem Biol. 2024;20:1305–16.
Shindo S, Kakizaki S, Sakaki T, Kawasaki Y, Sakuma T, Negishi M, et al. Phosphorylation of nuclear receptors: novelty and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Ther. 2023;248:108477.
Negishi M, Kobayashi K, Sakuma T, Sueyoshi T. Nuclear receptor phosphorylation in xenobiotic signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 2020;295:15210–25.
Yokobori K, Miyauchi Y, Williams JG, Negishi M. Phosphorylation of vaccinia-related kinase 1 at threonine 386 transduces glucose stress signal in human liver cells. Biosci Rep. 2020;40:BSR20200498.
Hashiguchi T, Arakawa S, Takahashi S, Gonzalez FJ, Sueyoshi T, Negishi M. Phosphorylation of farnesoid X receptor at serine 154 links ligand activation with degradation. Mol Endocrinol. 2016;30:1070–80.
Ploton M, Mazuy C, Gheeraert C, Dubois V, Berthier A, Dubois-Chevalier J, et al. The nuclear bile acid receptor FXR is a PKA- and FOXA2-sensitive activator of fasting hepatic gluconeogenesis. J Hepatol. 2018;69:1099–109.
Bilodeau S, Caron V, Gagnon J, Kuftedjian A, Tremblay A. A CK2-RNF4 interplay coordinates non-canonical SUMOylation and degradation of nuclear receptor FXR. J Mol Cell Biol. 2017;9:195–208.
Zhu Y, Lin X, Zhou X, Prochownik EV, Wang F, Li Y. Posttranslational control of lipogenesis in the tumor microenvironment. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15:120.
Xing C, Huang X, Wang D, Yu D, Hou S, Cui H, et al. Roles of bile acids signaling in neuromodulation under physiological and pathological conditions. Cell Biosci. 2023;13:106.
Byun S, Jung H, Chen J, Kim YC, Kim DH, Kong B, et al. Phosphorylation of hepatic farnesoid X receptor by FGF19 signaling-activated Src maintains cholesterol levels and protects from atherosclerosis. J Biol Chem. 2019;294:8732–44.
Cui S, Hu H, Chen A, Cui M, Pan X, Zhang P, et al. SIRT1 activation synergizes with FXR agonism in hepatoprotection via governing nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and degradation of FXR. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13:559–76.
Chen F, Ellis E, Strom SC, Shneider B, ATPase Class I. Type 8B Member 1 and protein kinase C zeta induce the expression of the canalicular bile salt export pump in human hepatocytes. Pediatr Res. 2010;67:183–7.
Petrescu AD, DeMorrow S, Farnesoid X. Receptor as target for therapies to treat cholestasis-induced liver injury. Cells. 2021;10:1846.
Lien F, Berthier A, Bouchaert E, Gheeraert C, Alexandre J, Porez G, et al. Metformin interferes with bile acid homeostasis through AMPK-FXR crosstalk. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:1037–51.
Ahmad TR, Haeusler RA. Bile acids in glucose metabolism and insulin signalling- mechanisms and researchneeds. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15:701712.
Wang Y, Liu K. Therapeutic potential of oleanolic acid in liver diseases. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024;397:4537–54.
Huang J, Liao S, Fu X, Wang Y, Zhou S, Lu Y. AMP-activated protein kinase-farnesoid X receptor pathway contributes to oleanolic acid-induced liver injury. J Appl Toxicol. 2023;43:1201–13.
Hu X, Zhou J, Song SS, Kong W, Shi YC, Chen LL, et al. TLR4/AP-1-targeted anti-inflammatory intervention attenuates insulin sensitivity and liver steatosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:2960517.
Zhou MM, Cole PA. Targeting lysine acetylation readers and writers. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025;24:112–33.
Dang F, Wei W. Targeting the acetylation signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;85:209–18.
Liu C, Pan Z, Wu Z, Tang K, Zhong Y, Chen Y, et al. Hepatic SIRT6 modulates transcriptional activities of FXR to alleviate acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;14:271–93.
