Abstract
Background
Adherence to imatinib may be even more limited in the adjuvant setting, as patients receiving adjuvant imatinib often do not experience disease symptoms after tumor removal. This real-world study aimed to gain insight into adherence to imatinib and the effect of adherence on treatment outcomes.
Methods
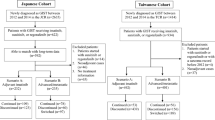
Postoperative GIST patients who visited the speciality clinic between January 2021 and September 2024 were included in the study.
Results
Out of 143 patients, 45 were non-adherent. The restricted mean survival time (RMST) at 3 years was measured for progression-free survival (PFS). Non-adherent patients had an RMST of 24.65 months, whereas adherent patients had an RMST of 32.66 months (P < 0.05). In addition, the plasma trough concentration of imatinib (Cmin) was lower in non-adherent patients than in adherent patients (737.68 vs. 1404.45 ng/mL, P < 0.05). Using therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) as an objective measurement to assess adherence, Cmin of 1211.50 ng/mL could be the optimal cutoff value to predict the risk of non-adherence.
Conclusions
Poor adherence to imatinib was a notable problem in postoperative adjuvant treatment and appeared to be associated with shorter PFS. Monitoring trough levels gives physicians an objective measurement to assess individual adherence and can support treatment decisions.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Casali PG, Blay JY, Abecassis N, Bajpai J, Bauer S, Biagini R, et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: ESMO-EURACAN-GENTURIS Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol. 2022;33:20–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2021.09.005
Rustgi SD, McKinley M, McBay B, Zylberberg HM, Gomez SL, Hur C, et al. Epidemiology of gastric malignancies 2000-2018 according to histology: a population-based analysis of incidence and temporal trends. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;21:3285–95.e3288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2023.01.037
Blay JY, Kang YK, Nishida T, von Mehren M. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2021;7:22 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-021-00254-5
Joensuu H, Eriksson M, Sundby Hall K, Hartmann JT, Pink D, Schütte J, et al. One vs three years of adjuvant imatinib for operable gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2012;307:1265–72. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012.347
von Mehren M, Kane JM, Riedel RF, Sicklick JK, Pollack SM, Agulnik M, et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors, Version 2.2022. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2022;20:1204–14. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2022.0058
Wang Y, Zhang P, Han Y, Nelson RS, McLeod HL, Tao K, et al. Adherence to adjuvant imatinib therapy in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor in clinical practice: a cross-sectional study. Chemotherapy. 2019;64:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1159/000505177
Kang S, Ryu MH, Bang YH, Kim HD, Lee HE, Kang YK. Adjuvant imatinib treatment for 5 years versus 3 years in patients with ruptured localized gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a retrospective analysis. Cancer Res Treat. 2022;54:1167–74. https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2021.1040
Blay JY, Le Cesne A, Ray-Coquard I, Bui B, Duffaud F, Delbaldo C, et al. Prospective multicentric randomized phase III study of imatinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors comparing interruption versus continuation of treatment beyond 1 year: the French Sarcoma Group. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1107–13. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2006.09.0183
Le Cesne A, Ray-Coquard I, Bui BN, Adenis A, Rios M, Bertucci F, et al. Discontinuation of imatinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours after 3 years of treatment: an open-label multicentre randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:942–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(10)70222-9
von Mehren M, Widmer N. Correlations between imatinib pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, adherence, and clinical response in advanced metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): an emerging role for drug blood level testing? Cancer Treat Rev. 2011;37:291–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.10.001
Liu M, Guo T, Ma Z, Du L, Hou J, Tian Y, et al. Correlation between N-demethyl imatinib trough concentration and serious adverse reactions in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a retrospective cohort study. Ther Drug Monitor. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1097/ftd.0000000000001160
