Abstract
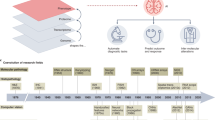
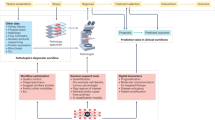
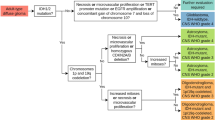
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming histologic assessment, evolving from a diagnostic adjunct to an integral component of clinical decision-making. Over the past decade, AI applications have significantly advanced histopathology, facilitating tasks from tissue classification to predicting cancer prognosis, gene alterations, and therapy responses. These developments are supported by the availability of high-quality whole-slide images (WSIs) and publicly accessible databases like The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), which integrate histologic, genomic, and clinical data. Deep learning techniques replicate and enhance pathologists’ decisions, addressing challenges such as inter-observer variability and diagnostic reproducibility. Moreover, AI enables robust predictions of patient prognosis, actionable gene statuses, and therapy responses, offering rapid, cost-effective alternatives to conventional methods. Innovations such as histomorphologic phenotype clusters and spatial transcriptomics have further refined cancer stratification and treatment personalization. In addition, multimodal approaches integrating histologic images with clinical and molecular data have achieved superior predictive accuracy and explainability. Nevertheless, challenges remain in verifying AI predictions, particularly for prognostic applications and ensuring accessibility in resource-limited settings. Addressing these challenges will require standardized datasets, ethical frameworks, and scalable infrastructure. While AI is revolutionizing histologic assessment for cancer diagnosis and treatment, optimizing digital infrastructure and long-term strategies is essential for its widespread adoption in clinical practice.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Change history
31 October 2025
The original online version of this article was revised: In this article the author’s name Manabu Takamatsu was incorrectly written as Takamatsu Manabu.
04 November 2025
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-03255-3
References
Echle A, Rindtorff NT, Brinker TJ, Luedde T, Pearson AT, Kather JN. Deep learning in cancer pathology: a new generation of clinical biomarkers. Br J Cancer. 2021;124:686–96.
Perincheri S, Levi AW, Celli R, Gershkovich P, Rimm D, Morrow JS, et al. An independent assessment of an artificial intelligence system for prostate cancer detection shows strong diagnostic accuracy. Mod Pathol. 2021;34:1588–95.
Wei JW, Tafe LJ, Linnik YA, Vaickus LJ, Tomita N, Hassanpour S. Pathologist-level classification of histologic patterns on resected lung adenocarcinoma slides with deep neural networks. Sci Rep. 2019;9:3358.
Haggenmüller S, Wies C, Abels J, Winterstein JT, Heinlein L, Nogueira Garcia C, et al. Discordance, accuracy and reproducibility study of pathologists’ diagnosis of melanoma and melanocytic tumors. Nat Commun. 2025;16:789.
Marrón-Esquivel JM, Duran-Lopez L, Linares-Barranco A, Dominguez-Morales JP. A comparative study of the inter-observer variability on Gleason grading against Deep Learning-based approaches for prostate cancer. Comput Biol Med. 2023;159:106856.
Tomczak K, Czerwińska P, Wiznerowicz M. The cancer genome atlas (TCGA): an immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2015;19:A68–77.
Grossman RL, Heath AP, Ferretti V, Varmus HE, Lowy DR, Kibbe WA, et al. Toward a shared vision for cancer genomic data. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1109–12.
Alam MR, Seo KJ, Abdul-Ghafar J, Yim K, Lee SH, Jang HJ, et al. Recent application of artificial intelligence on histopathologic image-based prediction of gene mutation in solid cancers. Brief Bioinform. 2023;24:1–26.
Davri A, Birbas E, Kanavos T, Ntritsos G, Giannakeas N, Tzallas AT, et al. Deep learning for lung cancer diagnosis, prognosis and prediction using histological and cytological images: a systematic review. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15:3981.
Ding H, Feng Y, Huang X, Xu J, Zhang T, Liang Y, et al. Deep learning-based classification and spatial prognosis risk score on whole-slide images of lung adenocarcinoma. Histopathology. 2023;83:211–28.
