Abstract
Background
Garsorasib (D-1553), a highly selective, oral KRASG12C inhibitor, has shown clinical efficacy in NSCLC and CRC and is under evaluation in pancreatic cancer.
Methods
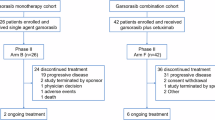
Pancreatic cancer patients with KRAS G12C mutation were enroled and received garsorasib 600 mg twice daily treatment in two international, multicenter, open-label phase 1/2 trials (NCT04585035 and NCT05383898) with similar eligibility criteria. Their data were pooled for analyses of efficacy and safety endpoints.
Results
As of April 30, 2024, 24 KRAS G12C–mutated pancreatic cancer patients were enroled with a median follow-up of 8.9 months (range 1.1–22.9). Among 22 evaluable patients, the confirmed objective response rate (ORR) was 45.5% (95% CI, 24.4 to 67.8) with a median duration of response (DOR) of 6.4 months (95% CI, 4.2 to 16.4). The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 7.6 months (95% CI, 3.3 to 8.5) and the 6-month OS rate was 79.2% (95% CI, 57.0, 90.8). Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) occurred in 18 (75.0%) patients, including 6 (25.0%) with grade ≥3 events. No TRAEs led to treatment discontinuation. The safety profile was consistent with previous reports of garsorasib.
Conclusion
Garsorasib demonstrated encouraging antitumor activity and a tolerable safety profile in patients with KRAS G12C-mutated advanced pancreatic cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
InventisBio will honor legitimate requests for clinical trial data from qualified researchers, upon request, as necessary for conducting clinically meaningful and GCP compliant research. InventisBio will provide completed clinical trial data to be posted on the clinicaltrials.gov registry for products or indications that have been approved by regulators. In general, data will be made available for request approximately 12 months after clinical trial completion.
References
Bray, F, Laversanne, M, Sung, H, Ferlay, J, Siegel, RL, Soerjomataram, I et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2004. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21834.
Hu ZI, O’Reilly EM. Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;21:7–24.
Chen X, Zeh HJ, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. Cell death in pancreatic cancer: from pathogenesis to therapy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18:804–23.
Raphael MJ, Raskin W, Habbous S, Tai X, Beca J, Dai WF, et al. The Association of Drug-Funding Reimbursement with survival outcomes and use of new systemic therapies among patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e2133388.
Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouche O, Guimbaud R, Becouarn Y, et al. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1817–25.
Von Hoff DD, Ervin T, Arena FP, Chiorean EG, Infante J, Moore M, et al. Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1691–703.
Witkiewicz AK, McMillan EA, Balaji U, Baek G, Lin WC, Mansour J, et al. Whole-exome sequencing of pancreatic cancer defines genetic diversity and therapeutic targets. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6744.
Luo J. KRAS mutation in pancreatic cancer. Semin Oncol. 2021;48:10–18.
Bekaii-Saab TS, Yaeger R, Spira AI, Pelster MS, Sabari JK, Hafez N, et al. Adagrasib in advanced solid tumors harboring a KRAS(G12C) mutation. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41:4097–106.
Strickler JH, Satake H, George TJ, Yaeger R, Hollebecque A, Garrido-Laguna I, et al. Sotorasib in KRAS p.G12C-mutated advanced pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023;388:33–43.
Li J, Shen L, Gu Y, Calles A, Wu L, Ba Y, et al. Preliminary activity and safety results of KRAS G12C inhibitor glecirasib (JAB-21822) in patients with pancreatic cancer and other solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42:604.
Shi Z, Weng J, Niu H, Yang H, Liu R, Weng Y, et al. D-1553: A novel KRAS(G12C) inhibitor with potent and selective cellular and in vivo antitumor activity. Cancer Sci. 2023;114:2951–60.
Li Z, Song Z, Zhao Y, Wang P, Jiang L, Gong Y, et al. D-1553 (Garsorasib), a potent and selective inhibitor of KRAS(G12C) in patients with NSCLC: phase 1 study results. J Thorac Oncol. 2023;18:940–51.
Ruan D-y, Lee MA, Deng Y, Lee K-W, Millward M, Grewal JS, et al. Safety and efficacy of D-1553 in KRAS G12C-mutated colorectal cancer: results from a phase I/II study. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41:3563.
Xu RH, Xu Y, Yan D, Munster P, Ruan D, Deng Y, et al. 550O Safety and efficacy of D-1553 in combination with cetuximab in KRAS G12C mutated colorectal cancer (CRC): a phase II study. Ann Oncol. 2023;34:S410–S1.