Teranishi R, Takahashi T, Nishida T, Kurokawa Y, Nakajima K, Koh M, et al. Plasma trough concentration of imatinib and its effect on therapeutic efficacy and adverse events in Japanese patients with GIST. Int J Clin Oncol. 2023;28:680–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-023-02325-x
Clarke WA, Chatelut E, Fotoohi AK, Larson RA, Martin JH, Mathijssen RHJ, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring in oncology: International Association of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology consensus guidelines for imatinib therapy. Eur J Cancer. 2021;157:428–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2021.08.033
Guilhot F, Hughes TP, Cortes J, Druker BJ, Baccarani M, Gathmann I, et al. Plasma exposure of imatinib and its correlation with clinical response in the tyrosine kinase inhibitor optimization and selectivity trial. Haematologica. 2012;97:731–8. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2011.045666
Skaali T, Blomhoff R, Lindemann K, Smeland S, Bruheim K, Seland M, et al. Self-reported distress and problems after treatment for gynecological cancer - Correlation between a short screening tool and longer measures of anxiety/depression and health-related quality of life. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2024;103:387–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/aogs.14709
Baba N, Schrage T, Hartmann A, Baba K, Wuensch A, Schultze-Seemann W, et al. Mental distress and need for psychosocial support in prostate cancer patients: an observational cross-sectional study. Int J psychiatry Med. 2021;56:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091217420938896
Spoelstra SL, Rittenberg CN. Assessment and measurement of medication adherence: oral agents for cancer. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2015;19:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1188/15.S1.Cjon.47-52
Byerly MJ, Nakonezny PA, Rush AJ. The Brief Adherence Rating Scale (BARS) validated against electronic monitoring in assessing the antipsychotic medication adherence of outpatients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Schizophr Res. 2008;100:60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2007.12.470
Allard NL, MacLachlan JH, Dev A, Dwyer J, Srivatsa G, Spelman T, et al. Adherence in chronic hepatitis B: associations between medication possession ratio and adverse viral outcomes. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020;20:140. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-020-01219-w
Wako Z, Mengistu D, Dinegde NG, Asefa T, Wassie M. Adherence to adjuvant hormonal therapy and associated factors among women with breast cancer attending the Tikur Anbessa Specialized Hospital, Addis Ababa Ethiopia, 2019: a cross-sectional study. Breast Cancer. 2021;13:383–92. https://doi.org/10.2147/bctt.S311445
Middendorff G, Elsey R, Lounsbery B, Chadwell R. Impact of a specialty pharmacy case management service on adherence in patients receiving oral antineoplastic agents. J Oncol Pharm Pract: Off Publ Int Soc Oncol Pharm Practitioners. 2018;24:371–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078155217708022
Seal BS, Anderson S, Shermock KM. Factors associated with adherence rates for oral and intravenous anticancer therapy in commercially insured patients with metastatic colon cancer. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016;22:227–35. https://doi.org/10.18553/jmcp.2016.22.3.227
Tan X, Marshall VD, Anderson RT, Donohoe J, Camacho F, Balkrishnan R. Adjuvant therapy use among Appalachian breast cancer survivors. Medicine. 2015;94:e1071. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000001071
Nakonezny PA, Lindow JC, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, et al. A single assessment with the Brief Adherence Rating Scale (BARS) discriminates responders to long-acting injectable antipsychotic treatment in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2020;220:92–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2020.03.053
Eechoute K, Fransson MN, Reyners AK, de Jong FA, Sparreboom A, van der Graaf WT, et al. A long-term prospective population pharmacokinetic study on imatinib plasma concentrations in GIST patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:5780–7. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-12-0490
Roth O, Spreux-Varoquaux O, Bouchet S, Rousselot P, Castaigne S, Rigaudeau S, et al. Imatinib assay by HPLC with photodiode-array UV detection in plasma from patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: comparison with LC-MS/MS. Clin Chim Acta. 2010;411:140–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2009.10.007
FDA Bioanalytical method validation guidance for industry. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/bioanalytical-method-validation-guidance-industry (2018).