Urabe A, Adachi M, Sakamoto N, Kojima M, Ishikawa S, Ishii G, et al. Deep learning detected histological differences between invasive and non-invasive areas of early esophageal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2024 https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.16426.
Tagami M, Nishio M, Yoshikawa A, Misawa N, Sakai A, Haruna Y, et al. Artificial intelligence-based differential diagnosis of orbital MALT lymphoma and IgG4 related ophthalmic disease using hematoxylin-eosin images. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024;262:3355–66.
Calderaro J, Ghaffari Laleh N, Zeng Q, Maille P, Favre L, Pujals A, et al. Deep learning-based phenotyping reclassifies combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Commun. 2023;14:8290.
Polónia A, Campelos S, Ribeiro A, Aymore I, Pinto D, Biskup-Fruzynska M, et al. Artificial intelligence improves the accuracy in histologic classification of breast lesions. Am J Clin Pathol. 2021;155:527–36.
Angeloni M, van Doeveren T, Lindner S, Volland P, Schmelmer J, Foersch S, et al. A deep-learning workflow to predict upper tract urothelial carcinoma protein-based subtypes from H&E slides supporting the prioritization of patients for molecular testing. J Pathol Clin Res. 2024;10:e12369.
Patkar S, Harmon S, Sesterhenn I, Lis R, Merino M, Young D, et al. A selective CutMix approach improves generalizability of deep learning-based grading and risk assessment of prostate cancer. J Pathol Inf. 2024;15:100381.
Takamatsu M, Yamamoto N, Kawachi H, Nakano K, Saito S, Fukunaga Y, et al. Prediction of lymph node metastasis in early colorectal cancer based on histologic images by artificial intelligence. Sci Rep. 2022;12:2963.
Hayashi K, Ono Y, Takamatsu M, Oba A, Ito H, Sato T, et al. Prediction of recurrence pattern of pancreatic cancer post-pancreatic surgery using histology-based supervised machine learning algorithms: a single-center retrospective study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-022-11471-x.
Zadeh Shirazi A, Fornaciari E, Bagherian NS, Ebert LM, Koszyca B, Gomez GA. DeepSurvNet: deep survival convolutional network for brain cancer survival rate classification based on histopathological images. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2020;58:1031–45.
Bychkov D, Linder N, Turkki R, Nordling S, Kovanen PE, Verrill C, et al. Deep learning based tissue analysis predicts outcome in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 2018;8:3395.
Skrede OJ, De Raedt S, Kleppe A, Hveem TS, Liestøl K, Maddison J, et al. Deep learning for prediction of colorectal cancer outcome: a discovery and validation study. Lancet. 2020;395:350–60.
Wessels F, Schmitt M, Krieghoff-Henning E, Kather JN, Nientiedt M, Kriegmair MC, et al. Deep learning can predict survival directly from histology in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2022;17:e0272656.
Klimov S, Miligy IM, Gertych A, Jiang Y, Toss MS, Rida P, et al. A whole slide image-based machine learning approach to predict ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) recurrence risk. Breast Cancer Res. 2019;21:83.
Wulczyn E, Steiner DF, Xu Z, Sadhwani A, Wang H, Flament-Auvigne I, et al. Deep learning-based survival prediction for multiple cancer types using histopathology images. PLoS One. 2020;15:e0233678.
Kather JN, Krisam J, Charoentong P, Luedde T, Herpel E, Weis CA, et al. Predicting survival from colorectal cancer histology slides using deep learning: A retrospective multicenter study. PLoS Med. 2019;16:e1002730.
Foersch S, Eckstein M, Wagner DC, Gach F, Woerl AC, Geiger J, et al. Deep learning for diagnosis and survival prediction in soft tissue sarcoma. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:1178–87.
Sun Q, Li T, Wei Z, Ye Z, Zhao X, Jing J. Integrating transcriptomic data and digital pathology for NRG-based prediction of prognosis and therapy response in gastric cancer. Ann Med. 2024;56:2426758.
Markowski MC, Ren Y, Tierney M, Royce TJ, Yamashita R, Croucher D, et al. Digital pathology-based artificial intelligence biomarker validation in metastatic prostate cancer. Eur Urol Oncol. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euo.2024.11.009.