Kim DH, Xiao Z, Kwon S, Sun X, Ryerson D, Tkac D, et al. A dysregulated acetyl/SUMO switch of FXR promotes hepatic inflammation in obesity. EMBO J. 2015;34:184–99.
Zhao M, Li G, Zhao L. The role of SIRT1-FXR signaling pathway in valproic acid induced liver injury: a quantitative targeted metabolomic evaluation in epileptic children. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1477619.
Lai J, Li F, Li H, Huang R, Ma F, Gu X, et al. Melatonin alleviates necrotizing enterocolitis by reducing bile acid levels through the SIRT1/FXR signalling axis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;128:111360.
Chen C, Liu X, Wang J, Wen X, Zhao H, Chen G, et al. Zinc-mediated deacetylation of FXR activates the adipose triglyceride lipase pathway to reduce hepatic lipid accumulation and enhance lipolysis in yellow catfish. J Nutr. 2025;155:1350–63.
Ge J, Li G, Chen Z, Xu W, Lei X, Zhu S. Kaempferol and nicotiflorin ameliorated alcohol-induced liver injury in mice by miR-138-5p/SIRT1/FXR and gut microbiota. Heliyon. 2023;10:e23336.
Rodríguez-Agudo R, González-Recio I, Serrano-Maciá M, Bravo M, Petrov P, Blaya D, et al. Anti-miR-873-5p improves alcohol-related liver disease by enhancing hepatic deacetylation via SIRT1. JHEP Rep. 2023;6:100918.
Yang Y, Yu F. Abnormal protein SUMOylation in liver disease: novel target for therapy. J Mol Med. 2024;102:719–31.
Acuña ML, García-Morin A, Orozco-Sepúlveda R, Ontiveros C, Flores A, Diaz AV, et al. Alternative splicing of the SUMO1/2/3 transcripts affects cellular SUMOylation and produces functionally distinct SUMO protein isoforms. Sci Rep. 2023;13:2309.
Cheng X, Yang W, Lin W, Mei F. Paradoxes of cellular SUMOylation regulation: a role of biomolecular condensates?. Pharmacol Rev. 2023;75:979–1006.
Li K, Xia Y, He J, Wang J, Li J, Ye M, et al. The SUMOylation and ubiquitination crosstalk in cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023;149:16123–46.
Gao L, Zhang W, Shi XH, Chang X, Han Y, Liu C, et al. The mechanism of linear ubiquitination in regulating cell death and correlative diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14:659.
Loix M, Zelcer N, Bogie JFJ, Hendriks JJA. The ubiquitous role of ubiquitination in lipid metabolism. Trends Cell Biol. 2024;34:416–29.
Zhou J, Cui S, He Q, Guo Y, Pan X, Zhang P, et al. SUMOylation inhibitors synergize with FXR agonists in combating liver fibrosis. Nat Commun. 2020;11:240.
Gao Y, Zhao Y, Yuan A, Xu L, Huang X, Su Y, et al. Effects of farnesoid-X-receptor SUMOylation mutation on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Exp Cell Res. 2018;371:301–10.
Pang S, Yu L, Lu Y, Jiang Q, Hou L, Shi R, et al. Farnesoid X receptor expression reduced in obese rat model with insulin resistance. Am J Med Sci. 2015;350:467–70.
Duran-Sandoval D, Mautino G, Martin G, Percevault F, Barbier O, Fruchart JC, et al. Glucose regulates the expression of the farnesoid X receptor in liver. Diabetes. 2004;53:890–8.
Wagner SA, Beli P, Weinert BT, Schölz C, Kelstrup CD, Young C, et al. Proteomic analyses reveal divergent ubiquitylation site patterns in murine tissues. Mol Cell Proteom. 2012;11:1578–85.
Chatham JC, Patel RP. Protein glycosylation in cardiovascular health and disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024;21:525–44.
Schjoldager KT, Narimatsu Y, Joshi HJ, Clausen H. Global view of human protein glycosylation pathways and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21:729–49.
