Abstract
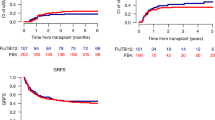
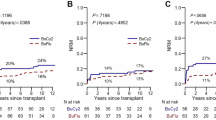
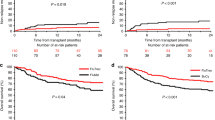
The optimal myeloablative conditioning (MAC) regimens in adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) undergoing allogeneic hemopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) in complete remission (CR) remain unclear. We performed a systematic review and network meta-analysis to compare the effects of different MAC regimens. Bayesian network meta-analysis was performed using WinBUGS version 1.4.3. The commonly used MAC regimen Bu/Cy (4-day busulfan for toal 16 mg/kg orally or 12.8 mg/kg intravenously, plus 2-day cyclophosphamide for toal 120 mg/kg intravenously) is chosen as the common comparator. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) with the associated 95% credibility interval (95% CrI) are obtained for all comparisons. We included 19 eligible studies, involving 8104 AML patients and 9 MAC regimens. Compared with Bu/Cy, 3-day busulfan plus fludarabine and thiotepa (Bu3/Flu/TT) is associated with significantly better overall survival (HR, 0.70; 95% CrI, 0.51 to 0.96) and lower risk of relapse (HR, 0.59; 95% CrI, 0.35 to 0.98). Bu3/Flu/TT is also associated with superior overall survival than Cy/TBI (cyclophosphamide plus total body irradiation), and lower risk of relapse than Bu4/Flu (4-day busulfan plus fludarabine). These results suggest that thiotepa-based new MAC regimen Bu3/Flu/TT is associated with improved outcomes in AML patients undergoing allo-HSCT in CR and worth further investigation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Short NJ, Rytting ME, Cortes JE. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. 2018;392:593–606.
National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia—Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). 2021. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html (accessed Jan 7, 2021).
Döhner H, Weisdorf DJ, Bloomfield CD. Acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl J Med. 2015;373:1136–52.
Cornelissen JJ, Blaise D. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with AML in first complete remission. Blood. 2016;127:62–70.
Koreth J, Schlenk R, Kopecky KJ, Honda S, Sierra J, Djulbegovic BJ, et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission: systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective clinical trials. Jama. 2009;301:2349–61.
Döhner H, Estey E, Grimwade D, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Büchner T, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood. 2017;129:424–47.
Gyurkocza B, Sandmaier BM. Conditioning regimens for hematopoietic cell transplantation: one size does not fit all. Blood. 2014;124:344–53.
Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V, et al. Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: working definitions. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2009;15:1628–33.
Scott BL, Pasquini MC, Logan BR, Wu J, Devine SM, Porter DL, et al. Myeloablative versus reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:1154–61.
Scott BL, Pasquini MC, Fei M, Fraser R, Wu J, Devine SM, et al. Myeloablative versus reduced-intensity conditioning for hematopoietic cell transplantation in acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes-long-term follow-up of the BMT CTN 0901 clinical trial. Transplant Cell Ther. 2021;27:483.e1–e6.
Hartman AR, Williams SF, Dillon JJ. Survival, disease-free survival and adverse effects of conditioning for allogeneic bone marrow transplantation with busulfan/cyclophosphamide vs total body irradiation: a meta-analysis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 1998;22:439–43.
Gupta T, Kannan S, Dantkale V, Laskar S. Cyclophosphamide plus total body irradiation compared with busulfan plus cyclophosphamide as a conditioning regimen prior to hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with leukemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2011;4:17–29.
Copelan EA, Hamilton BK, Avalos B, Ahn KW, Bolwell BJ, Zhu X, et al. Better leukemia-free and overall survival in AML in first remission following cyclophosphamide in combination with busulfan compared with TBI. Blood. 2013;122:3863–70.
Nagler A, Rocha V, Labopin M, Unal A, Ben Othman T, Campos A, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in remission: comparison of intravenous busulfan plus cyclophosphamide (Cy) versus total-body irradiation plus Cy as conditioning regimen—a report from the acute leukemia working party of the European group for blood and marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3549–56.
Nagler A, Savani BN, Labopin M, Polge E, Passweg J, Finke J, et al. Outcomes after use of two standard ablative regimens in patients with refractory acute myeloid leukaemia: a retrospective, multicentre, registry analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2015;2:e384–92.
Lee JH, Joo YD, Kim H, Ryoo HM, Kim MK, Lee GW, et al. Randomized trial of myeloablative conditioning regimens: busulfan plus cyclophosphamide versus busulfan plus fludarabine. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:701–9.
