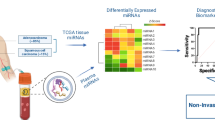
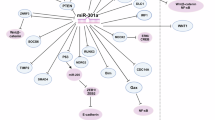
Abstract
Background
Circulating microRNAs (c-miRs) were shown to be effective biomarkers for lung cancer early detection. However, the understanding of c-miRs origin and their biological functions still remains elusive.
Methods
We analysed miRNA expression in a large panel of lung cancer (LC) and hematopoietic cell lines (N = 252; CCLE database) coupled with c-miR profile of a large cohort of serum samples (N = 975), from high-risk subjects underwent annual LD-CT for 5 years. Furthermore, we examined intracellular and extracellular miR-29a-3p/223-3p expression profile in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) tissues, in matched serum samples and in LC and stromal cell lines. Lastly, through the modulation of expression of selected c-miRs by using mimic (OE) or antisense microRNA (KD), we explored their impact on lung cancer transcriptome and cancer and immune phenotypes.
Results
Here, we investigated the origin of an extensively validated 13 c-miRs signature diagnostics for asymptomatic lung cancer (LC) in high-risk subjects (smokers, >20 packs/y; >50 y old). Overall, we found a mixed origin of these c-miRs, originating both from tumour cells and the tumour microenvironment (TME). Intriguingly, we revealed that circulating miR-29a-3p and miR-223-3p are abundantly released from LC epithelial cells and immune cells, respectively. In particular, we found that miR-223-3p triggered several lung cancer related phenotypes such as invasion, migration and tumour-promoting inflammation.
Conclusions
Our study highlights a mixed tumour epithelial and stroma-associated origin of LC c-miRs with new evidences on the multifaceted role of miR-223-3p in LC pathogenesis and immune modulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Raw Data of this study (Affymetrix data) can be found in Gene Expression Omnibus database with the following accession number: GSE271130.
References
Seijo LM, Peled N, Ajona D, Boeri M, Field JK, Sozzi G, et al. Biomarkers in lung cancer screening: achievements, promises, and challenges. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14:343–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2018.11.023.
Abdipourbozorgbaghi M, Vancura A, Radpour R, Haefliger S. Circulating miRNA panels as a novel non-invasive diagnostic, prognostic, and potential predictive biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Br J Cancer. 2024;131:1350–62. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-024-02831-3.
Asakura K, Kadota T, Matsuzaki J, Yoshida Y, Yamamoto Y, Nakagawa K, et al. A miRNA-based diagnostic model predicts resectable lung cancer in humans with high accuracy. Commun Biol. 2020;3:134 https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-0863-y.
Dama E, Colangelo T, Fina E, Cremonesi M, Kallikourdis M, Veronesi G, et al. Biomarkers and lung cancer early detection: state of the art. Cancers. 2021;13: https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153919.
Sozzi G, Boeri M, Rossi M, Verri C, Suatoni P, Bravi F, et al. Clinical utility of a plasma-based miRNA signature classifier within computed tomography lung cancer screening: a correlative MILD trial study. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:768–73. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.50.4357.
Montani F, Marzi MJ, Dezi F, Dama E, Carletti RM, Bonizzi G, et al. MiR-test: a blood test for lung cancer early detection. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107: https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djv063.
de Koning HJ, van der Aalst CM, de Jong PA, Scholten ET, Nackaerts K, Heuvelmans MA, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with volume CT screening in a randomized trial. N. Engl J Med. 2020;382:503–13. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1911793.
Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, Black WC, Clapp JD, Fagerstrom RM, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:395–409. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1102873.
Fortunato O, Borzi C, Milione M, Centonze G, Conte D, Boeri M, et al. Circulating mir‐320a promotes immunosuppressive macrophages M2 phenotype associated with lung cancer risk. Int J Cancer. 2019;144:2746–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31988.
Pritchard CC, Kroh E, Wood B, Arroyo JD, Dougherty KJ, Miyaji MM, et al. Blood cell origin of circulating microRNAs: a cautionary note for cancer biomarker studies. Cancer Prev Res. 2012;5:492–7. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-11-0370.
Thomou T, Mori MA, Dreyfuss JM, Konishi M, Sakaguchi M, Wolfrum C, et al. Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues. Nature. 2017;542:450–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21365.
Becker A, Thakur BK, Weiss JM, Kim HS, Peinado H, Lyden D. Extracellular vesicles in cancer: cell-to-cell mediators of metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:836–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.009.
Ghandi M, Huang FW, Jané-Valbuena J, Kryukov GV, Lo CC, McDonald ER, et al. Next-generation characterization of the cancer cell line encyclopedia. Nature. 2019;569:503–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1186-3.
