Abstract
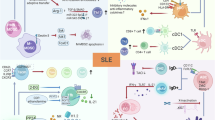
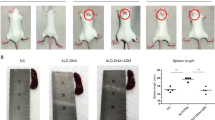
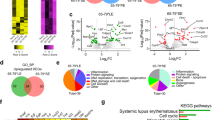
Triptolide has demonstrated potent immunosuppressive properties in multiple autoimmune disorders, but its severe toxicity has greatly hampered clinical application. Here, we synthesized a triptolide derivative STP1, which exhibits remarkably reduced toxicity compared with triptolide. Immune dysfunction plays a critical role in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an archetypical and refractory autoimmune disorder with limited therapeutic options and suboptimal outcomes. To elucidate the drugability and effect, we investigated the therapeutic potential, safety, regulatory mechanism and target of STP1 on SLE. Our data indicated that STP1 significantly ameliorates imiquimod-induced murine SLE by reducing anti-IgG, anti-dsDNA IgG, proteinuria, and renal pathological injury. Mechanistically, STP1 exerts markedly immunosuppressive roles by modulating the differentiation of B cell into plasma cells and T cell into Tfh cells. Further investigation showed that STP1 regulates B-cell receptor and T-cell receptor signaling by directly targeting Fyn kinase responsible for its immunosuppressive activity. For safety of STP1, our findings indicated that the STP1 did not show any toxicity in biochemical parameters and organ pathological analysis in subacute toxicity experiment. The findings suggested that STP1 is an attractive novel candidate for SLE and other autoimmune diseases for thorough evaluation.

STP1, a structurally modified derivative of triptolide with improved safety, alleviates murine systemic lupus erythematosus by targeting and inhibiting Fyn, a Src kinase family member that regulates B- and T- cell responses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaul A, Gordon C, Crow MK, Touma Z, Urowitz MB, van Vollenhoven R, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16039.
Wang M, Chen HK, Zhang T, Zhang ZK, Xiang XW, Gao M, et al. Targeting toll-like receptor 7 as a therapeutic development strategy for systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Pharmacol Sin B. 2024;14:4899–913.
Feng YF, Chen CJ, Shao AQ, Wu L, Hu HY, Zhang TT. Emerging interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) inhibitors or degraders as therapeutic agents for autoimmune diseases and cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin B. 2024;14:5091–105.
Feng Y, Yang M, Wu HJ, Lu QJ. The pathological role of B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: From basic research to clinical. Autoimmunity. 2020;53:56–64.
Liang YN, Chen L, Huang QY, Song YT, Fan YJ, Chen TQ, et al. Immune cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: biology and traditional Chinese medicine therapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025;46:2587–96.
Wang CQ, Ming BX, Wu XF, Wu T, Cai SZ, Hu P, et al. Sphingomyelin synthase 1 enhances BCR signaling to promote lupus-like autoimmune response. Ebiomedicine. 2019;45:578–87.
Chalupny NJ, Aruffo A, Esselstyn JM, Chan PY, Bajorath J, Blake J, et al. Specific binding of Fyn and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to the B-cell surface glycoprotein CD19 through their Src homology-2 domains. Eur J Immunol. 1995;25:2978–84.
Mkaddem SB, Murua A, Flament H, Titeca-Beauport D, Bounaix C, Danelli L, et al. Lyn and Fyn function as molecular switches that control immunoreceptors to direct homeostasis or inflammation. Nat Commun. 2017;8:246.
Sharma N, Akhade AS, Qadri A. Src kinases central to T-cell receptor signaling regulate TLR-activated innate immune responses from human T cells. Innate Immun. 2016;3:238–44.
Dallari S, Macal M, Loureiro ME, Jo Y, Swanson L, Hesser C, et al. Src family kinases Fyn and Lyn are constitutively activated and mediate plasmacytoid dendritic cell responses. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14380.
Zamoyska R, Basson A, Filby A, Legname G, Lovatt M, Seddon B. The influence of the src-family kinases, Lck and Fyn, on T cell differentiation, survival and activation. Immunol Rev. 2003;191:107–18.