Ben-Barouch S, Cohen O, Vidal L, Avivi I, Ram R. Busulfan fludarabine vs busulfan cyclophosphamide as a preparative regimen before allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2016;51:232–40.
Jethava YS, Sica S, Savani B, Socola F, Jagasia M, Mohty M, et al. Conditioning regimens for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants in acute myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2017;52:1504–11.
Hutton B, Salanti G, Caldwell DM, Chaimani A, Schmid CH, Cameron C, et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:777–84.
Sheth V, Labopin M, Canaani J, Volin L, Brecht A, Ganser A, et al. Comparison of FLAMSA-based reduced intensity conditioning with treosulfan/fludarabine conditioning for patients with acute myeloid leukemia: an ALWP/EBMT analysis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019;54:531–9.
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials. 2007;8:16.
Woods BS, Hawkins N, Scott DA. Network meta-analysis on the log-hazard scale, combining count and hazard ratio statistics accounting for multi-arm trials: a tutorial. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2010;10:54.
Liao WC, Chien KL, Lin YL, Wu MS, Lin JT, Wang HP, et al. Adjuvant treatments for resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:1095–103.
Rambaldi A, Grassi A, Masciulli A, Boschini C, Mico MC, Busca A, et al. Busulfan plus cyclophosphamide versus busulfan plus fludarabine as a preparative regimen for allogeneic haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia: an open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1525–36.
Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from: https://training.cochrane.org/handbooks.
Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. 2021. Available from: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.
Dias S, Welton NJ, Sutton AJ, Ades A. NICE DSU Technical Support Document 2: a generalised linear modelling framework for pairwise and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. 2011. Available from: http://www.nicedsu.org.uk.
van Beurden-Tan CHY, Franken MG, Blommestein HM, Uyl-de Groot CA, Sonneveld P. Systematic literature review and network meta-analysis of treatment outcomes in relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:1312–9.
Skoetz N, Trelle S, Rancea M, Haverkamp H, Diehl V, Engert A, et al. Effect of initial treatment strategy on survival of patients with advanced-stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:943–52.
Blaise D, Maraninchi D, Archimbaud E, Reiffers J, Devergie A, Jouet JP, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in first remission: a randomized trial of a busulfan-Cytoxan versus Cytoxan-total body irradiation as preparative regimen: a report from the Group d’Etudes de la Greffe de Moelle Osseuse. Blood. 1992;79:2578–82.
Blaise D, Maraninchi D, Michallet M, Reiffers J, Jouet JP, Milpied N, et al. Long-term follow-up of a randomized trial comparing the combination of cyclophosphamide with total body irradiation or busulfan as conditioning regimen for patients receiving HLA-identical marrow grafts for acute myeloblastic leukemia in first complete remission. Blood. 2001;97:3669–71.
Bornhauser M, Kienast J, Trenschel R, Burchert A, Hegenbart U, Stadler M, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning versus standard conditioning before allogeneic haemopoietic cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia in first complete remission: a prospective, open-label randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:1035–44.
Clift RA, Buckner CD, Appelbaum FR, Bearman SI, Petersen FB, Fisher LD, et al. Allogeneic marrow transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first remission: a randomized trial of two irradiation regimens. Blood. 1990;76:1867–71.
Clift RA, Buckner CD, Appelbaum FR, Sullivan KM, Storb R, Thomas ED. Long-term follow-Up of a randomized trial of two irradiation regimens for patients receiving allogeneic marrow transplants during first remission of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1998;92:1455–6.
Fasslrinner F, Schetelig J, Burchert A, Kramer M, Trenschel R, Hegenbart U, et al. Long-term efficacy of reduced-intensity versus myeloablative conditioning before allogeneic haemopoietic cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia in first complete remission: retrospective follow-up of an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2018;5:e161–e9.
Liu H, Zhai X, Song Z, Sun J, Xiao Y, Nie D, et al. Busulfan plus fludarabine as a myeloablative conditioning regimen compared with busulfan plus cyclophosphamide for acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a prospective and multicenter study. J Hematol Oncol. 2013;6:15.
Zhang WP, Wang ZW, Hu XX, Chen J, Yang D, Song XM, et al. Preconditioning with fludarabine, busulfan and cytarabine versus standard BuCy2 for patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a prospective, randomized phase II study. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019;54:894–902.
Farag SS, Bolwell BJ, Elder PJ, Kalaycio M, Lin T, Pohlman B, et al. High-dose busulfan, cyclophosphamide, and etoposide does not improve outcome of allogeneic stem cell transplantation compared to BuCy2 in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2005;35:653–61.