Li X, Pinou Lv DuY, Chen X, Liu C. Emerging roles of O-glycosylation in regulating protein aggregation, phase separation, and functions. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2023;75:102314.
Berrabah W, Aumercier P, Gheeraert C, Dehondt H, Bouchaert E, Alexandre J, et al. Glucose sensing O-GlcNAcylation pathway regulates the nuclear bile acid receptor farnesoid X receptor (FXR). Hepatology. 2014;59:2022–33.
Hu YJ, Zhang X, Lv HM, Liu Y, Li SZ. Protein O-GlcNAcylation: the sweet hub in liver metabolic flexibility from a (patho)physiological perspective. Liver Int. 2024;44:293–315.
Caron S, Huaman Samanez C, Dehondt H, Ploton M, Briand O, Lien F, et al. Farnesoid X receptor inhibits the transcriptional activity of carbohydrate response element binding protein in human hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33:2202–11.
Sayago C, Sánchez-Wandelmer J, García F, Hurtado B, Lafarga V, Prieto P, et al. Decoding protein methylation function with thermal stability analysis. Nat Commun. 2023;14:3016.
Małecki JM, Davydova E, Falnes PØ. Protein methylation in mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 2022;298:101791.
Wang Y, Bedford MT. Effectors and effects of arginine methylation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023;51:725–34.
Daks A, Shuvalov O, Fedorova O, Parfenyev S, Simon HU, Barlev NA. Methyltransferase Set7/9 as a multifaceted regulator of ROS response. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19:2304–18.
Batista IAA, Helguero LA. Biological processes and signal transduction pathways regulated by the protein methyltransferase SETD7 and their significance in cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2018;3:19.
Baghdasaryan A, Chiba P, Trauner M. Clinical application of transcriptional activators of bile salt transporters. Mol Asp Med. 2014;37:57–76.
Ko S, Ahn J, Song CS, Kim S, Knapczyk-Stwora K, Chatterjee B. Lysine methylation and functional modulation of androgen receptor by Set9 methyltransferase. Mol Endocrinol. 2011;25:433–44.
Takemoto Y, Ito A, Niwa H, Okamura M, Fujiwara T, Hirano T, et al. Identification of cyproheptadine as an inhibitor of SET domain containing lysine methyltransferase 7/9 (Set7/9) that regulates estrogen-dependent transcription. J Med Chem. 2016;59:3650–60.
Liu Z, Wu X, Lv J, Sun H, Zhou F. Resveratrol induces p53 in colorectal cancer through SET7/9. Oncol Lett. 2019;17:3783–9.
Ma H, Baumann CT, Li H, Strahl BD, Rice R, Jelinek MA, et al. Hormone-dependent, CARM1-directed, arginine-specific methylation of histone H3 on a steroid-regulated promoter. Curr Biol. 2001;11:1981–5.
Ananthanarayanan M, Li S, Balasubramaniyan N, Suchy FJ, Walsh MJ. Ligand-dependent activation of the farnesoid X-receptor directs arginine methylation of histone H3 by CARM1. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:54348–57.
Cirino G, Szabo C, Papapetropoulos A. Physiological roles of hydrogen sulfide in mammalian cells, tissues, and organs. Physiol Rev. 2023;103:31–276.
Chen SM, Tang XQ. Homocysteinylation and sulfhydration in diseases. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20:1726–35.
Mustafa AK, Gadalla MM, Sen N, Kim S, Mu W, Gazi SK, et al. H2S signals through protein S-sulfhydration. Sci Signal. 2009;2:ra72.
Wu D, Sun Y, Gu Y, Zhu D. Cystathionine γ-lyase S-sulfhydrates SIRT1 to attenuate myocardial death in isoprenaline-induced heart failure. Redox Rep. 2023;28:2174649.
Hajdu B, Hunyadi-Gulyás É, Kato K, Kawaguchi A, Nagata K, Gyurcsik B. Zinc binding of a Cys2His2-type zinc finger protein is enhanced by the interaction with DNA. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2023;28:301–15.