Zhang XZ, Mei D, Zhang LL, Wei W. Src family protein kinase controls the fate of B cells in autoimmune diseases. Inflammation. 2021;44:423–33.
Ji W, Lu YY, Ma ZY, Gan K, Liu Y, Cheng Y, et al. Triptolide attenuates inhibition of ankylosing spondylitis-derived mesenchymal stem cells on the osteoclastogenesis through modulating exosomal transfer of circ-0110634. J Orthop Transl. 2022;36:132–44.
Zhao X, Ji W, Lu Y, Liu WW, Guo F. Triptolide regulates the balance of Tfr/Tfh in lupus mice. Adv Rheumatol. 2023;63:29.
Piao X, Zhou J, Xue L. Triptolide decreases rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte proliferation, invasion, inflammation and presents a therapeutic effect in collagen-induced arthritis rats via inactivating lncRNA RP11-83J16.1 mediated URI1 and β-catenin signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;99:108010.
Xi C, Peng SJ, Wu ZP, Zhou QP, Zhou J. Toxicity of triptolide and the molecular mechanisms involved. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;90:531–41.
Wang L, Xu YP, Fu L, Li YC, Lou LG. (5R)-5-hydroxytriptolide (LLDT-8), a novel immunosuppressant in clinical trials, exhibits potent antitumor activity via transcription inhibition. Cancer Lett. 2012;324:75–82.
Reno TA, Tong SW, Wu J, Fidler JM, Nelson R, Kim JY, et al. The triptolide derivative MRx102 inhibits Wnt pathway activation and has potent anti-tumor effects in lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:439.
Fidler JM, Li K, Chung C, Wei K, Ross JA, Gao MX, et al. PG490-88, a derivative of triptolide, causes tumor regression and sensitizes tumors to chemotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003;2:855–62.
Yokogawa M, Takaishi M, Nakajima K, Kamijima R, Fujimoto C, Kataoka S, et al. Epicutaneous application of toll-like receptor 7 agonists leads to systemic autoimmunity in wild-type mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66:694–706.
Chen XY, Guan JC, Lin YZ, Luo HW, Liu JY, Ma J, et al. Design and synthesis of novel sulfur-substituted triptolide with the ability to induce autophagy through inhibition of SRSF1 expression. Eur J Med Chem. 2025;287:117342.
Lee J, Park Y, Jang SG, Hong SM, Song YS, Kim MJ, et al. Baricitinib attenuates autoimmune phenotype and podocyte injury in a murine model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2021;12:704526.
Zhou Y, Li MR, Shen T, Yang TM, Shi GN, Wei YZ, et al. Celastrol targets cullin-associated and neddylation-dissociated 1 to prevent fibroblast-myofibroblast transformation against pulmonary fibrosis. ACS Chem Biol. 2022;17:2734–43.
Pawar RD, Ramanjaneyulu A, Kulkarni OP, Lech M, Segerer S, Anders HJ. Inhibition of Toll-like receptor-7 (TLR-7) or TLR-7 plus TLR-9 attenuates glomerulonephritis and lung injury in experimental lupus. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:1721–31.
Genestier L, Taillardet M, Mondiere P, Gheit H, Bella C, Defrance T. TLR agonists selectively promote terminal plasma cell differentiation of B cell subsets specialized in thymus-independent responses. J Immunol. 2007;178:7779–86.
Breitfeld D, Ohl L, Kremmer E, Ellwart J, Sallusto F, Lipp M, et al. Follicular B helper T cells express CXC chemokine receptor 5, localize to B cell follicles, and support immunoglobulin production. J Exp Med. 2000;192:1545–51.
Weinstein JS, Bertino SA, Hernandez SG, Poholek AC, Teplitzky TB, Nowyhed HN, et al. B cells in T follicular helper cell development and function: separable roles in delivery of ICOS ligand and antigen. J Immunol. 2014;192:3166–79.
Kawabe T, Naka T, Yoshida K, Tanaka T, Fujiwara H, Suematsu S, et al. The immune-responses in CD40-deficient mice - impaired immunoglobulin class switching and germinal center formation. Immunity. 1994;1:167–78.