Fedele R, Messina G, Martinello T, Gallo GA, Pontari A, Moscato T, et al. Tolerability and efficacy of busulfan and fludarabine as allogeneic pretransplant conditioning therapy in acute myeloid leukemia: comparison with busulfan and cyclophosphamide regimen. Clin Lymphoma, Myeloma Leuk. 2014;14:493–500.
Giebel S, Labopin M, Sobczyk-Kruszelnicka M, Stelljes M, Byrne JL, Fegueux N, et al. Total body irradiation + fludarabine compared to busulfan + fludarabine as “reduced-toxicity conditioning” for patients with acute myeloid leukemia treated with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in first complete remission: a study by the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021;56:481–91.
Litzow MR, Perez WS, Klein JP, Bolwell BJ, Camitta B, Copelan EA, et al. Comparison of outcome following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation with cyclophosphamide-total body irradiation versus busulphan-cyclophosphamide conditioning regimens for acute myelogenous leukaemia in first remission. Br J Haematol. 2002;119:1115–24.
Liu H, Fan ZP, Jiang QL, Huang F, Zhou HS, Zhang X, et al. A comparison of toxicity and efficacy between busulfan plus fludarabine and busulfan plus cyclophosphamide for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia. Chung-Hua Nei Ko Tsa Chih Chin J Intern Med. 2012;51:880–4.
Morsink LM, Bezerra ED, Othus M, Wood BL, Fang M, Sandmaier BM, et al. Comparative analysis of total body irradiation (TBI)-based and non-TBI-based myeloablative conditioning for acute myeloid leukemia in remission with or without measurable residual disease. Leukemia. 2020;34:1701–5.
Patel SS, Rybicki L, Pohlman B, Bolwell B, Gerds AT, Hamilton BK, et al. Comparative effectiveness of busulfan/cyclophosphamide versus busulfan/fludarabine myeloablative conditioning for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Hematol/Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2020;13:160–5.
Pidala J, Kim J, Anasetti C, Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Nishihori T, Field T, et al. Pharmacokinetic targeting of intravenous busulfan reduces conditioning regimen related toxicity following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2010;3:36.
Saraceni F, Beohou E, Labopin M, Arcese W, Bonifazi F, Stepensky P, et al. Thiotepa, busulfan and fludarabine compared to busulfan and cyclophosphamide as conditioning regimen for allogeneic stem cell transplant from matched siblings and unrelated donors for acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2018;93:1211–9.
Saraceni F, Labopin M, Hamladji RM, Mufti G, Socié G, Shimoni A, et al. Thiotepa-busulfan-fludarabine compared to busulfan-fludarabine for sibling and unrelated donor transplant in acute myeloid leukemia in first remission. Oncotarget. 2018;9:3379–93.
Sora F, Grazia CD, Chiusolo P, Raiola AM, Bregante S, Mordini N, et al. Allogeneic hemopoietic stem cell transplants in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) prepared with busulfan and fludarabine (BUFLU) or thiotepa, busulfan, and fludarabine (TBF): a retrospective study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020;26:698–703.
Eder S, Labopin M, Finke J, Bunjes D, Olivieri A, Santarone S, et al. Safety and efficacy of thiotepa-based conditioning for allogeneic transplantation in AML: a survey from the ALWP of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2017;52:238–44.
Sanz J, Boluda JC, Martín C, González M, Ferrá C, Serrano D, et al. Single-unit umbilical cord blood transplantation from unrelated donors in patients with hematological malignancy using busulfan, thiotepa, fludarabine and ATG as myeloablative conditioning regimen. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2012;47:1287–93.
Spyridonidis A, Labopin M, Savani BN, Niittyvuopio R, Blaise D, Craddock C, et al. Redefining and measuring transplant conditioning intensity in current era: a study in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55:1114–25.
Funding
SX was supported by National Natural Science Fund (NSFC81800172) and the Project from Army Medical University (2017XQN11). JC was supported by the Logistics Project (AWS17J007). XL was supported by the National Natural Science Fund (NSFC81700185). The funders had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SNX, JPC, and XL contributed to the study conception and design, supervised the study and made critical revision in the manuscript. CXL and GXW performed database searching, study selection, data extraction, statistical analyses and manuscript writing. XTH, YQD, YRH, and YH helped with data extraction, data checking and data interpretation. QYS contributed to statistical analyses and data interpretation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, C., Wu, G., Huang, X. et al. Myeloablative conditioning regimens in adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in complete remission: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant 58, 175–185 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-022-01865-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-022-01865-6