Goedhart J, Luijsterburg MS. VolcaNoseR is a web app for creating, exploring, labeling and sharing volcano plots. Sci Rep. 2020;10:20560 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76603-3.
Jeffries J, Zhou W, Hsu AY, Deng Q. miRNA-223 at the crossroads of inflammation and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019;451:136–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.02.051.
Wang FF, Zhang XJ, Yan YR, Zhu XH, Yu J, Ding Y, et al. FBX8 is a metastasis suppressor downstream of miR-223 and targeting mTOR for degradation in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2017;388:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.11.031.
Lin G, Lin L, Lin H, Xu Y, Chen W, Liu Y, et al. C1QTNF6 regulated by miR‐29a-3p promotes proliferation and migration in stage I lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Pulm Med. 2022;22:285 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-022-02055-2.
Sun D, Wang C, Long S, Ma Y, Guo Y, Huang Z, et al. C/EBP-β-activated microRNA-223 promotes tumour growth through targeting RASA1 in human colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2015;112:1491–1500. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2015.107.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature. 2014;511:543–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13385.
Cai M, Zhao X, Cao M, Ma P, Chen M, Wu J, et al. T‐cell exhaustion interrelates with immune cytolytic activity to shape the inflamed tumor microenvironment. J Pathol. 2020;251:147–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5435.
Alvisi G, Brummelman J, Puccio S, Mazza EMC, Tomada EP, Losurdo A, et al. IRF4 instructs effector Treg differentiation and immune suppression in human cancer. J Clin Investig. 2020;130:3137–50. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI130426.
Nicolás-Ávila JÁ, Adrover JM, Hidalgo A. Neutrophils in homeostasis, immunity, and cancer. Immunity. 2017;46:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2016.12.012.
Melocchi V, Dama E, Mazzarelli F, Cuttano R, Colangelo T, Di Candia L, et al. Aggressive early-stage lung adenocarcinoma is characterized by epithelial cell plasticity with acquirement of stem-like traits and immune evasion phenotype. Oncogene. 2021;40:4980–91. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01909-z.
Dama E, Melocchi V, Dezi F, Pirroni S, Carletti RM, Brambilla D, et al. An aggressive subtype of stage I lung adenocarcinoma with molecular and prognostic characteristics typical of advanced lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:62–72. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-3005.
Melo SA, Sugimoto H, O’Connell JT, Kato N, Villanueva A, Vidal A, et al. Cancer exosomes perform cell-independent microRNA biogenesis and promote tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2014;26:707–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2014.09.005.
Le MTN, Hamar P, Guo C, Basar E, Perdigão-Henriques R, Balaj L, et al. miR-200-containing extracellular vesicles promote breast cancer cell metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:5109–28. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI75695.
Huang W, Yan Y, Liu Y, Lin M, Ma J, Zhang W, et al. Exosomes with low miR-34c-3p expression promote invasion and migration of non-small cell lung cancer by upregulating integrin α2β1. Sig Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:39 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-0133-y.
Ma L, Singh J, Schekman R. Two RNA-binding proteins mediate the sorting of miR223 from mitochondria into exosomes. ELife. 2023;12:e85878 https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.85878.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Teresa Nittoli for helping us in experiments setting up as well as Orazio Palumbo for Affymetrix experiments.
Funding
The research leading to these results has received funding from the Italian Ministry of Health [GR-2016-02363975 to FB; RF-2021-12372433 to F.B.; GR-2019-12370460 to TC] and from Fondazione AIRC per la Ricerca sul Cancro ETS [IG 2019—ID. 22827 project to FB; IG2024 – ID. 30689]. FM was a recipient of a fellowship (Italy Pre-Doc) from AIRC ETS (ID. 28243). MKA is a recipient of a fellowship (Italy Pre-Doc) from AIRC ETS (ID. 29714).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualisation: FB; methodology: TC, FM, RC, MKA, RMP, VM, ED, PG, FB; investigation: TC, FM, RC, RMP, VM, FB; visualisation: TC, FM, VM, FB; supervision: FB; writing (original draft): FB; writing (review and editing): TC, RC, FB.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The study funders had no role in the design of the study, the collection, analysis and interpretation of the data, the writing of the manuscript and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Study was approved by internal IRB at IRCCS Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza Hospital (protocol name: BIOPOLMONE v1.0_08 Giu 16). Patients signed an informed consent in accordance with the Helsinki’s declaration.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Colangelo, T., Mazzarelli, F., Cuttano, R. et al. Unveiling the origin and functions of diagnostic circulating microRNAs in lung cancer. Br J Cancer 132, 947–956 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-02982-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-02982-x