Woodhouse BC, Dianov GL. Poly ADP-ribose polymerase-1: an international molecule of mystery. DNA Repair. 2008;7:1077–86.
Mangerich A, Burkle A. Pleiotropic cellular functions of PARP1 in longevity and aging: genome maintenance meets inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:321653.
Alemasova EE, Lavrik OI. Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation by PARP1: reaction mechanism and regulatory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:3811–27.
Sheng Y, Meng G, Zhou Z, Du R, Wang Y, Jiang M. PARP-1 inhibitor alleviates liver lipid accumulation of atherosclerosis via modulating bile acid metabolism and gut microbes. Mol Omics. 2023;19:560–73.
Cao L, Wang M, Xu K. Research progress of role and mechanism of SETD7 in tumor occurrence and progression. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2023;26:38–45.
Xiong XL, Ding Y, Chen ZL, Wang Y, Liu P, Qin H, et al. Emodin rescues intrahepatic cholestasis via stimulating FXR/BSEP pathway in promoting the canalicular export of accumulated bile. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:522.
Guillemette B, Drogaris P, Lin HH, Armstrong H, Hiragami-Hamada K, Imhof A, et al. H3 lysine 4 is acetylated at active gene promoters and is regulated by H3 lysine 4 methylation. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1001354.
Imai S, Armstrong CM, Kaeberlein M, Guarente L. Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature. 2000;403:795–800.
Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73–84.
Lombardi R, Iuculano F, Pallini G, Fargion S, Fracanzani AL. Nutrients, genetic factors, and their interaction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:8761.
Nie H, Song C, Wang D, Cui S, Ren T, Cao Z, et al. MicroRNA-194 inhibition improves dietary-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice through targeting on FXR. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863:3087–94.
Wu X, Fan X, Miyata T, Kim A, Cajigas-Du Ross CK, Ray S, et al. Recent advances in understanding of pathogenesis of alcohol-associated liver disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2023;18:411–38.
Mackowiak B, Fu Y, Maccioni L, Gao B. Alcohol-associated liver disease. J Clin Invest. 2024;134:e176345.
Xu T, Li L, Hu H, Meng XM, Huang C, Zhang L, et al. MicroRNAs in alcoholic liver disease: recent advances and future applications. J Cell Physiol. 2018;234:382–94.
Liu Y, Zhang M, Zhang H, Qian X, Luo L, He Z. Anthocyanins inhibit airway inflammation by downregulating the NF-κB pathway via the miR-138-5p/SIRT1 Axis in asthmatic mice. J Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2022;183:539–51.
Guo S, Ma B, Jiang X, Li X, Jia Y. Astragalus polysaccharides inhibits tumorigenesis and lipid metabolism through miR-138-5p/SIRT1/SREBP1 pathway in prostate cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:598.
Yu L, Liu Y, Wang S, Zhang Q, Zhao J, Zhang H, et al. Cholestasis: exploring the triangular relationship of gut microbiota-bile acid-cholestasis and the potential probiotic strategies. Gut Microbes. 2023;15:2181930.
Pieters A, Gijbels E, Cogliati B, Annaert P, Devisscher L, Vinken M. Biomarkers of cholestasis. Biomark Med. 2021;15:437–54.
Byun S, Kim DH, Ryerson D, Kim YC, Sun H, Kong B, et al. Postprandial FGF19-induced phosphorylation by Src is critical for FXR function in bile acid homeostasis. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2590.
Zhao Q, Liu F, Cheng Y, Xiao XR, Hu DD, Tang YM, et al. Celastrol protects from cholestatic liver injury through modulation of SIRT1–FXR signaling. Mol Cell Proteom. 2019;18:520–33.
Alshehri AS, El-Kott AF, El-Kenawy AE, Khalifa HS, AlRamlawy AM. Cadmium chloride induces non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats by stimulating miR-34a/SIRT1/FXR/p53 axis. Sci Total Environ. 2021;784:147182.
