Abstract
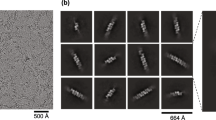
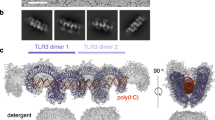
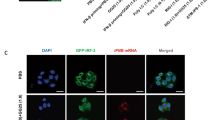
The pre-dimerization of endosome-localized RNA sensor Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) is required for its innate recognition, yet how TLR3 pre-dimers are formed and precisely primed for innate activation remains unclear. Here, we demonstrate that endosome-localized self RNA Rmrp directly binds to TLR3 and induces TLR3 dimerization in the early endosome but does not interact with endosome-localized TLR7, TLR8, TLR9 or cytoplasmic RNA sensor RIG-I under homeostatic conditions. Cryo-EM structure of Rmrp–TLR3 complex reveals a novel lapped conformation of TLR3 dimer engaged by Rmrp, which is distinct from the activation mechanism by dsRNA and the specific structural feature at the 3’-end of Rmrp is critical for its functional interaction with TLR3. Furthermore, K42 residue of TLR3 is essential for binding to Rmrp and subsequent dimerization. Rmrp dissociates from TLR3 following endosomal acidification, generating a matured TLR3 dimer which is primed for innate recognition and activation. Myeloid-cell deficiency of Rmrp reduces TLR3 dimerization and attenuates TLR3-mediated antiviral responses against influenza A both in vitro and in vivo. These findings elucidate the structural mode of self RNA Rmrp-primed TLR3 dimerization and ready for efficient innate recognition on endosomal membrane, extending our knowledge of how membrane-associated TLRs pre-dimerize and suggesting a new function of subcellular localized self RNAs in empowering innate activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available in the main text or supplementary materials. RNA-seq and iCLIP data are deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus under accession number GSE159459. The 3D cryo-EM density maps have been deposited into the Electron Microscopy Data Bank under accession numbers EMD-30624, EMD-30626. The coordinates have been deposited into the Protein Data Bank under accession numbers 7DA7, 7DAS.
References
Alexopoulou, L., Holt, A. C., Medzhitov, R. & Flavell, R. A. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413, 732–738 (2001).
Zinngrebe, J. et al. LUBAC deficiency perturbs TLR3 signaling to cause immunodeficiency and autoinflammation. J. Exp. Med. 213, 2671–2689 (2016).
Cao, X. Self-regulation and cross-regulation of pattern-recognition receptor signalling in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 35–50 (2016).
Liu, J. & Cao, X. RBP-RNA interactions in the control of autoimmunity and autoinflammation. Cell Res. 33, 97–115 (2023).
Yu, Z. et al. The RNA-binding E3 ligase MKRN2 selectively disrupts Il6 translation to restrain inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 26, 1036–1047 (2025).
Stok, J. E., Vega Quiroz, M. E. & van der Veen, A. G. Self RNA sensing by RIG-I-like receptors in viral infection and sterile inflammation. J. Immunol. 205, 883–891 (2020).
Jiang, M. et al. Self-recognition of an inducible host lncRNA by RIG-I feedback restricts innate immune response. Cell 173, 906–919.e13 (2018).
Wang, P. et al. The STAT3-binding long noncoding RNA lnc-DC controls human dendritic cell differentiation. Science 344, 310–313 (2014).
Yang, Z. et al. Promotion of TLR7-MyD88-dependent inflammation and autoimmunity in mice through stem-loop changes in Lnc-Atg16l1. Nat. Commun. 15, 10224 (2024).
Li, Z., Zou, J. & Chen, X. In response to precision medicine: current subcellular targeting strategies for cancer therapy. Adv. Mater. 35, e2209529 (2023).
Miyake, K. et al. Mechanisms controlling nucleic acid-sensing Toll-like receptors. Int. Immunol. 30, 43–51 (2018).
Gavin, A. L. et al. Cleavage of DNA and RNA by PLD3 and PLD4 limits autoinflammatory triggering by multiple sensors. Nat. Commun. 12, 5874 (2021).
Liu, Y. et al. Tumor exosomal RNAs promote lung pre-metastatic niche formation by activating alveolar epithelial TLR3 to recruit neutrophils. Cancer Cell 30, 243–256 (2016).
Kawai, T. & Akira, S. Toll-like receptor and RIG-I-like receptor signaling. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1143, 1–20 (2008).
Aslaksen, S. et al. Identification and characterization of rare toll-like receptor 3 variants in patients with autoimmune Addison’s disease. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 1, 100005 (2019).