Chen S, Xiang J, Wang X, Zhang J, Yang S, Yang W, et al. Deep learning-based pathology signature could reveal lymph node status and act as a novel prognostic marker across multiple cancer types. Br J Cancer. 2023;129:46–53.
Mobadersany P, Yousefi S, Amgad M, Gutman DA, Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Velázquez Vega JE, et al. Predicting cancer outcomes from histology and genomics using convolutional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E2970–e2979.
Roetzer-Pejrimovsky T, Nenning KH, Kiesel B, Klughammer J, Rajchl M, Baumann B, et al. Deep learning links localized digital pathology phenotypes with transcriptional subtype and patient outcome in glioblastoma. Gigascience. 2024;13:giae057.
Turkki R, Byckhov D, Lundin M, Isola J, Nordling S, Kovanen PE, et al. Breast cancer outcome prediction with tumour tissue images and machine learning. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019;177:41–52.
Jang HJ, Lee A, Kang J, Song IH, Lee SH. Prediction of clinically actionable genetic alterations from colorectal cancer histopathology images using deep learning. World J Gastroenterol. 2020;26:6207–23.
Kather JN, Heij LR, Grabsch HI, Loeffler C, Echle A, Muti HS, et al. Pan-cancer image-based detection of clinically actionable genetic alterations. Nat Cancer. 2020;1:789–99.
Tsou P, Wu CJ. Mapping driver mutations to histopathological subtypes in papillary thyroid carcinoma: applying a deep convolutional neural network. J Clin Med. 2019;8:1675.
Terada Y, Takahashi T, Hayakawa T, Ono A, Kawata T, Isaka M, et al. Artificial intelligence-powered prediction of ALK gene rearrangement in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. JCO Clin Cancer Inf. 2022;6:e2200070.
Shamai G, Livne A, Polónia A, Sabo E, Cretu A, Bar-Sela G, et al. Deep learning-based image analysis predicts PD-L1 status from H&E-stained histopathology images in breast cancer. Nat Commun. 2022;13:6753.
Park JH, Lim JH, Kim S, Kim CH, Choi JS, Lim JH, et al. Deep learning-based analysis of EGFR mutation prevalence in lung adenocarcinoma H&E whole slide images. J Pathol Clin Res. 2024;10:e70004.
Echle A, Grabsch HI, Quirke P, van den Brandt PA, West NP, Hutchins GGA, et al. Clinical-Grade Detection of Microsatellite Instability in Colorectal Tumors by Deep Learning. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1406–1416.e1411.
Kather JN, Pearson AT, Halama N, Jager D, Krause J, Loosen SH, et al. Deep learning can predict microsatellite instability directly from histology in gastrointestinal cancer. Nat Med. 2019;25:1054–6.
Tsai PC, Lee TH, Kuo KC, Su FY, Lee TM, Marostica E, et al. Histopathology images predict multi-omics aberrations and prognoses in colorectal cancer patients. Nat Commun. 2023;14:2102.
Zeng H, Chen L, Zhang M, Luo Y, Ma X. Integration of histopathological images and multi-dimensional omics analyses predicts molecular features and prognosis in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2021;163:171–80.
Coudray N, Ocampo PS, Sakellaropoulos T, Narula N, Snuderl M, Fenyö D, et al. Classification and mutation prediction from non-small cell lung cancer histopathology images using deep learning. Nat Med. 2018;24:1559–67.
Yang Y, Yang J, Liang Y, Liao B, Zhu W, Mo X, et al. Identification and Validation of Efficacy of Immunological Therapy for Lung Cancer From Histopathological Images Based on Deep Learning. Front Genet. 2021;12:642981.
Fremond S, Andani S, Barkey Wolf J, Dijkstra J, Melsbach S, Jobsen JJ, et al. Interpretable deep learning model to predict the molecular classification of endometrial cancer from haematoxylin and eosin-stained whole-slide images: a combined analysis of the PORTEC randomised trials and clinical cohorts. Lancet Digit Health. 2023;5:e71–e82.
Zhao Y, Xiong S, Ren Q, Wang J, Li M, Yang L, et al. Deep learning using histological images for gene mutation prediction in lung cancer: a multicentre retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2024 https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(24)00599-0.
