Abstract
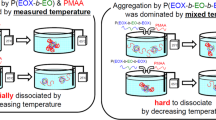
The structure of interpolymer complex formed by poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) and poly(methacrylic acid) was changed by controlling the hydrogen bonds between the polymer chains by changing the solvent pH or adding urea. The viscosity of solution containing the interpolymer complex drastically increased in solvent at pH~12, then decreased at pH~13. The infrared spectra of the interpolymer complexes formed in solvents at different pH indicated that the formation of hydrogen bonds among the polymer chains decreased with an increase of pH. These results were explained by a model in which the dimension of the interpolymer complex increased at pH~12, and the interpolymer complex dissociated into free polymer chains at pH~13. The hydrogen bonds of the interpolymer complex were also suppressed by adding urea to solvents. The viscosity of the solution containing the polymer-complex increased drastically when the urea concentration was over 6 M. The increase induced by the addition of urea can also be explained by the increase in the dimension of the interpolymer complex.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kwon IC, Bae YH, Kim SW. Electrically erodible polymer gel for controlled release of drugs. Nature. 1991;354:291–3.
Matsuda Y, Takatsuji K, Shiokawa Y, Kikuchi M, Kidoaki S, Takahara A, et al. Characterization of complexes formed by mixing aqueous solutions of poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) and poly(methacrylic acid) with a wide range of concentrations. Polymer. 2013;54:1896–904.
Wang C-H, Hsiue G-H. Synthesis and characterization of temperature- and pH- sensitive hydrogels based on poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) and poly(D,L-lactide). J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem. 2002;40:1112–21.
Wang C-H, Hsiue G-H. New amphiphilic poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) poly(L-lactide) triblock copolymers. Biomacromolecules. 2003;4:1487–90.
Hsiue G-H, Wang C-H, Lo C-L, Wang C-H, Li J-P, Yang J-L. Environmental- sensitive micelles based on poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)-b-poly(L-lactide) diblock copolymer for application in drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2006;317:69–75.
Wang C-H, Wang W-T, Hsiue G-H. Development of polyion complex micelles for encapsulating and delivering amphotericin B. Biomaterials. 2009;30:3352–8.
Lee KY, Kwon IC, Jeong SY. Physicochemical characteristics of poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)/poly(ε-caprolactone) block copolymer micelles in water. Polym Bull. 2006;26:385–93.
Matsuda Y, Shiokawa Y, Kikuchi M, Takahara A, Tasaka S. Structure of insoluble complex formed by a block copolymer of 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline and ethylene oxide and poly(methacrylic acid). Polymer. 2014;55:4757–64.
Wang C-H, Hsiue G-H. Synthesis and characterization of temperature- and pH-sensitive hydrogels based on poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) and poly(D,L-lactide). J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem. 2002;40:1112–21.
Wang C-H, Hsiue G-H. New amphiphilic poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)/poly(l-lactide) triblock copolymers. Biomacromolecules. 2003;4:1487–90.
Su C, Sun J, Zhang X, Shen D. Hydrogen-bonded polymer complex thin film of poly(2-oxazoline) and poly(acrylic acid). Polymers. 2017;9:363.
An N, Wang X, Li Y, Zhang L, Lu Z, Sun J. Healable and mechanically super-strong polymeric composites derived from hydrogen-bonded polymeric complexes. Adv Mater. 2019;31:1904882.
Matsuda Y, Akao R, Nakazawa M, Ando H, Tasaka S. Characterization of colloidal particles formed in plastic coating solution at room temperature. J Coat Technol Res. 2020;17:1343–9.
Lichkus AM, Painter PC, Coleman MM. Hydrogen bonding in polymer blends. 5. Blends involving polymers containing methacrylic acid and oxazoline groups. Macromolecules. 1988;21:2636–41.
Meaurio E, Katime I. FT-IR study of blends and complexes of poly(mono n-alkyl itaconates) with poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) and poly(ethyloxazoline). Macromol Mater Eng. 2005;290:1166–75.
Tajiri T, Morita S, Ozaki Y. Hydration mechanism on a poly(methacrylic acid) film studied by in situ attenuated total reflection infrared spectroscopy. Polymer. 2009;50:5765–70.
Tang E, Cheng G, Ma X, Pang X, Zhao Q. Surface modification of zinc oxide nanoparticle by PMAA and its dispersion in aqueous system. Appl Surf Sci. 2006;252:5227–32.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially performed under Cooperative Research Program of “Network Joint Research Center for Materials and Devices”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuda, Y., Emi, H. Changes in the structure and viscosity of interpolymer complexes formed by poly(ethyl oxazoline) and poly(methacrylic acid) by controlling interpolymer hydrogen bonds. Polym J 58, 159–165 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-025-01112-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-025-01112-x