Gao Z, Zhang JC, Wei L, Yang X, Zhang Y, Cheng B, et al. The protective effects of imperatorin on acetaminophen overdose-induced acute liver injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:8026838.
Kulkarni SR, Soroka CJ, Hagey LR, Boyer JL. Sirtuin 1 activation alleviates cholestatic liver injury in a cholic acid-fed mouse model of cholestasis. Hepatology. 2016;64:2151–64.
Blokker BA, Maijo M, Echeandia M, Galduroz M, Patterson AM, Ten A, et al. Fine-tuning of sirtuin 1 expression is essential to protect the liver from cholestatic liver disease. Hepatology. 2019;69:699–716.
Liu PY, Chen CC, Chin CY, Liu TJ, Tsai WC, Chou JL, et al. E3 ubiquitin ligase Grail promotes hepatic steatosis through SIRT1 inhibition. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:323.
Li M, Hong W, Hao C, Li L, Xu H, Li P, et al. Hepatic stellate cell-specific deletion of SIRT1 exacerbates liver fibrosis in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863:3202–11.
Li M, Hong W, Hao C, Li L, Wu D, Shen A, et al. SIRT1 antagonizes liver fibrosis by blocking hepatic stellate cell activation in mice. FASEB J. 2018;32:500–11.
Qin T, Hasnat M, Wang Z, Hassan HM, Zhou Y, Yuan Z, et al. Geniposide alleviated bile acid-associated NLRP3 inflammasome activation by regulating SIRT1/FXR signaling in bile duct ligation-induced liver fibrosis. Phytomedicine. 2023;118:154971.
Liao S, Fu X, Huang J, Wang Y, Lu Y, Zhou S. Suppression of SIRT1/FXR signaling pathway contributes to oleanolic acid-induced liver injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2023;467:116509.
Fontana RJ, Bjornsson ES, Reddy R, Andrade RJ. The evolving profile of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;21:2088–99.
Rani J, Dhull SB, Rose PK, Kidwai MK. Drug-induced liver injury and anti-hepatotoxic effect of herbal compounds: a metabolic mechanism perspective. Phytomedicine. 2024;122:155142.
Thalha AM, Mahadeva S, Boon Tan AT, Mun KS. Kombiglyze (metformin and saxagliptin)-induced hepatotoxicity in a patient with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. JGH Open. 2018;2:242–5.
Milkiewicz P, Heathcote J. Cholestasis induced by Chinese herbal remedy Xia-Ku-Hua-Tan-Pian. Liver Int. 2011;31:746–7.
Kalantary-Charvadeh A, Nazari Soltan Ahmad S, Aslani S, Beyrami M, Mesgari-Abbasi M. β-lapachone protects against doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity through modulation of NAD+/SIRT-1/FXR/p-AMPK/NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling axis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024;38:e23564.
Feng J, Ye S, Hai B, Lou Y, Duan M, Guo P, et al. RNF115/BCA2 deficiency alleviated acute liver injury in mice by promoting autophagy and inhibiting inflammatory response. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14:855.
Horn P, Tacke F. Metabolic reprogramming in liver fibrosis. Cell Metab. 2024;36:1439–55.
Li X, Ren Y, Chang K, Wu W, Griffiths HR, Lu S, et al. Adipose tissue macrophages as potential targets for obesity and metabolic diseases. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1153915.
Yang H, Chen L, Sun Q, Yao F, Muhammad S, Sun C. The role of HDAC11 in obesity-related metabolic disorders: a critical review. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236:5582–91.
Yang JW, Zou Y, Chen J, Cui C, Song J, Yang MM, et al. Didymin alleviates metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) via the stimulation of Sirt1-mediated lipophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis. J Transl Med. 2023;21:921.
Lu C, Zhao H, Liu Y, Yang Z, Yao H, Liu T, et al. Novel role of the SIRT1 in endocrine and metabolic diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19:484–501.
Wang XX, Wang D, Luo Y, Myakala K, Dobrinskikh E, Rosenberg AZ, et al. FXR/TGR5 dual agonist prevents progression of nephropathy in diabetes and obesity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29:118–37.