Qu WZ, Wang L, Chen JJ, Wang Y. Raf kinase inhibitor protein combined with phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase offers valuable prognosis in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. World J Gastroenterol. 2023;29:4200–13. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i26.4200
Han K, Jung I. Restricted mean survival time for survival analysis: a quick guide for clinical researchers. Korean J Radiol. 2022;23:495–9. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2022.0061
Chang PW, Newman TB. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves: the basics and beyond. Hosp Pediatr. 2024;14:e330–4. https://doi.org/10.1542/hpeds.2023-007462
Sun Y, Yue L, Xu P, Hu W. An overview of agents and treatments for PDGFRA-mutated gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Front Oncol. 2022;12:927587. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.927587
Guérit E, Arts F, Dachy G, Boulouadnine B, Demoulin JB. PDGF receptor mutations in human diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78:3867–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03753-y
Mueller-Schoell A, Groenland SL, Scherf-Clavel O, van Dyk M, Huisinga W, Michelet R, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring of oral targeted antineoplastic drugs. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2021;77:441–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-020-03014-8
Groenland SL, van Eerden RAG, Westerdijk K, Meertens M, Koolen SLW, Moes D, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring-based precision dosing of oral targeted therapies in oncology: a prospective multicenter study. Ann Oncol. 2022;33:1071–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2022.06.010
Demetri GD, Wang Y, Wehrle E, Racine A, Nikolova Z, Blanke CD, et al. Imatinib plasma levels are correlated with clinical benefit in patients with unresectable/metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3141–7. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2008.20.4818
Bouchet S, Poulette S, Titier K, Moore N, Lassalle R, Abouelfath A, et al. Relationship between imatinib trough concentration and outcomes in the treatment of advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours in a real-life setting. Eur J Cancer. 2016;57:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2015.12.029
NS IJ, Groenland SL, Koenen AM, Kerst M, van der Graaf WTA, Rosing H, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring of imatinib in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumours - Results from daily clinical practice. Eur J Cancer. 2020;136:140–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2020.05.025
Lankheet NA, Knapen LM, Schellens JH, Beijnen JH, Steeghs N, Huitema AD. Plasma concentrations of tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib, erlotinib, and sunitinib in routine clinical outpatient cancer care. Ther Drug Monit. 2014;36:326–34. https://doi.org/10.1097/ftd.0000000000000004
Larson RA, Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Riviere GJ, Krahnke T, et al. Imatinib pharmacokinetics and its correlation with response and safety in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: a subanalysis of the IRIS study. Blood. 2008;111:4022–8. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-10-116475
Groenland EH, Dasgupta I, Visseren FLJ, van der Elst KCM, Lorde N, Lawson AJ, et al. Clinical characteristics do not reliably identify non-adherence in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Blood Press. 2022;31:178–86. https://doi.org/10.1080/08037051.2022.2104215
Groenland EH, van Kleef M, Bots ML, Visseren FLJ, van der Elst KCM, Spiering W. Plasma trough concentrations of antihypertensive drugs for the assessment of treatment adherence: a meta-analysis. Hypertension. 2021;77:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.120.16061
Ramachandiran B, Dubashi B, Kayal S, Menon V, Yuvaraj K, Deepika C, et al. Assessment of oral anticancer medication adherence: a survey from a tertiary cancer center. South Asian J Cancer. 2021;10:127–30. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1723120
Leporini C, De Sarro G, Russo E. Adherence to therapy and adverse drug reactions: is there a link? Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014;13(Suppl 1):S41–55. https://doi.org/10.1517/14740338.2014.947260
Marin D, Bazeos A, Mahon FX, Eliasson L, Milojkovic D, Bua M, et al. Adherence is the critical factor for achieving molecular responses in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia who achieve complete cytogenetic responses on imatinib. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2381–8. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2009.26.3087
Donovan KA, Grassi L, McGinty HL, Jacobsen PB. Validation of the distress thermometer worldwide: state of the science. Psychooncology. 2014;23:241–50. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.3430
Zhang P, Zhang J, Zhang B, Yang WC, Hu JB, Sun XF. et al.[Adherence to adjuvant 514 with therapy imatinib in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a national multi-center cross515 sectional study]. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;24:775–82.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the dedicated staff at the Department of Pharmacy and Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University for their valuable work.
Funding
This research was supported by the Clinical Research Program of Zhejiang Medical Doctors Association (No. YS2022-2-006) and the Program of Zhejiang Provincial Medical and Health Science and Technology Plan (No. 2020KY813).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Hongbin Xu; Methodology: Tao Xu; Formal analysis and investigation: Chenrui Jiang, Suyan Zhu; Writing - original draft preparation: Tao Xu; Writing - review and editing: Tao Xu, Zhilong Yan; Funding acquisition: Tao Xu, Jianming Xie; Resources: Jianming Xie; Supervision: Hongbin Xu. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University (NO.2023043A-03) and was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was waived by our Institutional Review Board because of the retrospective nature of our study. Clinical trial registration: ChiCTR2300075731.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, T., Xie, J., Jiang, C. et al. Unveiling the impact of adherence: imatinib plasma levels and survival in postoperative gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) patients. Br J Cancer 133, 1307–1316 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-03173-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-03173-4