Tan X, Li Y, Wang S, Xia H, Meng R, Xu J, et al. Predicting EGFR mutation, ALK rearrangement, and uncommon EGFR mutation in NSCLC patients by driverless artificial intelligence: a cohort study. Respir Res. 2022;23:132.
Mayer C, Ofek E, Fridrich DE, Molchanov Y, Yacobi R, Gazy I, et al. Direct identification of ALK and ROS1 fusions in non-small cell lung cancer from hematoxylin and eosin-stained slides using deep learning algorithms. Mod Pathol. 2022;35:1882–7.
Pizurica M, Zheng Y, Carrillo-Perez F, Noor H, Yao W, Wohlfart C, et al. Digital profiling of gene expression from histology images with linearized attention. Nat Commun. 2024;15:9886.
Chen M, Zhang B, Topatana W, Cao J, Zhu H, Juengpanich S, et al. Classification and mutation prediction based on histopathology H&E images in liver cancer using deep learning. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2020;4:14.
Loeffler CML, Ortiz Bruechle N, Jung M, Seillier L, Rose M, Laleh NG, et al. Artificial intelligence-based detection of FGFR3 mutational status directly from routine histology in bladder cancer: a possible preselection for molecular testing?. Eur Urol Focus. 2022;8:472–9.
Velmahos CS, Badgeley M, Lo YC. Using deep learning to identify bladder cancers with FGFR-activating mutations from histology images. Cancer Med. 2021;10:4805–13.
Kim J, Ko S, Kim M, Park NJ, Han H, Cho J, et al. Deep learning prediction of tert promoter mutation status in thyroid cancer using histologic images. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;59:536.
Pareja F, Dopeso H, Wang YK, Gazzo AM, Brown DN, Banerjee M, et al. A genomics-driven artificial intelligence-based model classifies breast invasive lobular carcinoma and discovers cdh1 inactivating mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2024;84:3478–89.
Wang X, Zou C, Zhang Y, Li X, Wang C, Ke F, et al. Prediction of BRCA gene mutation in breast cancer based on deep learning and histopathology images. Front Genet. 2021;12:661109.
Bourgade R, Rabilloud N, Perennec T, Pécot T, Garrec C, Guédon AF, et al. Deep learning for detecting BRCA mutations in high-grade ovarian cancer based on an innovative tumor segmentation method from whole slide images. Mod Pathol. 2023;36:100304.
Ekholm A, Wang Y, Vallon-Christersson J, Boissin C, Rantalainen M. Prediction of gene expression-based breast cancer proliferation scores from histopathology whole slide images using deep learning. BMC Cancer. 2024;24:1510.
Milewski D, Jung H, Brown GT, Liu Y, Somerville B, Lisle C, et al. Predicting molecular subtype and survival of rhabdomyosarcoma patients using deep learning of H&E images: a report from the children’s oncology group. Clin Cancer Res. 2023;29:364–78.
Liu S, Shah Z, Sav A, Russo C, Berkovsky S, Qian Y, et al. Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) status prediction in histopathology images of gliomas using deep learning. Sci Rep. 2020;10:7733.
Howard FM, Hieromnimon HM, Ramesh S, Dolezal J, Kochanny S, Zhang Q, et al. Generative adversarial networks accurately reconstruct pan-cancer histology from pathologic, genomic, and radiographic latent features. Sci Adv. 2024;10:eadq0856.
Gao R, Yuan X, Ma Y, Wei T, Johnston L, Shao Y, et al. Harnessing TME depicted by histological images to improve cancer prognosis through a deep learning system. Cell Rep Med. 2024;5:101536.
Cisternino F, Ometto S, Chatterjee S, Giacopuzzi E, Levine AP, Glastonbury CA. Self-supervised learning for characterising histomorphological diversity and spatial RNA expression prediction across 23 human tissue types. Nat Commun. 2024;15:5906.
Wang Y, Ali MA, Vallon-Christersson J, Humphreys K, Hartman J, Rantalainen M. Transcriptional intra-tumour heterogeneity predicted by deep learning in routine breast histopathology slides provides independent prognostic information. Eur J Cancer. 2023;191:112953.