Wang L, Huang X, Hu S, Ma X, Wang S, Pang S. Effect of simvastatin on the expression of farnesoid X receptor in diabetic animal models of altered glucose homeostasis. Chin Med J. 2014;127:218–24.
Hu C, Liao S, Lv L, Li C, Mei Z. Intestinal immune imbalance is an alarm in the development of IBD. Mediators Inflamm. 2023;2023:1073984.
Dong X, Qi M, Cai C, Zhu Y, Li Y, Coulter S, et al. Farnesoid X receptor mediates macrophage-intrinsic responses to suppress colitis-induced colon cancer progression. JCI Insight. 2024;9:e170428.
Zhou M, Pei B, Cai P, Yi C, Akanyibah FA, Lyu C, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes repair IBD by activating the SIRT1-FXR pathway in macrophages. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025;16:233.
Klimeck L, Heisser T, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H. Colorectal cancer: a health and economic problem. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2023;66:101839.
Yin Y, Wang M, Gu W, Chen L. Intestine-specific FXR agonists as potential therapeutic agents for colorectal cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;186:114430.
Lu L, Jiang YX, Liu XX, Jin JM, Gu WJ, Luan X, et al. FXR agonist GW4064 enhances anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. Oncoimmunology. 2023;12:2217024.
Nenkov M, Shi Y, Ma Y, Gaßler N, Chen Y, Targeting Farnesoid X. Receptor in tumor and the tumor microenvironment: implication for therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;25:6.
Modica S, Murzilli S, Salvatore L, Schmidt DR, Moschetta A. Nuclear bile acid receptor FXR protects against intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2008;68:9589–94.
Fu T, Coulter S, Yoshihara E, Oh TG, Fang S, Cayabyab F, et al. FXR regulates intestinal cancer stem cell proliferation. Cell. 2019;176:1098–112.
Sun L, Cai J, Gonzalez FJ. The role of farnesoid X receptor in metabolic diseases, and gastrointestinal and liver cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18:335–47.
Lu Y, Li D, Wang L, Zhang H, Jiang F, Zhang R, et al. Comprehensive investigation on associations between dietary intake and blood levels of fatty acids and colorectal cancer risk. Nutrients. 2023;15:730.
Asafo-Agyei KO, Samant H. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls; 2023.
Liu Y, Zhu J, Jin Y, Sun Z, Wu X, Zhou H, et al. Disrupting bile acid metabolism by suppressing Fxr causes hepatocellular carcinoma induced by YAP activation. Nat Commun. 2025;16:3583.
Zhang XY, Luo M, Qin S, Fu WG, Zhang MY. FXR, MRP-1 and SLC7A5: new targets for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024;23:15330338241276889.
Mazucanti CH, Cabral-Costa JV, Vasconcelos AR, Andreotti DZ, Scavone C, Kawamoto EM. Longevity pathways (mTOR, SIRT, Insulin/IGF-1) as key modulatory targets on aging and neurodegeneration. Curr Top Med Chem. 2015;15:2116–38.
Back JH, Rezvani HR, Zhu Y, Guyonnet-Duperat V, Athar M, Ratner D, et al. Cancer cell survival following DNA damage-mediated premature senescence is regulated by mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-dependent Inhibition of sirtuin 1. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:19100–8.
Gao Z, Zhang J, Kheterpal I, Kennedy N, Davis RJ, Ye J. Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) protein degradation in response to persistent c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) activation contributes to hepatic steatosis in obesity. The. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:22227–34.
Ricciardelli C, Lokman NA, Cheruvu S, Tan IA, Ween MP, Pyragius CE, et al. Transketolase is upregulated in metastatic peritoneal implants and promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2015;32:441–55.
Wang J, Zhang X, Ma D, Lee WP, Xiao J, Zhao Y, et al. Inhibition of transketolase by oxythiamine altered dynamics of protein signals in pancreatic cancer cells. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2013;2:18.
