Abstract
Introduction With the advancement of artificial intelligence, large language models (LLMs) have emerged as technology that can generate human-like text across various domains. They hold vast potential in the dental field, able to be integrated into clinical dentistry, administrative dentistry, and for student and patient education. However, the successful integration of LLMs into dentistry is reliant on the dental knowledge of the models used, as inaccuracies can lead to significant risks in patient care and education.
Aims We are the first to compare different LLMs on their dental knowledge through testing the accuracy of different model responses to Integrated National Board Dental Examination (INBDE) questions.
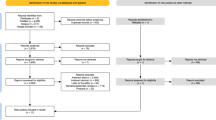
Methods We include closed-source and open-source models and analysed responses to both ‘patient box' style board questions and more traditional, textual-based, multiple-choice questions.
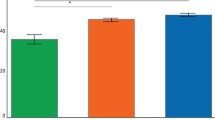
Results For the entire INBDE question bank, ChatGPT-4 had the highest dental knowledge, with an accuracy of 75.88%, followed by Claude-2.1 with 66.38% and then Mistral-Medium at 54.77%. There was a statistically significant difference in performance across all models.
Conclusion Our results highlight the high potential of LLM integration into the dental field, the importance of which LLM is chosen when developing new technologies, and the limitations that must be overcome before unsupervised clinical integration can be adopted.
Key points
-
Directly compares the dental knowledge of different large language models (LLMs).
-
Provides insight into the dental knowledge of existing LLMs as applied to dental medicine.
-
Showcases the best LLMs for future use in dentistry (clinical, administrative, education) and when creating new technology.
-
Establishes a comparison in the dental knowledge of open-source versus close-source LLMs for future technological development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Rafailov R, Sharma A, Mitchell E, Ermon S, Manning C D, Finn C. Direct Preference Optimization: Your Language Model is Secretly a Reward Model. 2024. Available at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.18290 (accessed February 2024).
Johnson A. Here's What To Know About OpenAI's ChatGPT - What It's Disrupting And How To Use It. 2022. Available at https://www.forbes.com/sites/ariannajohnson/2022/12/07/heres-what-to-know-about-openais-chatgpt-what-its-disrupting-and-how-to-use-it/ (accessed May 2023).
Yuskevych M. What is the Best Generative AI Tool: ChatGPT vs LlaMa vs Google Bard vs Claude. 2023. Available at https://perpet.io/blog/which-ai-tool-to-pick-for-your-next-project-chatgpt-llama-google-bard-claude/ (accessed February 2024).
Danesh A, Pazouki H, Danesh K, Danesh F, Danesh A. The performance of artificial intelligence language models in board-style dental knowledge assessment: A preliminary study on ChatGPT. J Am Dent Assoc 2023; 154: 970-974.
Kung T H, Cheatham M, Medenilla A et al. Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Potential for AI-assisted medical education using large language models. PLOS Digit Health 2023; DOI: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000198.
Joint Commission on National Dental Examinations. INBDE Practice Questions. Available at https://dental.pacific.edu/sites/default/files/users/user244/INBDE_practice%20questions.pdf (accessed February 2024).
ITD Online. INBDE Preparation Course. Available at https://www.itdonline.ca/courses/INBDE-preparation-course (accessed February 2024).
INBDE Bootcamp. Homepage. Available at https://app.bootcamp.com/inbde (accessed February 2024).
Wei J, Wang X, Schuurmans D et al. Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models. 2023. Available at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2201.11903 (accessed February 2024).
Joint Commission on National Dental Examinations. Integrated National Board Dental Examination 2024 Candidate Guide. 2024. Available at https://jcnde.ada.org/-/media/project/ada-organization/ada/jcnde/files/inbde_guide.pdf?rev=f50ad911104c40d7b5cf9497311e0a78&hash=F95A720E35BAE32EACDD59C0E4E0CED8 (accessed February 2024).
Dang A. Winning the Adversarial Battle with Open-Source AI Models. 2023. Available at https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=4651571 (accessed February 2024).
Naveed H, Khan A U, Qiu S et al. A Comprehensive Overview of Large Language Models. 2024. Available at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2307.06435 (accessed February 2024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Camila Tussie and Abraham Starosta ideated the study; Camila Tussie wrote the manuscript; Abraham Starosta conducted the data analysis; Camila Tussie and Abraham Starosta critically reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors have no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, to disclose.
Given how no human subjects were included in this study and no identifying information was used from publicly acquired question banks, institutional review board approval and consent was not necessary.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tussie, C., Starosta, A. Comparing the dental knowledge of large language models. Br Dent J (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-024-8015-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-024-8015-2
This article is cited by
-
Machine learning in dentistry and oral surgery: charting the course with bibliometric insights
Head & Face Medicine (2025)
-
Performance of large language models (ChatGPT4-0, Grok2 and Gemini) in UK dentistry and dental hygiene and therapy assessments
British Dental Journal (2025)
-
Large language models’ capabilities in responding to tuberculosis medical questions: testing ChatGPT, Gemini, and Copilot
Scientific Reports (2025)