Cavassani, K. A. et al. TLR3 is an endogenous sensor of tissue necrosis during acute inflammatory events. J. Exp. Med. 205, 2609–2621 (2008).
Bernard, J. J. et al. Ultraviolet radiation damages self noncoding RNA and is detected by TLR3. Nat. Med. 18, 1286–1290 (2012).
Garcia-Cattaneo, A. et al. Cleavage of Toll-like receptor 3 by cathepsins B and H is essential for signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 9053–9058 (2012).
Choe, J., Kelker, M. S. & Wilson, I. A. Crystal structure of human toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) ectodomain. Science 309, 581–585 (2005).
Zhang, Z. et al. Structural analysis reveals that Toll-like receptor 7 is a dual receptor for guanosine and single-stranded RNA. Immunity 45, 737–748 (2016).
Tanji, H., Ohto, U., Shibata, T., Miyake, K. & Shimizu, T. Structural reorganization of the Toll-like receptor 8 dimer induced by agonistic ligands. Science 339, 1426–1429 (2013).
Ohto, U. et al. Structural basis of CpG and inhibitory DNA recognition by Toll-like receptor 9. Nature 520, 702–705 (2015).
Liu, L. et al. Structural basis of toll-like receptor 3 signaling with double-stranded RNA. Science 320, 379–381 (2008).
Jin, M. S. et al. Crystal structure of the TLR1-TLR2 heterodimer induced by binding of a tri-acylated lipopeptide. Cell 130, 1071–1082 (2007).
Kanno, A. et al. Essential role for Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7)-unique cysteines in an intramolecular disulfide bond, proteolytic cleavage and RNA sensing. Int. Immunol. 25, 413–422 (2013).
Wang, Y., Liu, L., Davies, D. R. & Segal, D. M. Dimerization of Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) is required for ligand binding. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 36836–36841 (2010).
Latz, E. et al. Ligand-induced conformational changes allosterically activate Toll-like receptor 9. Nat. Immunol. 8, 772–779 (2007).
Asami, J. & Shimizu, T. Structural and functional understanding of the toll-like receptors. Protein Sci. 30, 761–772 (2021).
Acharya, D. et al. Actin cytoskeleton remodeling primes RIG-I-like receptor activation. Cell 185, 3588–3602.e21 (2022).
Ridanpaa, M. et al. Mutations in the RNA component of RNase MRP cause a pleiotropic human disease, cartilage-hair hypoplasia. Cell 104, 195–203 (2001).
Toscano, F. et al. Cleaved/associated TLR3 represents the primary form of the signaling receptor. J. Immunol. 190, 764–773 (2013).
Lu, A. et al. Unified polymerization mechanism for the assembly of ASC-dependent inflammasomes. Cell 156, 1193–1206 (2014).
Kawai, T. & Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 11, 373–384 (2010).
Rosenbluh, J. et al. RMRP is a non-coding RNA essential for early murine development. PLoS One 6, e26270 (2011).
Leonard, J. N. et al. The TLR3 signaling complex forms by cooperative receptor dimerization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 258–263 (2008).
Bell, J. K. et al. The molecular structure of the Toll-like receptor 3 ligand-binding domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 10976–10980 (2005).
Sakaniwa, K. et al. TLR3 forms a laterally aligned multimeric complex along double-stranded RNA for efficient signal transduction. Nat. Commun. 14, 164 (2023).
Lan, P. et al. Structural insight into precursor ribosomal RNA processing by ribonuclease MRP. Science 369, 656–663 (2020).
Perederina, A. et al. Cryo-EM structure of catalytic ribonucleoprotein complex RNase MRP. Nat. Commun. 11, 3474 (2020).
Lim, C. S. et al. TLR3 forms a highly organized cluster when bound to a poly(I:C) RNA ligand. Nat. Commun. 13, 6876 (2022).
Ohto, U. et al. Toll-like receptor 9 contains two DNA binding sites that function cooperatively to promote receptor dimerization and activation. Immunity 48, 649–658.e4 (2018).
Abramson, J. et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 630, 493–500 (2024).
Le Goffic, R. et al. Detrimental contribution of the Toll-like receptor (TLR)3 to influenza A virus-induced acute pneumonia. PLoS Pathog. 2, e53 (2006).
Kariko, K., Buckstein, M., Ni, H. & Weissman, D. Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: the impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity 23, 165–175 (2005).
Jain, S. et al. Modulation of translational decoding by m(6)A modification of mRNA. Nat. Commun. 14, 4784 (2023).
