Abstract
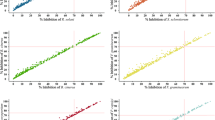
Phytopathogenic bacteria are a major cause of crop mortality and yield reduction, especially in field cultivation. The lack of effective chemistry agri-bactericides is responsible for challenging field prevention and treatment, prompting the development of long-lasting solutions to prevent, reduce, or manage some of the most devastating plant diseases facing modern agriculture today and in the future. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find lead drugs preventing and treating phytopathogenic bacterial infection. Drug repurposing, a strategy used to identify novel uses for existing approved drugs outside of their original indication, takes less time and investment than Traditional R&D Strategies in the process of drug development. Based on this method, we conduct a screen of 700 chemically diverse and potentially safe drugs against Xanthomonas oryzae PV. oryzae ACCC 11602 (Xoo), Xanthomonas axonopodis PV. citri (Xac), and Pectobacterium atrosepticum ACCC 19901 (Pa). Furthermore, the structure-activity relationship and structural similarity analysis of active drugs classify potent agri-bactericides into 8 lead series: salicylanilides, cationic nitrogen-containing drugs, azole antifungals, N-containing group, hydroxyquinolines, piperazine, kinase inhibitor and miscellaneous groups. MIC values were evaluated as antibacterial activities in this study. Identifying highly active lead compounds from the screening of approved drugs and comparison with the currently applied plant pathogenic bactericide to validate the bactericidal activity of the best candidates and assess if selected molecules or scaffolds lead to develop new antibacterial agents in the future. In conclusion, this study provides a possibility for the development of potent and highly selective agri-bactericides leads.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doebley JF, Gaut BS, Smith BD. The molecular genetics of crop domestication. Cell. 2006;127:1309–21.
Oerke EC, Dehne HW. Safeguarding production—losses in major crops and the role of crop protection. Crop Prot. 2004;23:275–85.
Atkinson D, Litterick AM, Walker KC, Walker R, Watson CA. Crop protection–what will shape the future picture? Pest Manag Sci. 2004;60:105–12.
Quintana-Rodriguez E, Duran-Flores D, Heil M, Camacho-Coronel X. Damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) as future plant vaccines that protect crops from pests. Sci horticulturae. 2018;237:207–20.
Mansfield J, Genin S, Magori S, Citovsky V, Sriariyanum M, Ronald P, et al. Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology: Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria. Mol plant Pathol. 2012;13:614–29.
Mattinen L, Nissinen R, Riipi T, Kalkkinen N, Pirhonen M. Host-extract induced changes in the secretome of the plant pathogenic bacterium Pectobacterium atrosepticum. Proteom (Weinh). 2007;7:3527–37.
Ke Y, Wu M, Zhang Q, Li X, Xiao J, Wang S. Hd3a and OsFD1 negatively regulate rice resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Biochemical biophysical Res Commun. 2019;513:775–80.
Cernadas RAS, Camillo LR, Benedetti CE. Transcriptional analysis of the sweet orange interaction with the citrus canker pathogens Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri and Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. aurantifolii. Mol plant Pathol. 2008;9:609–31.
Seck PA, Diagne A, Mohanty S, Wopereis MCS. Crops that feed the world 7: Rice. Food Security. 2012;4:7–24.
Li C, Zhang J, Ren Z, Xie R, Yin C, Ma W, et al. Development of ‘multiresistance rice’ by an assembly of herbicide, insect and disease resistance genes with a transgene stacking system. Pest Manag Sci. 2021;77:1536–47.
Le Dang Q, Shin TS, Park MS, Choi YH, Choi GJ, Jang KS, et al. Antimicrobial activities of novel mannosyl lipids isolated from the biocontrol fungus Simplicillium lamellicola BCP against phytopathogenic bacteria. J Agric Food Chem. 2014;62:3363–70.
Xiang M, Song YL, Ji J, Zhou X, Liu LW, Wang PY, et al. Synthesis of novel 18beta-glycyrrhetinic piperazine amides displaying significant in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities against intractable plant bacterial diseases. Pest Manag Sci. 2020;76:2959–71.
Wang P, Gao M, Zhou L, Wu Z, Hu D, Hu J, et al. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of pyridinium-tailored aromatic amphiphiles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016;26:1136–9.
Pan X, Xu S, Wu J, Luo J, Duan Y, Wang J, et al. Screening and characterization of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strains with resistance to pheazine-1-carboxylic acid. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2018;145:8–14.
Dai X, Zhao Y, Li J, Li S, Lei R, Chen X, et al. Thiazolium-derivative functionalized silver nanocomposites for suppressing bacterial resistance and eradicating biofilms. N. J Chem. 2018;42:1316–25.
Hao G-F, Yang S-G, Huang W, Wang L, Shen Y-Q, Tu W-L et al. Rational design of highly potent and slow-binding cytochrome bc(1) inhibitor as fungicide by computational substitution optimization. Sci Rep. 2015;5:1–10.
Lamberth C, Jeanmart S, Luksch T, Plant A. Current Challenges and Trends in the Discovery of Agrochemicals. Sci (Am Assoc Advancement Sci). 2013;341:742–6.
Demarque DP, Espindola LS. Challenges, advances and opportunities in exploring natural products to control arboviral disease vectors. Front Chem. 2021;9:1–10.
Sparks TC, Lorsbach BA. Perspectives on the agrochemical industry and agrochemical discovery. Pest Manag Sci. 2017;73:672–7.
Sparks TC, Wessels FJ, Lorsbach BA, Nugent BM, Watson GB. The new age of insecticide discovery-the crop protection industry and the impact of natural products. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2019;161:12–22.
