Abstract
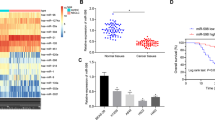
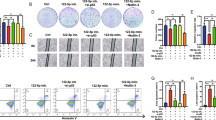
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer, and is characterized by extensive metastasis and poor prognosis. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from endothelial cells carrying microRNAs (miRNAs/miRs) have diagnostic and therapeutic potential for NSCLC. We herein investigate the potential of EVs derived from human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) to transfer miR-203 to affect the progression of NSCLC. miR-203 and p21 were poorly expressed while DTL was highly expressed both in NSCLC tissues and cell lines. We employed CCK-8 proliferation, colony formation, and Transwell migration and invasion assays to evaluate the effects of miR-203 on NSCLC cell behaviors using loss- and gain-function approaches. EVs were isolated from HUVECs and then co-cultured with the A549 cells transfected with mimic-NC or miR-203 inhibitor. miR-203 targeted DTL and downregulated its expression, subsequently leading to increased stability of p21 which is a tumor suppressor. EV-enriched miR-203 from HUVECs suppressed malignant phenotypes of NSCLC cells and delayed tumor growth. In conclusion, miR-203 from HUVEC-derived EVs exerts inhibitory effects on the progression of NSCLC by targeting DTL and promoting p21 protein stability.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou C. Lung cancer molecular epidemiology in China: recent trends. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2014;3:270–9.
Boeckx B, Shahi RB, Smeets D, De Brakeleer S, Decoster L, Van Brussel T et al. The genomic landscape of nonsmall cell lung carcinoma in never smokers. Int J Cancer. 2019;146:3207-18.
Li W, Yu H. Separating or combining immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and radiotherapy in the treatment of NSCLC brain metastases. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020;146:137–52.
Rebuzzi SE, Alfieri R, La Monica S, Minari R, Petronini PG, Tiseo M. Combination of EGFR-TKIs and chemotherapy in advanced EGFR mutated NSCLC: review of the literature and future perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2020;146:102820.
Uramoto H, Tanaka F. Recurrence after surgery in patients with NSCLC. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2014;3:242–9.
Oettel A, Lorenz M, Stangl V, Costa SD, Zenclussen AC, Schumacher A. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells foster conversion of CD4+CD25-Foxp3- T cells into CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells via transforming growth factor-beta. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23278.
Mu X, Fang C, Zhou J, Xi Y, Zhang L, Wei Y, et al. Fusion with human lung cancer cells elongates the life span of human umbilical endothelial cells and enhances the anti-tumor immunity. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016;142:111–23.
Fuhrmann G, Serio A, Mazo M, Nair R, Stevens MM. Active loading into extracellular vesicles significantly improves the cellular uptake and photodynamic effect of porphyrins. J Control Release. 2015;205:35–44.
Yue KY, Zhang PR, Zheng MH, Cao XL, Cao Y, Zhang YZ, et al. Neurons can upregulate Cav-1 to increase intake of endothelial cells-derived extracellular vesicles that attenuate apoptosis via miR-1290. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:869.
Walker S, Busatto S, Pham A, Tian M, Suh A, Carson K, et al. Extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Theranostics. 2019;9:8001–17.
Couto N, Caja S, Maia J, Strano Moraes MC, Costa-Silva B. Exosomes as emerging players in cancer biology. Biochimie. 2018;155:2–10.
Zhou S, Hu T, Zhang F, Tang D, Li D, Cao J, et al. Integrated microfluidic device for accurate extracellular vesicle quantification and protein markers analysis directly from human whole blood. Anal Chem. 2020;92:1574–81.
Wang Y, Xu YM, Zou YQ, Lin J, Huang B, Liu J, et al. Identification of differential expressed PE exosomal miRNA in lung adenocarcinoma, tuberculosis, and other benign lesions. Medicine (Baltim). 2017;96:e8361.
Shen M, Dong C, Ruan X, Yan W, Cao M, Pizzo D, et al. Chemotherapy-induced extracellular vesicle miRNAs promote breast cancer stemness by targeting ONECUT2. Cancer Res. 2019;79:3608–21.
Takano Y, Masuda T, Iinuma H, Yamaguchi R, Sato K, Tobo T, et al. Circulating exosomal microRNA-203 is associated with metastasis possibly via inducing tumor-associated macrophages in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:78598–613.
Zhou Y, Liang H, Liao Z, Wang Y, Hu X, Chen X, et al. miR-203 enhances let-7 biogenesis by targeting LIN28B to suppress tumor growth in lung cancer. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42680.
Xu YW, Cao LR, Wang M, Xu Y, Wu X, Liu J, et al. Maternal DCAF2 is crucial for maintenance of genome stability during the first cell cycle in mice. J Cell Sci. 2017;130:3297–307.
Perez-Pena J, Corrales-Sanchez V, Amir E, Pandiella A, Ocana A. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T (UBE2T) and denticleless protein homolog (DTL) are linked to poor outcome in breast and lung cancers. Sci Rep. 2017;7:17530.
Abbas T, Sivaprasad U, Terai K, Amador V, Pagano M, Dutta A. PCNA-dependent regulation of p21 ubiquitylation and degradation via the CRL4Cdt2 ubiquitin ligase complex. Genes Dev. 2008;22:2496–506.
Vigneron A, Cherier J, Barre B, Gamelin E, Coqueret O. The cell cycle inhibitor p21waf1 binds to the myc and cdc25A promoters upon DNA damage and induces transcriptional repression. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:34742–50.
