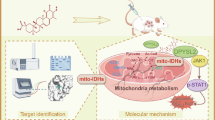
Abstract
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations are the most common cause in aberrant mitochondrion-leading cancer, exploration of direct targeting mutated mtDNA still remains incomplete. Secoemestrin C (Sec C) is epitetrathiodioxopiperazine derived from the endophytic fungus, which exhibited a rapid and prominent anti-breast cancer effect in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). In this study we investigated the anticancer mechanism of Sec C, especially its effect on TNBC cells. We showed that Sec C potently inhibited the viability of both TNBC (MDA-MB-231, HS578T, BT-549) and non-TNBC (MCF-7, T47D, SK-BR-3) cells in vitro with IC50 values of 1−2 μM. In MDA-MB-231 cells, treatment with Sec C (2 μM) induced DNA breakage and subsequent apoptosis. Furthermore, treatment with Sec C (2 μM) caused mtDNA damage, mitochondrial ubiquitination and subsequent mitophagy in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells. RNA-seq analysis revealed that Sec C mitigated YAP level in time and dose-dependent manner either in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells. By re-analyzing the Sec C-responsive gene network proteins, we identified SLX4 as an oncogene promoting breast cancer development, potentially by stabilizing mtDNA to suppress pathologic mitochondrion mitophagy. Specifically, Sec C initiated MDA-MB-231 cells to yield ROS that induced SLX4 ubiquitination and degradation, leading to mtDNA damage and exacerbated mitophagy and promoted YAP degradation bypassing YAP-driven DNA repair pathways. This study not only demonstrates that Sec C is a rapid and prominent anti-breast cancer drug for TNBC, but also reveals SLX4 as a novel mtDNA stabilizer supporting breast cancer progression, positioning it as both a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ikeda G, Santoso MR, Tada Y, Li AM, Vaskova E, Jung J, et al. Mitochondria-rich extracellular vesicles from autologous stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes restore energetics of ischemic myocardium. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77:1073–88.
Hinton AJ, Claypool SM, Neikirk K, Senoo N, Wanjalla CN, Kirabo A, et al. Mitochondrial structure and function in human heart failure. Circ Res. 2024;135:372–96.
Prantl L, Eigenberger A, Gehmert S, Haerteis S, Aung T, Rachel R, et al. Enhanced resorption of liposomal packed vitamin c monitored by ultrasound. J Clin Med. 2020;9:1616.
Liu Y, Shi Y. Mitochondria as a target in cancer treatment. MedComm. 2020;1:129–39.
Fontana GA, Gahlon HL. Mechanisms of replication and repair in mitochondrial DNA deletion formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:11244–58.
Chang SC, Gopal P, Lim S, Wei X, Chandramohan A, Mangadu R, et al. Targeted degradation of PCNA outperforms stoichiometric inhibition to result in programed cell death. Cell Chem Biol. 2022;29:1601–15.
Fielden J, Siegner SM, Gallagher DN, Schroder MS, Dello Stritto MR, Lam S, et al. Comprehensive interrogation of synthetic lethality in the DNA damage response. Nature. 2025;640:1093–102.
Yang C, Liu H, Feng X, Shi H, Jiang Y, Li J, et al. Research hotspots and frontiers of neoadjuvant therapy in triple-negative breast cancer: a bibliometric analysis of publications between 2002 and 2023. Int J Surg. 2024;110:4976–92.
Foulkes WD, Smith IE, Reis-Filho JS. Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1938–48.
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, Andre F, Tordai A, Mejia JA, et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1275–81.
Lichota A, Gwozdzinski K. Anticancer activity of natural compounds from plant and marine environment. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:3533.
Buyel JF. Plants as sources of natural and recombinant anti-cancer agents. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36:506–20.
Zhu L, Chen L. Progress in research on paclitaxel and tumor immunotherapy. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019;24:40.
Behroozaghdam M, Dehghani M, Zabolian A, Kamali D, Javanshir S, Hasani Sadi F, et al. Resveratrol in breast cancer treatment: From cellular effects to molecular mechanisms of action. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79:539.
Vitasse Y, Ursenbacher S, Klein G, Bohnenstengel T, Chittaro Y, Delestrade A, et al. Phenological and elevational shifts of plants, animals and fungi under climate change in the European Alps. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2021;96:1816–35.
Dinglasan JLN, Otani H, Doering DT, Udwary D, Mouncey NJ. Microbial secondary metabolites: advancements to accelerate discovery towards application. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2025;23:338–54.
Ooike M, Nozawa K, Kawai K-I. An epitetrathiodioxopiperazine related to emestrin from Emericella foveolata. Phytochemistry. 1997;46:123–6.
Wang J, Chen M, Wang M, Zhao W, Zhang C, Liu X, et al. The novel ER stress inducer Sec C triggers apoptosis by sulfating ER cysteine residues and degrading YAP via ER stress in pancreatic cancer cells. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12:210–27.
