Abstract
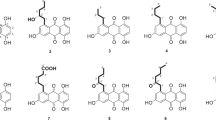
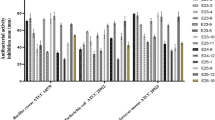
Five new anthraquinones, morakotins A–E (1–5), together with seven known compounds, lunatin (6), rheoemodin (7), YM187781 (8), bislunatin (9), 6-(1-hydroxypentyl)-4-methoxypyran-2-one, 9,11-dehydoergrosterol peroxide, and cerevisterol, were isolated from the insect pathogenic fungus Cordyceps morakotii BCC 56811. The morakotin structures were elucidated from NMR spectroscopic and mass spectrometric data. The absolute configurations of bianthraquinone compounds, morakotins C–E (3–5), were determined by application of the exciton chirality method. Compounds 3, 7, 8, and 9 showed weak to moderate antimycobacterial and antifungal activities. Compounds 4 and 8 exhibited antibacterial activity against both Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus aureus (MIC 3.13–25 µg ml−1), whereas compounds 3 and 9 were active against B. cereus (MIC 12.5 and 3.13 µg ml−1, respectively), and compound 7 was active against Acinetobacter baumannii (MIC 12.5 µg ml−1).
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Fouillaud M, Venkatachalam M, Girard-Valenciennes E, Caro Y, Dufossé L. Anthraquinones and derivatives from marine-derived fungi: Structural diversity and selected biological activities. Mar Drugs. 2016;14:64.
Gessler NN, Egorova AS, Belozerskaya TA. Fungal anthraquinones. Appl Biochem Microbiol. 2013;49:85–99.
Aly AH, Debbab A, Kjer J, Proksch P. Fungal endophytes from higher plants: a prolific source of phytochemicals and other bioactive natural products. Fungal Divers. 2010;41:1–16.
Borges WS, Pupo MT. Novel anthraquinone derivatives produced by Phoma sorghina, an endophyte found in association with the medicinal plant Tithonia diversifolia (Asteraceae). J Braz Chem Soc. 2006;17:929–34.
Huang W-Y, Cai Y-Z, Xing J, Corke H, Sun M. A potential antioxidant resource: Endophytic fungi from medicinal plants. Econ Bot. 2007;61:14–30.
Xu A, Wang Y, Wen J, Liu P, Liu Z, Li Z. Fungal community associated with fermentation and storage of Fuzhuan brick-tea. Int J Food Microbiol. 2011;146:14–22.
Isaka M, Kittakoop P, Kirtikara K, Hywel-Jones NL, Thebtaranonth Y. Bioactive substances from insect pathogenic fungi. Acc Chem Res. 2005;38:813–23.
Kittakoop P, et al. Bioactive naphthoquinones from Cordyceps unilateralis. Phytochemistry. 1999;52:453–7.
Jadulco R, et al. New metabolites from sponge-derived fungi Curvularia lunata and Cladosporium herbarum. J Nat Prod. 2002;65:730–3.
Huang R, Wang T, Xie X-S, Ma K-X, Fang X-W, Wu S-H. Secondary metabolites from an endophytic fungus Nigrospora sp. Chem Nat Compd. 2016;52:697–9.
Koichi T, Masato W, Koji N, Nami N, Akito Y, JP 2000239216 (A) (2000).
Agusta A, Ohashi K, Shibuya H. Bisanthraquinone metabolites produced by the endophytic fungus Diaporthe sp. Chem Pharm Bull. 2006;54:579–82.
Ayer WA, Trifonov LS, Hutchison LJ, Chakravarty P. Metabolites from a wood-inhabiting cup fungus. Urnula craterium Nat Prod Lett. 2000;14:405–10.
Gunatilaka AAL, Gopichand Y, Schmitz FJ, Djerassi C. Minor and trace sterols in marine invertebrates. 26. Isolation and structure elucidation of nine new 5.alpha.,8.alpha -epidoxy sterols from four marine organisms. J Org Chem. 1981;46:3860–6.
Jinming G, Lin H, Jikai L. A novel sterol from Chinese truffles Tuber indicum. Steroids. 2001;66:771–5.
Koyama J, Morita I, Tagahara K, Aqil M. Bianthraquinones from Cassia siamea. Phytochemistry. 2001;56:849–51.
Harada N, Suzuki S, Uda H, Nakanishi K. Circular dichroism studies of dimeric fungal pigments, (-)-luteoskyrin and (+)-rugulosin. Chem Lett. 1972;1:67–70.
Koyama K, Aida S, Natori S. Supplemental observations on atropisomerism of fungal bis(naphtho-γ-pyrone)s. Chem Pharm Bull. 1990;38:2259–61.
Koyama K, Natori S, Iitaka Y. Absolute configurations of chaetochromin A and related bis (naphtho-γ-pyrone) mold metabolites. Chem Pharm Bull. 1987;35:4049–55.
Mason SF, Seal RH, Roberts DR. Optical activity in the biaryl series. Tetrahedron. 1974;30:1671–82.
Changsen C, Franzblau SG, Palittapongarnpim P. Improved green fluorescent protein reporter gene-based microplate screening for antituberculosis compounds by utilizing an acetamidase promoter. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47:3682–7.
Hunt L, Jordan M, De Jesus M, Wurm FM. GFP-expressing mammalian cells for fast, sensitive, noninvasive cell growth assessment in a kinetic mode. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1999;65:201–5.
O'Brien J, Wilson I, Orton T, Pongnan F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267:5421–6.
CLSI. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility test for bacteria that growth aerobically; 7th Approve Standard. Wayne PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2006. CLSI document M7-A7
CLSI. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 16th Informational Supplement. Wayne PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2006. CLSI document M100-S16
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (BIOTEC), National Science and Technology Development Agency (NSTDA), and Joint research grant from Thailand Research Fund (grant No. DBG5980002) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 81561148013). We thank Dr. Philip J. Shaw for manuscript editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note:
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Kornsakulkarn, J., Srichomthong, K. et al. Antimicrobial anthraquinones from cultures of the ant pathogenic fungus Cordyceps morakotii BCC 56811. J Antibiot 72, 141–147 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-018-0135-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-018-0135-y
This article is cited by
-
Two new diketopiperazines from the Cordyceps fungus Samsoniella sp. XY4
The Journal of Antibiotics (2023)
-
Geosmithia—widespread and abundant but long ignored bark beetle symbionts
Mycological Progress (2023)
-
Production of antimicrobial metabolites against pathogenic bacteria and yeasts by Fusarium oxysporum in submerged culture processes
Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering (2021)
-
Antibacterial and cytotoxic metabolites of termite-associated Streptomyces sp. BYF63
The Journal of Antibiotics (2020)