Noorbakhsh J, Farahmand S, Foroughi Pour A, Namburi S, Caruana D, Rimm D, et al. Deep learning-based cross-classifications reveal conserved spatial behaviors within tumor histological images. Nat Commun. 2020;11:6367.
Schmauch B, Romagnoni A, Pronier E, Saillard C, Maillé P, Calderaro J, et al. A deep learning model to predict RNA-Seq expression of tumours from whole slide images. Nat Commun. 2020;11:3877.
Niu Y, Wang L, Zhang X, Han Y, Yang C, Bai H, et al. Predicting tumor mutational burden from lung adenocarcinoma histopathological images using deep learning. Front Oncol. 2022;12:927426.
Anand D, Kurian NC, Dhage S, Kumar N, Rane S, Gann PH, et al. Deep learning to estimate human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status from hematoxylin and eosin-stained breast tissue images. J Pathol Inf. 2020;11:19.
Li B, Li F, Liu Z, Xu F, Ye G, Li W, et al. Deep learning with biopsy whole slide images for pretreatment prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: a multicenter study. Breast. 2022;66:183–90.
Hörst F, Ting S, Liffers ST, Pomykala KL, Steiger K, Albertsmeier M, et al. Histology-based prediction of therapy response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for esophageal and esophagogastric junction adenocarcinomas using deep learning. JCO Clin Cancer Inf. 2023;7:e2300038.
Yu G, Zuo Y, Wang B, Liu H. Prediction of tumor-associated macrophages and immunotherapy benefits using weakly supervised contrastive learning in breast cancer pathology images. J Imaging Inf Med. 2024;37:3090–100.
Hinata M, Ushiku T. Detecting immunotherapy-sensitive subtype in gastric cancer using histologic image-based deep learning. Sci Rep. 2021;11:22636.
Liu Y, Chen W, Ruan R, Zhang Z, Wang Z, Guan T, et al. Deep learning based digital pathology for predicting treatment response to first-line PD-1 blockade in advanced gastric cancer. J Transl Med. 2024;22:438.
Lee JH, Song GY, Lee J, Kang SR, Moon KM, Choi YD, et al. Prediction of immunochemotherapy response for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using artificial intelligence digital pathology. J Pathol Clin Res. 2024;10:e12370.
Jasti J, Zhong H, Panwar V, Jarmale V, Miyata J, Carrillo D, et al. Histopathology based ai model predicts anti-angiogenic therapy response in renal cancer clinical trial. Nat Commun. 2025;16:2610.
Zeng Q, Klein C, Caruso S, Maille P, Allende DS, Mínguez B, et al. Artificial intelligence-based pathology as a biomarker of sensitivity to atezolizumab-bevacizumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicentre retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24:1411–22.
Zhang Y, Yang Z, Chen R, Zhu Y, Liu L, Dong J, et al. Histopathology images-based deep learning prediction of prognosis and therapeutic response in small cell lung cancer. NPJ Digit Med. 2024;7:15.
Dawood M, Vu QD, Young LS, Branson K, Jones L, Rajpoot N, et al. Cancer drug sensitivity prediction from routine histology images. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024;8:5.
Claudio Quiros A, Coudray N, Yeaton A, Yang X, Liu B, Le H, et al. Mapping the landscape of histomorphological cancer phenotypes using self-supervised learning on unannotated pathology slides. Nat Commun. 2024;15:4596.
Liu B, Polack M, Coudray N, Quiros AC, Sakellaropoulos T, Crobach A, et al. Self-supervised learning reveals clinically relevant histomorphological patterns for therapeutic strategies in colon cancer. bioRxiv. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.02.26.582106.
Zhang W, Wang W, Xu Y, Wu K, Shi J, Li M, et al. Prediction of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation subtypes in non-small cell lung cancer from hematoxylin and eosin-stained slides using deep learning. Lab Invest. 2024;104:102094.
Pan X, AbdulJabbar K, Coelho-Lima J, Grapa AI, Zhang H, Cheung AHK, et al. The artificial intelligence-based model ANORAK improves histopathological grading of lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Cancer. 2024;5:347–63.
Lashen AG, Wahab N, Toss M, Miligy I, Ghanaam S, Makhlouf S, et al. Characterization of breast cancer intra-tumor heterogeneity using artificial intelligence. Cancers (Basel). 2024;16:3849.
