Abstract
Background
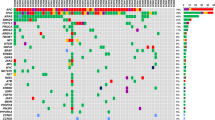
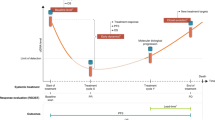
Circulating tumor DNA variations (∆ctDNA) were reported to be associated with treatment efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). The present study evaluated ∆ctDNA according to first-line treatment intensity.
Methods
Patients from two prospective ctDNA collections were divided into Group ≤ 2 drugs and Group ≥ 3 drugs. ∆ctDNA were analysed from baseline to cycle 3 or 4 (C3-4) according to three predefined subgroups: ∆ctDNA ≥ 80%_ undetectable, ∆ctDNA ≥ 80%_ detectable, and ∆ctDNA < 80%. Impact of ∆ctDNA on progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were analysed.
Results
Pretreatment ctDNA was detected in 129/152 (84.9%) of patients. A ∆ctDNA ≥ 80%_undetectable was more frequent in Group ≥ 3 than ≤ 2 drugs (respectively 51.5% vs. 32.7%, p = 0.015). Patients with ∆ctDNA ≥ 80%_undetectable had longer survival than other ∆ctDNA subgroups, in Group ≥ 3 drugs (mPFS 11.5 vs 7.8 vs 6.3 months, p = 0.02: mOS 30.2 vs 18.1 vs 16.4 month, p = 0.04) and in Group ≤ 2 drugs (mPFS 8.4 vs 6.0 vs 5.3 months, p = 0.05; mOS 29.6 vs 14.6 vs 14.6 months, p = 0.007).
Discussion
Early ∆ctDNA are associated to treatment intensity in first line mCRC with a significant impact on prognosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in the current study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.
Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Adam R, Sobrero A, Van Krieken JH, Aderka D, et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. 2016;27:1386–422.
Heinemann V, von Weikersthal LF, Decker T, Kiani A, Vehling-Kaiser U, Al-Batran SE, et al. FOLFIRI plus cetuximab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (FIRE-3): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:1065–75.
Venook AP, Niedzwiecki D, Lenz HJ, Innocenti F, Fruth B, Meyerhardt JA, et al. Effect of First-Line Chemotherapy Combined With Cetuximab or Bevacizumab on Overall Survival in Patients With KRAS Wild-Type Advanced or Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. JAMA. 2017;317:2392–401.
Cremolini C, Antoniotti C, Rossini D, Lonardi S, Loupakis F, Pietrantonio F, et al. Upfront FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab and reintroduction after progression versus mFOLFOX6 plus bevacizumab followed by FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab in the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (TRIBE2): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:497–507.
Falcone A, Ricci S, Brunetti I, Pfanner E, Allegrini G, Barbara C, et al. Phase III trial of infusional fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan (FOLFOXIRI) compared with infusional fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan (FOLFIRI) as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: the Gruppo Oncologico Nord Ovest. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1670–6.
Cremolini C, Antoniotti C, Lonardi S, Aprile G, Bergamo F, Masi G, et al. Activity and Safety of Cetuximab Plus Modified FOLFOXIRI Followed by Maintenance With Cetuximab or Bevacizumab for RAS and BRAF Wild-type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Randomized Phase 2 Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:529–36.
Loupakis F, Cremolini C, Masi G, Lonardi S, Zagonel V, Salvatore L, et al. Initial therapy with FOLFOXIRI and bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1609–18.
Crowley E, Di Nicolantonio F, Loupakis F, Bardelli A. Liquid biopsy: monitoring cancer-genetics in the blood. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10:472–84.
Bardelli A, Pantel K. Liquid Biopsies, What We Do Not Know (Yet). Cancer Cell. 2017;31:172–9.
El Messaoudi S, Rolet F, Mouliere F, Thierry AR. Circulating cell free DNA: Preanalytical considerations. Clin Chim Acta Int J Clin Chem. 2013;424:222–30.
Jung M, Klotzek S, Lewandowski M, Fleischhacker M, Jung K. Changes in concentration of DNA in serum and plasma during storage of blood samples. Clin Chem. 2003;49:1028–9.
Diaz LA, Bardelli A. Liquid biopsies: genotyping circulating tumor DNA. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2014;32:579–86.
Diehl F, Schmidt K, Choti MA, Romans K, Goodman S, Li M, et al. Circulating mutant DNA to assess tumor dynamics. Nat Med. 2008;14:985–90.
Spindler KLG, Pallisgaard N, Vogelius I, Jakobsen A. Quantitative cell-free DNA, KRAS, and BRAF mutations in plasma from patients with metastatic colorectal cancer during treatment with cetuximab and irinotecan. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2012;18:1177–85.