Kondo S, Yan D, Ganju V, Richardson G, Hou X, Shan J, et al. 1622P D-1553 in patients with KRAS G12C mutated advanced pancreatic cancer (PCA). Ann Oncol. 2023;34:S898–S899.
Li Z, Dang X, Huang D, Jin S, Li W, Shi J, et al. Abstract CT246: Open-label, single-arm, multicenter, phase 2 trial of garsorasib in KRAS G12C-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2024;84:CT246.
Wang-Gillam A, Hubner RA, Siveke JT, Von Hoff DD, Belanger B, de Jong FA, et al. NAPOLI-1 phase 3 study of liposomal irinotecan in metastatic pancreatic cancer: final overall survival analysis and characteristics of long-term survivors. Eur J Cancer. 2019;108:78–87.
Oettle H, Riess H, Stieler JM, Heil G, Schwaner I, Seraphin J, et al. Second-line oxaliplatin, folinic acid, and fluorouracil versus folinic acid and fluorouracil alone for gemcitabine-refractory pancreatic cancer: outcomes from the CONKO-003 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:2423–9.
Gill S, Ko YJ, Cripps C, Beaudoin A, Dhesy-Thind S, Zulfiqar M, et al. PANCREOX: a randomized phase III study of fluorouracil/leucovorin with or without oxaliplatin for second-line advanced pancreatic cancer in patients who have received gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:3914–20.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the patients and their families, clinical staff, and the collaborators who contributed to this study. Medical writing assistance for this manuscript was provided by Yihong Zhang and Xinying Liu from InventisBio.
Funding
The study was sponsored by InventisBio Co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology: NY, ZX, WW, ZS, LZ, YW, R-HX. Investigation: NY, DY, VG, XH, HP, JS, LW, SK, GR, RES, JZ, R-HX. Writing original draft: NY, ZX, WW, ZS, LZ, R-HX. Writing, review and editing: NY, DY, VG, XH, HP, JS, LW, SK, GR, RES, JZ, ZX, WW, ZS, LZ, YW, R-HX. Supervision: ZS, LZ, YW. Project administration: ZX, WW.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
NY reports honoraria from Chugai Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan, Eisai, reports consulting or advisory fees from Eisai, Boehringer Ingelheim, CMIC, Chugai Pharma, Healios, Merck, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Rakuten Medical Japan, Noile-Immune Biotech, Inc, reports research funding from Chugai Pharma, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Eisai, Astellas Pharma, Novartis, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly Japan, Boehringer Ingelheim, Takeda, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Bayer, Pfizer, Ono Pharmaceutical, Janssen, MSD, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Serono, GlaxoSmithKline, Sumitomo Dainippon, Chiome Bioscience, Otsuka, Carna Biosciences, Genmab/Seattle Genetics, Shionogi, Toray Industries, Kaken Pharmaceutical, AstraZeneca, CMIC, InventisBio, Rakuten Medical, Amgen, Bicycle Therapeutics. RES reports grants or contracts from AstraZeneca and Merck; reports consulting fees from GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Janssen Oncology, Macrogenics, Daiichi, Sanofi, BeiGene, Gilead, Regeneron, Targeted Oncology, G1 Therapeutics, GE HealthCare, Amgen, and Lilly Oncology; reports payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations from EMD Serono, Illumina, GameOn!, OncLive, Binay Foundation, APP Oncology, and Masters in Thoracic Oncology Summit; participates on advisory board for GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Janssen Oncology, Macrogenics, Daiichi, Sanofi, BeiGene, Gilead, Regeneron, Targeted Oncology, G1 Therapeutics, GE HealthCare, Amgen, and Lilly Oncology. ZX, WW, ZS, LZ, YW reports InventisBio employment and stock. R-HX reports speaker fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche, MerckSerono, Hutchison, Hengrui, Junshi, Qilu, CPPC, Henlius, and participates on advisory board for Astellas, MSD, AstraZeneca, Junshi, Hengrui, BeiGene. Innovent, CPPC, and Keymed. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The studies were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice and were approved by the ethics committee of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, and by the ethics committees of the other participating sites. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to screening.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, N., Yan, D., Ganju, V. et al. Efficacy and safety of garsorasib in patients with KRAS G12C-mutated advanced pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 134, 457–462 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-03286-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-025-03286-w