Chaimowitz NS, Falanga YT, Ryan JJ, Conrad DH. Fyn kinase is required for optimal humoral responses. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60640.
Green TP, Fennell M, Whittaker R, Curwen J, Jacobs V, Allen J, et al. Preclinical anticancer activity of the potent, oral Src inhibitor AZD0530. Mol Oncol. 2009;3:248–61.
Nygaard HB. Targeting Fyn kinase in alzheimer’s disease. Biol Psychiatry. 2018;83:369–76.
Zhang Y, Zhang FQ, Gao YN, Wang MJ, Gao Y, Li HC, et al. Triptolide in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus - regulatory effects on miR-146a in B cell TLR7 signaling pathway in mice. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:952775.
Zhao X, Tang XJ, Yan Q, Song H, Li ZT, Wang DD, et al. Triptolide ameliorates lupus via the induction of miR-125a-5p-mediating Treg upregulation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;71:14–21.
Zhou R, Zhang F, He PL, Zhou WL, Wu QL, Xu JY, et al. (5R)-5-hydroxytriptolide (LLDT-8), a novel triptolide analog mediates immunosuppressive effects in vitro and in vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2005;5:1895–903.
Chugh R, Sangwan V, Patil SP, Dudeja V, Dawra RK, Banerjee S, et al. A preclinical evaluation of minnelide as a therapeutic agent against pancreatic cancer. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:156ra139.
Fu JM, Zang YD, Zhou Y, Chen CJ, Shao S, Hu M, et al. A novel triptolide derivative ZT01 exerts anti-inflammatory effects by targeting TAK1 to prevent macrophage polarization into pro-inflammatory phenotype. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;126:110084.
Zhang C, Gu CH, Peng F, Liu W, Wan JL, Xu HB, et al. Preparation and optimization of triptolide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for oral delivery with reduced gastric irritation. Molecules. 2013;18:13340–56.
Zhou LL, Du Y, Shang YT, Xiang DB, Xia XH. A novel triptolide nano-liposome with mitochondrial targeting for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Nanomed. 2024;19:12975–98.
Cheng YX, Zhao YH, Zheng Y. Therapeutic potential of triptolide in autoimmune diseases and strategies to reduce its toxicity. Chin Med. 2021;16:114.
Wang L, Yin HY, Jiang J, Li QL, Gao CX, Li WR, et al. A rationally designed CD19 monoclonal antibody-triptolide conjugate for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Pharmacol Sin B. 2024;10:4560–76.
Ma KY, Li JY, Fang YF, Lu LW. Roles of B cell-intrinsic TLR signals in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16:13084–105.
Meffre E, O’Connor KC. Impaired B-cell tolerance checkpoints promote the development of autoimmune diseases and pathogenic autoantibodies. Immunol Rev. 2019;292:90–101.
Kuraoka M, Snowden PB, Nojima T, Verkoczy L, Haynes BF, Kitamura D, et al. BCR and endosomal TLR signals synergize to increase AID expression and establish central B cell tolerance. Cell Rep. 2017;18:1627–35.
Kim LC, Song LX, Haura EB. Src kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6:587–95.
Mamchak AA, Sullivan BM, Hou BD, Lee LM, Gilden JK, Krummel MF, et al. Normal development and activation but altered cytokine production of Fyn-deficient CD4 T cells. J Immunol. 2008;181:5374–85.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82293684, 82204410, 22277144), the National Key R&D Program of China (2020YFA0908004), CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Science of China (2022-I2M-1-028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QYD and YZ performed the experiments; QYD analyzed the data and wrote the paper; YZW contributed to the investigation; YFF and HWL performed data visualization; HWL, YDZ, and DMZ provided the compound; YZ and TTZ provided funding support; LW, CJC, and TTZ supervised the work and revised the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Qy., Zhou, Y., Luo, Hw. et al. Triptolide derivative STP1 ameliorates murine systemic lupus erythematosus via targeting Fyn kinase. Acta Pharmacol Sin (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-026-01753-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-026-01753-5