Xi XM, Li Y, Shao RG, Si SY, Chen MH, Zhao WL. The anti-cancer mechanism of secoemestrin C in liver cancer cells. Chin Med Biotechnol. 2024;19:4–12.
Li Y, Zhao WL, Si SY, Chen MH, Shao RG. The mechanism of Secoemestrin C inhibiting the proliferation and inducing apoptosis of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Chin Med Biotechnol. 2023;18:2–10.
Zhu Z, Liu M, Wang J, Shu Z, Cao J. Secoemestrin c ameliorates psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice by suppressing the TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Curr Med Sci. 2024;44:232–40.
Kopp B, Khoury L, Audebert M. Validation of the gammaH2AX biomarker for genotoxicity assessment: a review. Arch Toxicol. 2019;93:2103–14.
Tarsounas M, Sung P. The antitumorigenic roles of BRCA1-BARD1 in DNA repair and replication. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21:284–99.
Dias Nunes J, Demeestere I, Devos M. BRCA mutations and fertility preservation. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;25:204.
Zong D, Pavani R, Nussenzweig A. New twist on BRCA1-mediated DNA recombination repair and tumor suppression. Trends Cell Biol. 2025;25:112–6.
Button RW, Roberts SL, Willis TL, Hanemann CO, Luo S. Accumulation of autophagosomes confers cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem. 2017;292:13599–614.
Liu J, Ma H, Wu Z, Ji Y, Liang Y. The knowns and unknowns of membrane features and changes during autophagosome-lysosome/vacuole fusion. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25:11160.
Chen Y, Yi H, Liao S, He J, Zhou Y, Lei Y. LC3B: A microtubule-associated protein influences disease progression and prognosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2025;81:16–26.
Eiyama A, Okamoto K. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in mammalian cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015;33:95–101.
Wei B, Wei M, Huang H, Fan T, Zhang Z, Song X. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: a promising therapeutic strategy for age-related diseases. Cell Prolif. 2025;58:e13795.
Kaarniranta K, Pawlowska E, Szczepanska J, Jablkowska A, Blasiak J. Role of mitochondrial DNA damage in ROS-Mediated pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:2374.
Yan C, Duanmu X, Zeng L, Liu B, Song Z. Mitochondrial DNA: distribution, mutations, and elimination. Cells. 2019;8:379.
Li C, Zhang Y, Liu J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Tang D. Mitochondrial DNA stress triggers autophagy-dependent ferroptotic death. Autophagy. 2021;17:948–60.
Longchamps RJ, Castellani CA, Yang SY, Newcomb CE, Sumpter JA, Lane J, et al. Evaluation of mitochondrial DNA copy number estimation techniques. PLoS One. 2020;15:e228166.
Wang J, Zhao H, Yu J, Xu X, Jing H, Li N, et al. MiR-320b/RAD21 axis affects hepatocellular carcinoma radiosensitivity to ionizing radiation treatment through DNA damage repair signaling. Cancer Sci. 2021;112:575–88.
Lennicke C, Cocheme HM. Redox metabolism: ROS as specific molecular regulators of cell signaling and function. Mol Cell. 2021;81:3691–707.
Song I, Lee J, Cho J, Jeong J, Shin D, Lee K. Degradation of Redox-Sensitive proteins including peroxiredoxins and DJ-1 is promoted by oxidation-induced conformational changes and ubiquitination. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34432.
Su Z, Li Y, Zhou Z, Feng B, Chen H, Zheng G. Herbal medicine for colorectal cancer treatment: molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Cell Prolif. 2025;58:e70065.
Chang H, Ou Yang R, Su J, Nguyen TMH, Sung J, Tang M, et al. YAP nuclear translocation induced by HIF-1alpha prevents DNA damage under hypoxic conditions. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9:385.
Shu Y, Jin X, Ji M, Zhang Z, Wang X, Liang H, et al. Ku70 binding to YAP alters PARP1 ubiquitination to regulate genome stability and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2024;84:2836–55.
Zender L, Spector MS, Xue W, Flemming P, Cordon-Cardo C, Silke J, et al. Identification and validation of oncogenes in liver cancer using an integrative oncogenomic approach. Cell. 2006;125:1253–67.
Zanconato F, Cordenonsi M, Piccolo S. YAP/TAZ at the roots of cancer. Cancer Cell. 2016;29:783–803.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (2021-I2M-1-030, 2023-I2M-2-001); and Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7254505).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WLZ, YX and YSC contributed to the experimental design; WLZ and LQQ contributed to data acquisition and analysis; XJZ and CHZ carried out the immunoassays, Western blot assays, and other key experiments; XWW, MYW and LL reviewed the manuscript; CZ and ZXG assisted in data analysis; WLZ and RGS obtained the funding; WLZ and XJZ wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Xj., Xu, Y., Zhang, Ch. et al. Secoemestrin C exerts rapid and prominent anti-breast cancer effect in triple-negative breast cancer by inducing SLX4 and YAP degradation. Acta Pharmacol Sin (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01730-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-025-01730-4