Hou J, Jia X, Xie Y, Qin, W. Integrative histology-genomic analysis predicts hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis using deep learning. Genes (Basel).2022;13:1770.
Xu Y, Guo J, Yang N, Zhu C, Zheng T, Zhao W, et al. Predicting rectal cancer prognosis from histopathological images and clinical information using multi-modal deep learning. Front Oncol. 2024;14:1353446.
Yu Y, Cai G, Lin R, Wang Z, Chen Y, Tan Y, et al. Multimodal data fusion AI model uncovers tumor microenvironment immunotyping heterogeneity and enhanced risk stratification of breast cancer. MedComm (2020). 2024;5:e70023.
Chen RJ, Lu MY, Williamson DFK, Chen TY, Lipkova J, Noor Z, et al. Pan-cancer integrative histology-genomic analysis via multimodal deep learning. Cancer Cell. 2022;40:865–878 e866.
Min W, Shi Z, Zhang J, Wan J, Wang C. Multimodal contrastive learning for spatial gene expression prediction using histology images. Brief Bioinform. 2024;25:bbae551.
Jia Y, Liu J, Chen L, Zhao T, Wang Y. THItoGene: a deep learning method for predicting spatial transcriptomics from histological images. Brief Bioinform. 2023;25:bbad464.
Gui CP, Chen YH, Zhao HW, Cao JZ, Liu TJ, Xiong SW, et al. Multimodal recurrence scoring system for prediction of clear cell renal cell carcinoma outcome: a discovery and validation study. Lancet Digit Health. 2023;5:e515–e524.
Sato S, Maki S, Yamanaka T, Hoshino D, Ota Y, Yoshioka E, et al. Machine learning-based image analysis for accelerating the diagnosis of complicated preneoplastic and neoplastic ductal lesions in breast biopsy tissues. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021;188:649–59.
Yu KH, Hu V, Wang F, Matulonis UA, Mutter GL, Golden JA, et al. Deciphering serous ovarian carcinoma histopathology and platinum response by convolutional neural networks. BMC Med. 2020;18:236.
Phan NN, Huang CC, Tseng LM, Chuang EY. Predicting breast cancer gene expression signature by applying deep convolutional neural networks from unannotated pathological images. Front Oncol. 2021;11:769447.
Wang GY, Zhu JF, Wang QC, Qin JX, Wang XL, Liu X, et al. Prediction of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer recurrence using deep learning of pathology image. Sci Rep. 2024;14:18931.
Hong R, Liu W, DeLair D, Razavian N, Fenyö D. Predicting endometrial cancer subtypes and molecular features from histopathology images using multi-resolution deep learning models. Cell Rep Med. 2021;2:100400.
Foroughi Pour A, White BS, Park J, Sheridan TB, Chuang JH. Deep learning features encode interpretable morphologies within histological images. Sci Rep. 2022;12:9428.
Diao JA, Wang JK, Chui WF, Mountain V, Gullapally SC, Srinivasan R, et al. Human-interpretable image features derived from densely mapped cancer pathology slides predict diverse molecular phenotypes. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1613.
Zhang DY, Venkat A, Khasawneh H, Sali R, Zhang V, Pei Z. Implementation of digital pathology and artificial intelligence in routine pathology practice. Lab Invest. 2024;104:102111.
Xu H, Usuyama N, Bagga J, Zhang S, Rao R, Naumann T, et al. A whole-slide foundation model for digital pathology from real-world data. Nature. 2024;630:181–8.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank all the collaborators who contributed to publishing articles on histopathologic AI, which provided me with the opportunity to write this review article. I would also like to thank SciTechEdit International LLC (Highlands Ranch, CO, USA) for English-language editing.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP21K15393 and JP25K10276.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MT collected proper citations, drafted the manuscript, conducted critical revisions, and approved the final version for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: In this article the author’s name Manabu Takamatsu was incorrectly written as Takamatsu Manabu.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Takamatsu, M. Transforming histologic assessment: artificial intelligence in cancer diagnosis and personalized treatment. Br J Cancer 133, 1765–1775 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-03206-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-03206-y