Torres NS, Abercrombie JJ, Srinivasan A, Lopez-Ribot JL, Ramasubramanian AK, Leung KP. Screening a commercial library of pharmacologically active small molecules against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Antimicrobial agents Chemother. 2016;60:5663–72.
Wilkinson GF, Pritchard K. In vitro screening for drug repositioning. 20. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE Publications; 2015. p. 167–79.
Dudley JT, Deshpande T, Butte AJ. Exploiting drug-disease relationships for computational drug repositioning. Brief Bioinforma. 2011;12:303–11.
Kaiser M, Maser P, Tadoori LP, Ioset J-R, Brun R. Antiprotozoal activity profiling of approved drugs: a starting point toward drug repositioning. PloS One. 2015;10:e0135556–e0135556.
Novac N. Challenges and opportunities of drug repositioning. Trends Pharmacol Sci (Regul ed). 2013;34:267–72.
Oliveira IM, Borges A, Simões M The potential of drug repurposing to face bacterial and fungal biofilm infections. Recent Trends in Biofilm Science and Technology, 2020, pp 307-28.
Ashburn TT, Thor KB. Drug repositioning: identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat Rev Drug Disco. 2004;3:673–83.
Munos B. Lessons from 60 years of pharmaceutical innovation. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8:959–68.
Gu J, Gui Y, Chen L, Yuan G, Lu HZ, Xu X. Use of natural products as chemical library for drug discovery and network pharmacology. PloS One 2013;8:e6283.
Ohlson S, Duong-Thi M-D. Fragment screening for drug leads by weak affinity chromatography (WAC-MS). Methods (San Diego, Calif). 2018;146:26–38.
Nosengo N. New tricks for old drugs. Nat (Lond). 2016;534:314–6.
Delaney J, Clarke E, Hughes D, Rice M. Modern agrochemical research: a missed opportunity for drug discovery? Drug Discov today. 2006;11:839–45.
Li P, Hu D, Xie D, Chen J, Jin L, Song B. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of New Sulfone Derivatives Containing a 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Moiety as Active Antibacterial Agents. J Agric Food Chem. 2018;66:3093–3100.
Fan Z, Shi J, Luo N, Ding M, Bao X. Synthesis, crystal structure, and agricultural antimicrobial evaluation of novel quinazoline thioether derivatives incorporating the 1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyridine moiety. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67:11598–606.
Guo T, Xia R, Chen M, He J, Su S, Liu L, et al. Biological activity evaluation and action mechanism of chalcone derivatives containing thiophene sulfonate. RSC Adv. 2019;9:24942–50.
Luo HZ, Guan Y, Yang R, Qian GL, Yang XH, Wang JS, et al. Growth inhibition and metabolomic analysis of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae treated with resveratrol. BMC Microbiol. 2020;20:117.
Chen J, Wang X, Han H. A new function of graphene oxide emerges: inactivating phytopathogenic bacterium Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae. J Nanoparticle Res. 2013;15:1–14.
Wu S, Shi J, Chen J, Hu D, Zang L, Song B. Synthesis, Antibacterial Activity, and Mechanisms of Novel 6-Sulfonyl-1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole Derivatives. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69:4645–54.
Lefevere H, Bauters L, Gheysen G. Salicylic acid biosynthesis in plants. Front Plant Sci. 2020;11:1–7.
Kratky M, Stepankova S, Houngbedji N-H, Vosatka R, Vorcakova K, Vinsova J. 2-Hydroxy-N-phenylbenzamides and Their Esters Inhibit Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase. Biomolecules (Basel, Switzerland). 2019;9:698–714.
Yin X-D, Sun Y, Lawoe RK, Yang G-Z, Liu Y-Q, Shang X-F, et al. Synthesis and anti-phytopathogenic activity of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives. RSC Adv. 2019;9:387–99.
Park M, Cho Y-J, Lee YW, Jung WH. Understanding the mechanism of action of the anti-dandruff agent zinc pyrithione against Malassezia restricta. Sci Rep. 2018;8:12086–97.
Kim W, Zou G, Hari TPA, Wilt IK, Zhu W, Galle N, et al. A selective membrane-targeting repurposed antibiotic with activity against persistent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2019;116:16529–34.
Borelli C, Schaller M, Niewerth M, Nocker K, Baasner B, Berg D, et al. Modes of action of the new arylguanidine abafungin beyond interference with ergosterol biosynthesis and in vitro activity against medically important fungi. Chemother (Basel). 2008;54:245–59.
Srivastava J, Chandra H, Nautiyal AR, Kalra SJS. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and plant-derived antimicrobials (PDA(m)s) as an alternative drug line to control infections. 3 Biotech. 2014;4:451–60.
Cheng G, Ning J, Ahmed S, Huang J, Ullah R, An B et al. Selection and dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in Agri-food production. Antimicrobial Resistance Infection Control. 2019;8:158–71.
Compri M, Mader R, Mazzolini E, de Angelis G, Mutters NT, Rajendran NB, et al. White Paper: Bridging the gap between surveillance data and antimicrobial stewardship in the animal sector-practical guidance from the JPIAMR ARCH and COMBACTE-MAGNET EPI-Net networks. J Antimicrobial Chemother. 2020;75:52–66.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22177043, 21877056) and The Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (20JR5RA311); Support was also supplied by the Key Program for international S&T cooperation projects of China Gansu Province (18YF1WA115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Wang, YR., He, YH. et al. Drug repurposing strategy part 1: from approved drugs to agri-bactericides leads. J Antibiot 76, 27–51 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-022-00574-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-022-00574-y