Xu IM, Lai RK, Lin SH, Tse AP, Chiu DK, Koh HY, et al. Transketolase counteracts oxidative stress to drive cancer development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:E725–34.
Alharthi J, Pan Z, Gloss BS, McLeod D, Weltman M, George J, et al. Loss of metabolic adaptation in lean MAFLD is driven by endotoxemia leading to epigenetic reprogramming. Metabolism. 2023;144:155583.
Wu X, Xu M, Geng M, Chen S, Little PJ, Xu S, et al. Targeting protein modifications in metabolic diseases: molecular mechanisms and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8:220.
Badman MK, Chen J, Desai S, Vaidya S, Neelakantham S, Zhang J, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the novel non-bile acid FXR agonist tropifexor (LJN452) in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2020;9:395–410.
Naoumov NV, Brees D, Loeffler J, Chng E, Ren Y, Lopez P, et al. Digital pathology with artificial intelligence analyses provides greater insights into treatment-induced fibrosis regression in NASH. J Hepatol. 2022;77:1399–409.
Patel K, Harrison SA, Elkhashab M, Trotter JF, Herring R, Rojter SE, et al. Cilofexor, a nonsteroidal FXR agonist, in patients with noncirrhotic NASH: a phase 2 randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 2020;72:58–71.
Alkhouri N, Herring R, Kabler H, Kayali Z, Hassanein T, Kohli A, et al. Safety and efficacy of combination therapy with semaglutide, cilofexor and firsocostat in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomised, open-label phase II trial. J Hepatol. 2022;77:607–18.
Loomba R, Noureddin M, Kowdley KV, Kohli A, Sheikh A, Neff G, et al. Combination therapies including cilofexor and firsocostat for bridging fibrosis and cirrhosis attributable to NASH. Hepatology. 2021;73:625–43.
Fan H, Yang F, Xiao Z, Luo H, Chen H, Chen Z, et al. Lactylation: novel epigenetic regulatory and therapeutic opportunities. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2023;324:E330–8.
Lian J, Liu W, Hu Q, Zhang X. Succinylation modification: a potential therapeutic target in stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19:781–7.
Zhou B, Hao Q, Liang Y, Kong E. Protein palmitoylation in cancer: molecular functions and therapeutic potential. Mol Oncol. 2023;17:3–26.
Yuan H, Wu X, Wu Q, Chatoff A, Megill E, Gao J, et al. Lysine catabolism reprograms tumour immunity through histone crotonylation. Nature. 2023;617:818–26.
Li C, Liu Z, Kong D, Li Z, Li L. Lactylation: a novel driver of drug resistance in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Drug Resist. 2025;8:39.
Liu Z, Wang R, Wang Y, Duan Y, Zhan H. Targeting succinylation-mediated metabolic reprogramming as a potential approach for cancer therapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;168:115713.
Chen Y, Li Y, Wu L. Protein S-palmitoylation modification: implications in tumor and tumor immune microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1337478.
Guo Y, Li J, Zhang K. Crotonylation modification and its role in diseases. Front Mol Biosci. 2024;11:1492212.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82404775, 82301823 and 82373928); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Project for Young Teachers) (2042023kf0064); Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University Science, Technology and Innovation Seed Fund (CXPY2024025); National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2024YFC2815900); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2042025kf0062); Research Fund from Medical Sci-Tech Innovation Platform of Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University (PTXM2025015); Translational Medicine and Interdisciplinary Research Joint Fund of Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University (ZNLH202319); and Undergraduate Training Programs for Innovation and Entrepreneurship of Wuhan University (S202510486461&W202510486456).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QRM conducted the literature review and wrote the draft of the manuscript. CQW assisted in the literature search. CGL, KEZ, and ZFL provided useful comments and suggestions. PFX and LL revised the manuscript. All the authors have agreed both to be personally accountable for their own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are addressed. All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mi, Qr., Wu, Cq., Lv, Cg. et al. Epigenetic regulation and posttranslational modifications of FXR: underlying mechanisms and implications in digestive diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01726-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01726-0