Abstract
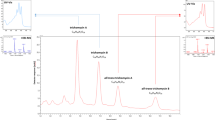
In an effort to identification of the unknown impurities in milbemycin oxime (MO) bulk drug, three impurities 1, 2 and 3 were isolated by two-dimensional (2 D) preparation method (Agilent Zorbax-C3 preparative column and Sepax Amethyst C18-H preparative column). Based on the extensive NMR analysis and ESIMS data, the structures of the three impurities were established as 14-desmethyl-14-ethyl-MO A4 (1), 24-desmethyl-24-ethyl-MO A4 (2) and 12-desmethyl-12-ethyl-MO A4 (3), respectively. They are the new isomer impurities of MO D and most likely originate from the oxidation and oximation of natural milbemycin homologs present in the original fermentation broth.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim MS, Cho WJ, Song MC, Park SW, Kim K, Kim E, et al. Engineered biosynthesis of milbemycins in the avermectin high-producing strain Streptomyces avermitilis. Micro Cell Fact. 2017;16:9.
Shoop WL, Mrozik H, Fisher MH. Structure and activity of avermectins and milbemycins in animal health. Vet Parasitol. 1995;59:139–56.
Carter GT, Nietsche JA, Hertz MR, Williams DR, Siegel MM. LL-F28249 antibiotic complex: a new family of antiparasitic macrocyclic lactones. J Antibiot. 1988;41:519–29.
Takiguchi Y, Mishima H, Okuda M, Terao M, Aoki A, Fukuda R. Milbemycins, a new family of macrolide antibiotics: fermentation, isolation and physico-chemical properties. J Antibiot. 2006;33:1120–7.
Wang HY, Liu YQ, Cheng X, Zhang YY, Li SS, Wang XJ, et al. Titer improvement of milbemycins via coordinating metabolic competition and transcriptional co-activation controlled by Streptomyces antibiotic regulatory protein family regulator in Streptomyces bingchenggensis. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2022;119:1252–63.
Yan YS, Xia HY. Recent advances in the research of milbemycin biosynthesis and regulation as well as strategies for strain improvement. Arch Micrbiol. 2021;203:5849–57.
Jung M, Saito A, Buescher G, Maurer M, Graf JF. Chemistry, pharmacology and safety: milbemycin oxime. In: Vercruysse J, Rew RS, editors. Macrocyclic lactones in antiparasitic therapy. New York: CABI Publishing; 2002. pp. 51–74.
European Medicines Agency. Milbemycin oxime for veterinary use monograph, European Pharmacopoeia. 10th ed. 2020. pp. 3272–5.
US Pharmcopeial Convention. Milbemycin oxime monograph, USP40-NF-35. 2017. pp. 8819–21.
Mishima H, Ide J, Muramatsu S, Ono M. Milbemycins, a new family of macrolide antibiotics. Structure determination of milbemycins D, E, F, G, H, J and K. J Antibiot. 1983;36:980–90.
Ono M, Mishima H, Takiguchi Y, Terao M, Kobayashi H, Iwasaki S, et al. Milbemycins, a new family of macrolide antibiotics. Studies on the biosynthesis of milbemycins α2, α4 and D using 13C labeled precursors. J Antibiot. 1983;36:991–1000.
Okazaki T, Ono M, Aoki A, Fukuda R. Milbemycins, a new family of macrolide antibiotics: producing organism and its mutants. J Antibiot. 1983;36:438–41.
Tsukamoto Y, Sato K, Mio S, Sugai S, Yanai T, Kitano N, et al. Synthesis of 5-keto-5-oxime derivatives of milbemycins and their activities against microfilariae. Agric Biol Chem. 1991;55:2615–21.
Adhikari S, Rustum AM. Structural elucidation of major degradation products of milbemycin oxime drug substance using LC-MS and NMR. J Pharm Biomed. 2022;217:114862.
Toranmal S, Buchade R, Tandale S, Wagh V, Chaure P. Development and validation of stability indicating HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of milbemycin oxime and praziquantel from bulk and marketed formulation. J Pharm Sci Res. 2019;11:3108–15.
Huang J, He J, Rustum AM. Development and validation of a stability-indicating HPLC method for assay of milbemycin oxime and estimation of its related compounds. Chromatographia. 2021;84:483–98.
Letendre L, Harriman J, Drag M, Mullins A, Malinski T, Rehbein S. The intravenous and oral pharmacokinetics of afoxolaner and milbemycin oxime when used as a combination chewable parasiticide for dogs. J Vet Pharm Ther. 2017;40:35–43.
ICH Guidelines, Q3A (R2), Impurities in new drug substances. In: The International Council On Harmonisation Of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals For Human Use, Geneva. 2006.
Zhang H, Zhang SY, Zhang J, Qi H, Wang H, Zhang LQ, et al. Acyltransferase domain swapping for the production of tenvermectin B metabolites in genetically engineered strain streptomyces avermitilis HU02. J Agric Food Chem. 2022;70:11994–2003.
Tsukamoto Y, Kajino H, Sato K, Tanaka KJ, Yanai T. Synthesis of 24a-substituted milbemycin A4 derivatives and their acaricidal activity against Tetranychus urticae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1997;61:806–12.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LGN22B020002), School-enterprise Cooperation Project from Domestic Visiting Engineers of Colleges and Universities (Grant No.: FG2023314), Huzhou Public Welfare Research Project (2021GZ25) and Taizhou Science and Technology Plan Project (24nyb10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, X., Lu, J., Wu, Y. et al. Isolation and identification of three new isomer impurities in milbemycin oxime drug substance. J Antibiot 78, 106–112 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-024-00791-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-024-00791-7