Sekulski, K., Cruz, V. E., Weirich, C. S. & Erzberger, J. P. rRNA methylation by Spb1 regulates the GTPase activity of Nog2 during 60S ribosomal subunit assembly. Nat. Commun. 14, 1207 (2023).
Abbassi, N. E. et al. Cryo-EM structures of the human Elongator complex at work. Nat. Commun. 15, 4094 (2024).
Mariani, A., Bonfio, C., Johnson, C. M. & Sutherland, J. D. pH-Driven RNA Strand Separation under Prebiotically Plausible Conditions. Biochemistry 57, 6382–6386 (2018).
Botos, I., Liu, L., Wang, Y., Segal, D. M. & Davies, D. R. The toll-like receptor 3:dsRNA signaling complex. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1789, 667–674 (2009).
Ishida, H. et al. Cryo-EM structures of Toll-like receptors in complex with UNC93B1. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 28, 173–180 (2021).
Fu, J., Schroder, K. & Wu, H. Mechanistic insights from inflammasome structures. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 24, 518–535 (2024).
Hermanns, P. et al. Consequences of mutations in the non-coding RMRP RNA in cartilage-hair hypoplasia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, 3723–3740 (2005).
Vakkilainen, S. et al. A wide spectrum of autoimmune manifestations and other symptoms suggesting immune dysregulation in patients with cartilage-hair hypoplasia. Front. Immunol. 9, 2468 (2018).
Goldfarb, K. C. & Cech, T. R. Targeted CRISPR disruption reveals a role for RNase MRP RNA in human preribosomal RNA processing. Genes Dev. 31, 59–71 (2017).
Gill, T., Cai, T., Aulds, J., Wierzbicki, S. & Schmitt, M. E. RNase MRP cleaves the CLB2 mRNA to promote cell cycle progression: novel method of mRNA degradation. Mol. Cell Biol. 24, 945–953 (2004).
Rheinbay, E. et al. Recurrent and functional regulatory mutations in breast cancer. Nature 547, 55–60 (2017).
Yin, H. et al. M6A RNA methylation-mediated RMRP stability renders proliferation and progression of non-small cell lung cancer through regulating TGFBR1/SMAD2/SMAD3 pathway. Cell Death Differ. 30, 605–617 (2023).
Lyu, Y., Wang, Y., Ding, H. & Li, P. Hypoxia-induced m6A demethylase ALKBH5 promotes ovarian cancer tumorigenicity by decreasing methylation of the lncRNA RMRP. Am. J. Cancer Res. 13, 4179–4191 (2023).
Sun, L. et al. RNA structure maps across mammalian cellular compartments. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 26, 322–330 (2019).
Murray, L. A. et al. Deleterious role of TLR3 during hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 178, 1227–1237 (2008).
Vakkilainen, S., Taskinen, M., Klemetti, P., Pukkala, E. & Makitie, O. A 30-year prospective follow-up study reveals risk factors for early death in cartilage-hair hypoplasia. Front. Immunol. 10, 1581 (2019).
Tavora, B. et al. Tumoural activation of TLR3-SLIT2 axis in endothelium drives metastasis. Nature 586, 299–304 (2020).
Mastronarde, D. N. Automated electron microscope tomography using robust prediction of specimen movements. J. Struct. Biol. 152, 36–51 (2005).
Zheng, S. Q. et al. MotionCor2: anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Methods 14, 331–332 (2017).
Punjani, A., Rubinstein, J. L., Fleet, D. J. & Brubaker, M. A. cryoSPARC: algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat. Methods 14, 290–296 (2017).
Pettersen, E. F. et al. UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1605–1612 (2004).
Liebschner, D. et al. Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 75, 861–877 (2019).
Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2126–2132 (2004).
Chen, V. B. et al. MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 12–21 (2010).
Goddard, T. D. et al. UCSF ChimeraX: Meeting modern challenges in visualization and analysis. Protein Sci. 27, 14–25 (2018).
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Quan Wang and Yan Gao for technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82388201) and CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (2024-I2M-ZD-005, 2021-I2M-1-017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.C. designed and supervised the study. Shikun Z., B.L., L.L., D.G., D.Z., F.L., X.Y., H.Q. performed the experiments. L.L. generated Rmrpfl/fl mice. D.K. and Shuyang Z. provided reagents and helpful discussion. Shikun Z., B.L., Z.R. and X.C. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Li, B., Liu, L. et al. Molecular characterization of endosomal self RNA Rmrp-engaged TLR3 dimerization to prime innate activation. Cell Res 35, 824–839 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-025-01178-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-025-01178-5
This article is cited by
-
Self-RNA Rmrp pre-dimerizes TLR3 for immune activation
Cell Research (2025)