Olivero M, Dettori D, Arena S, Zecchin D, Lantelme E, Di Renzo MF. The stress phenotype makes cancer cells addicted to CDT2, a substrate receptor of the CRL4 ubiquitin ligase. Oncotarget. 2014;5:5992–6002.
Liu JQ, Feng YH, Zeng S, Zhong MZ. linc01088 promotes cell proliferation by scaffolding EZH2 and repressing p21 in human non-small cell lung cancer. Life Sci. 2020;241:117134.
Tang Z, Kang B, Li C, Chen T, Zhang Z. GEPIA2: an enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:W556–60.
Wang S, Wu Y, Hou Y, Guan X, Castelvetere MP, Oblak JJ, et al. CXCR2 macromolecular complex in pancreatic cancer: a potential therapeutic target in tumor growth. Transl Oncol. 2013;6:216–25.
Grimolizzi F, Monaco F, Leoni F, Bracci M, Staffolani S, Bersaglieri C, et al. Exosomal miR-126 as a circulating biomarker in non-small-cell lung cancer regulating cancer progression. Sci Rep. 2017;7:15277.
Hu H, Wang B, Jiang C, Li R, Zhao J. Endothelial progenitor cell-derived exosomes facilitate vascular endothelial cell repair through shuttling miR-21-5p to modulate Thrombospondin-1 expression. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019;133:1629–44.
Karuppasamy R, Veerappapillai S, Maiti S, Shin WH, Kihara D. Current progress and future perspectives of polypharmacology: from the view of non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019;S1044-579X:30148–8.
Lin J, Wang Y, Zou YQ, Chen X, Huang B, Liu J, et al. Differential miRNA expression in pleural effusions derived from extracellular vesicles of patients with lung cancer, pulmonary tuberculosis, or pneumonia. Tumour Biol. 2017;37:15835–45.
Tang R, Zhong T, Dang Y, Zhang X, Li P, Chen G. Association between downexpression of MiR-203 and poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Transl Oncol. 2016;18:360–8.
Hu H, Xu Z, Li C, Xu C, Lei Z, Zhang HT, et al. MiR-145 and miR-203 represses TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion by inhibiting SMAD3 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 2016;97:87–94.
Chi Y, Jin Q, Liu X, Xu L, He X, Shen Y, et al. miR-203 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of non-small-cell lung cancer by downregulating RGS17. Cancer Sci. 2017;108:2366–72.
Chan SH, Wang LH. Regulation of cancer metastasis by microRNAs. J Biomed Sci. 2015;22:9.
Xue YB, Ding MQ, Xue L, Luo JH. CircAGFG1 sponges miR-203 to promote EMT and metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer by upregulating ZNF281 expression. Thorac Cancer. 2019;10:1692–701.
Karimian A, Ahmadi Y, Yousefi B. Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and transcriptional regulation after DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst). 2016;42:63–71.
Nie FQ, Sun M, Yang JS, Xie M, Xu TP, Xia R, et al. Long noncoding RNA ANRIL promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by silencing KLF2 and P21 expression. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015;14:268–77.
Zhao S, Han J, Zheng L, Yang Z, Zhao L, Lv Y. MicroRNA-203 regulates growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37:35–42.
Clere N, Renault S, Corre I. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:747.
Sobierajska K, Ciszewski W, Sacewicz-Hofman I, Niewiarowska J. Endothelial cells in the tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1234:71–86.
Shenoy A, Lu J. Cancer cells remodel themselves and vasculature to overcome the endothelial barrier. Cancer Lett. 2016; 380:534-44.
Nagl L, Horvath L, Pircher A, Wolf D. Tumor endothelial cells (TECs) as potential immune directors of the tumor microenvironment—new findings and future Perspectives. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:766
Sayed H, Hetta H, Shafik E, Zahran A. Flow cytometric analysis of circulating endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells in pediatric solid tumors: prognostic impact on treatment response and survival. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02719-0, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32945943/.
Bell E, Taylor MA. Functional roles for exosomal microRNAs in the tumour microenvironment. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2017;15:8–13.
Yang Q, Diamond MP, Al-Hendy A. The emerging role of extracellular vesicle-derived miRNAs: implication in cancer progression and stem cell related diseases. J Clin Epigenet. 2016;2:13.
Poroyko V, Mirzapoiazova T, Nam A, Mambetsariev I, Mambetsariev B, Wu X, et al. Exosomal miRNAs species in the blood of small cell and non-small cell lung cancer patients. Oncotarget 2018;9:19793–806.
Liu W, Liu J, Zhang Q, Wei L. Downregulation of serum exosomal miR-216b predicts unfavorable prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biomark 2020;27:113–20.
Li J, Yu J, Zhang H, Wang B, Guo H, Bai J, et al. Exosomes-derived MiR-302b suppresses lung cancer cell proliferation and migration via TGFbetaRII inhibition. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38:1715–26.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the helpful comments on this paper received from the reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tiangang Ma wrote the paper and conceived and designed the experiments; Yanbing Hu analyzed the data; Yinxue Guo and Qinghua Zhang collected and provided the sample for this study. All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, T., Hu, Y., Guo, Y. et al. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells-derived microRNA-203-containing extracellular vesicles alleviate non-small-cell lung cancer progression through modulating the DTL/p21 axis. Cancer Gene Ther 29, 87–100 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00292-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00292-3
This article is cited by
-
MiR-3202–DTL signaling axis impedes NSCLC malignancy via regulating the ubiquitination-proteasome degradation of p21
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2025)
-
Long non-coding RNA DLGAP1-AS1 modulates the development of non-small-cell lung cancer via the microRNA-193a-5p/DTL axis
Laboratory Investigation (2022)