Abstract
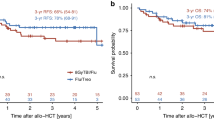
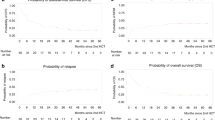
Patients with poor risk acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have a dismal outcome. We hypothesized that combining decitabine with a standard non-myeloablative (NMA) conditioning regimen prior to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo HCT), might decrease the relapse incidence. We conducted a multicenter prospective phase II study (NCT02252107) with 10-day decitabine (20 mg/m2/day) integrated in a standard non-myeloablative conditioning regimen (3 days fludarabine 30 mg/m2 with 2 Gray total body irradiation (TBI)). Patients with AML ≥ 18 years in 1st (in)complete remission (CR/CRi) with a poor or very poor risk profile, as defined by the HOVON-132 protocol, were eligible. Results: Forty-six patients (median age 60; range 23–74) were included. Median follow up time was 44 months (range 31–65 months). The cumulative 1-year incidence of relapse and NRM were respectively 23% and 11%. Incidence of grade III-IV acute graft-vs-host-disease (GVHD) and severe chronic GVHD were 13% and 20%, respectively. One-year OS was 70%. Application of ELN 2017 risk classification to the study cohort revealed a cumulative one-year relapse rate of respectively 31% and 13% for the adverse and intermediate risk patients. To conclude, the 10-day DEC/FLU/TBI conditioning regimen prior to allo HCT in poor risk AML patients is effective and feasible.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cornelissen JJ, Breems D, van Putten WL, Gratwohl AA, Passweg JR, Pabst T, et al. Comparative analysis of the value of allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia with monosomal karyotype versus other cytogenetic risk categories. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2140–6.
Yanada M, Mori J, Aoki J, Harada K, Mizuno S, Uchida N, et al. Effect of cytogenetic risk status on outcomes for patients with acute myeloid leukemia undergoing various types of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: an analysis of 7812 patients. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018;59:601–9.
Jethava YS, Sica S, Savani B, Socola F, Jagasia M, Mohty M, et al. Conditioning regimens for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants in acute myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2017;52:1504–11.
Gyurkocza B, Storb R, Storer BE, Chauncey TR, Lange T, Shizuru JA, et al. Nonmyeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2859–67.
Passweg JR, Labopin M, Cornelissen J, Volin L, Socie G, Huynh A, et al. Conditioning intensity in middle-aged patients with AML in first CR: no advantage for myeloablative regimens irrespective of the risk group-an observational analysis by the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2015;50:1063–8.
Konuma T, Kondo T, Mizuno S, Doki N, Aoki J, Fukuda T, et al. Conditioning intensity for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia patients with poor-prognosis cytogenetics in first complete remission. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2020;26:463–71.
Ciurea SO, Kongtim P, Varma A, Rondon G, Chen J, Srour S, et al. Is there an optimal conditioning for older patients with AML receiving allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation? Blood. 2020;135:449–52.
Scott BL, Pasquini MC, Logan BR, Wu J, Devine SM, Porter DL, et al. Myeloablative versus reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:1154–61.
Gilleece MH, Labopin M, Yakoub-Agha I, Volin L, Socie G, Ljungman P, et al. Measurable residual disease, conditioning regimen intensity, and age predict outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in first remission: A registry analysis of 2292 patients by the Acute Leukemia Working Party European Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Am J Hematol. 2018;93:1142–52.
Araki D, Wood BL, Othus M, Radich JP, Halpern AB, Zhou Y, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia: time to move toward a minimal residual disease-based definition of complete remission? J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:329–36.
Hourigan CS, Dillon LW, Gui G, Logan BR, Fei M, Ghannam J, et al. Impact of conditioning intensity of allogeneic transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia with genomic evidence of residual disease. J Clin Oncol. 2019;38:1273–84.
Welch JS, Petti AA, Miller CA, Fronick CC, O’Laughlin M, Fulton RS, et al. TP53 and decitabine in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2023–36.
Cruijsen M, Hobo W, van der Velden WJ, Bremmers ME, Woestenenk R, Bar B, et al. Addition of 10-day decitabine to fludarabine/total body irradiation conditioning is feasible and induces tumor-associated antigen-specific T cell responses. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016;22:1000–8.
Almstedt M, Blagitko-Dorfs N, Duque-Afonso J, Karbach J, Pfeifer D, Jager E, et al. The DNA demethylating agent 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine induces expression of NY-ESO-1 and other cancer/testis antigens in myeloid leukemia cells. Leuk Res. 2010;34:899–905.
Schuurhuis GJ, Heuser M, Freeman S, Bene MC, Buccisano F, Cloos J, et al. Minimal/measurable residual disease in AML: a consensus document from the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Blood. 2018;131:1275–91.
David Valcarcel AS. Graft failure. EBMT handbook: hematopoietic stem cell transplant cell therapies. 2019. p. 307.
Harris AC, Young R, Devine S, Hogan WJ, Ayuk F, Bunworasate U, et al. International, multicenter standardization of acute graft-versus-host disease clinical data collection: a report from the mount sinai acute GVHD International Consortium. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016;22:4–10.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ, et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2005;11:945–56.
Dohner H, Estey E, Grimwade D, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Buchner T, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood. 2017;129:424–47.
Ruggeri A, Labopin M, Ciceri F, Mohty M, Nagler A. Definition of GvHD-free, relapse-free survival for registry-based studies: an ALWP-EBMT analysis on patients with AML in remission. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2016;51:610–1.
Goodyear O, Agathanggelou A, Novitzky-Basso I, Siddique S, McSkeane T, Ryan G, et al. Induction of a CD8+ T-cell response to the MAGE cancer testis antigen by combined treatment with azacitidine and sodium valproate in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplasia. Blood. 2010;116:1908–18.
D’Angelo CR, Hall A, Woo KM, Kim K, Longo W, Hematti P, et al. Decitabine induction with myeloablative conditioning and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in high-risk patients with myeloid malignancies is associated with a high rate of infectious complications. Leuk Res. 2020;96:106419.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by an unrestricted grant from Jansen Cooperation and the Dutch Cancer Fund (KWF kankerbestrijding).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
GH joined advisory boards of Celgene and Jansen.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cruijsen, M., Hilberink, J.R., van der Velden, W.J.F.M. et al. Low relapse risk in poor risk AML after conditioning with 10-day decitabine, fludarabine and 2 Gray TBI prior to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 56, 1964–1970 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-021-01272-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-021-01272-3