El Messaoudi S, Mouliere F, Du Manoir S, Bascoul-Mollevi C, Gillet B, Nouaille M, et al. Circulating DNA as a Strong Multimarker Prognostic Tool for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patient Management Care. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2016;22:3067–77.
Parikh AR, Mojtahed A, Schneider JL, Kanter K, Van Seventer EE, Fetter IJ, et al. Serial ctDNA Monitoring to Predict Response to Systemic Therapy in Metastatic Gastrointestinal Cancers. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2020;26:1877–85.
Tabernero J, Lenz HJ, Siena S, Sobrero A, Falcone A, Ychou M, et al. Analysis of circulating DNA and protein biomarkers to predict the clinical activity of regorafenib and assess prognosis in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective, exploratory analysis of the CORRECT trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:937–48.
Tie J, Kinde I, Wang Y, Wong HL, Roebert J, Christie M, et al. Circulating tumor DNA as an early marker of therapeutic response in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. 2015;26:1715–22.
Garlan F, Laurent-Puig P, Sefrioui D, Siauve N, Didelot A, Sarafan-Vasseur N, et al. Early Evaluation of Circulating Tumor DNA as Marker of Therapeutic Efficacy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients (PLACOL Study). Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2017;23:5416–25.
Sefrioui D, Beaussire L, Gillibert A, Blanchard F, Toure E, Bazille C, et al. CEA, CA19-9, circulating DNA and circulating tumour cell kinetics in patients treated for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Br J Cancer. 2021;125:725–33.
Kim S, Lim Y, Kang JK, Kim HP, Roh H, Kim SY, et al. Dynamic changes in longitudinal circulating tumour DNA profile during metastatic colorectal cancer treatment. Br J Cancer. 2022;127:898–907.
Prewett MC, Hooper AT, Bassi R, Ellis LM, Waksal HW, Hicklin DJ. Enhanced antitumor activity of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody IMC-C225 in combination with irinotecan (CPT-11) against human colorectal tumor xenografts. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2002;8:994–1003.
Raymond E, Faivre S, Chaney S, Woynarowski J, Cvitkovic E. Cellular and molecular pharmacology of oxaliplatin. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002;1:227–35.
Prewett M, Deevi DS, Bassi R, Fan F, Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ, et al. Tumors established with cell lines selected for oxaliplatin resistance respond to oxaliplatin if combined with cetuximab. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2007;13:7432–40.
Pantel K, Alix-Panabières C. Liquid biopsy and minimal residual disease - latest advances and implications for cure. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019;16:409–24.
Bettegowda C, Sausen M, Leary RJ, Kinde I, Wang Y, Agrawal N, et al. Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA in Early- and Late-Stage Human Malignancies. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:224ra24.
Bachet JB, Bouché O, Taieb J, Dubreuil O, Garcia ML, Meurisse A, et al. RAS mutation analysis in circulating tumor DNA from patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: the AGEO RASANC prospective multicenter study. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. 2018;29:1211–9.
Dasari A, Morris VK, Allegra CJ, Atreya C, Benson AB, Boland P, et al. ctDNA applications and integration in colorectal cancer: an NCI Colon and Rectal-Anal Task Forces whitepaper. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020;17:757–70.
Martini G, Ciardiello D, Famiglietti V, Rossini D, Antoniotti C, Troiani T, et al. Cetuximab as third-line rechallenge plus either irinotecan or avelumab is an effective treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer patients with baseline plasma RAS/BRAF wild-type circulating tumor DNA: Individual patient data pooled analysis of CRICKET and CAVE trials. Cancer Med. 2023;12:9392–400.
Sartore-Bianchi A, Pietrantonio F, Lonardi S, Mussolin B, Rua F, Crisafulli G, et al. Circulating tumor DNA to guide rechallenge with panitumumab in metastatic colorectal cancer: the phase 2 CHRONOS trial. Nat Med. 2022;28:1612–8.
Funding
The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AGr FDF DS and VV wrote the manuscript. AGi, TC, EL, AGr, and FDF performed the statistical analysis. KBL, MPG, ALB, VB, CE, AGa, MD, DS and PM collected the data. AGr FDF and VV organized the data and performed the bibliography. LB and SNV performed the ctDNA analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This work combine data from two trials, registered on the clinicaltrials.gov website (No. NCT01212510 and NCT02872779), and approved by an ethic committee (Comité de Protection des Personnes Nord-Ouest 1, Rouen University, 76000 France). Each patient included in these two trials gave written consent. The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Grancher, A., Beaussire-Trouvay, L., Vernon, V. et al. ctDNA variations according to treatment intensity in first-line metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 132, 814–821 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-02971-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-02971-0
This article is cited by
-
Methylated ARHGAP40 DNA as a potential biomarker for early diagnosis in high-grade ovarian serous cancer
Journal of Ovarian Research (2025)