Abstract
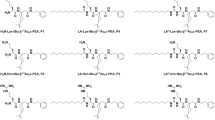
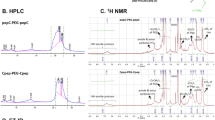
Despite decades of investigation, multidrug-resistant bacterial resistance has become the leading health concern globally related to MRSA infections, where conventional antibiotics have failed in this race. However, the development of short cationic antimicrobial peptides with higher efficacy and low cytotoxicity has encouraged our recent exploration. Herein, we describe the synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial evaluation of tetrahydropiperic acid (THPA) conjugate αβ-hybrid peptides, THPA-Lys-tBu-β3,3Ac6c-PEA, P1; THPA-Orn-tBu-β3,3Ac6c-PEA, P2, and THPA-Arg-tBu-β3,3Ac6c-PEA, P3. Our investigation revealed peptide P3 exhibited low hemolytic and best safety index along with higher bactericidal potency against MRSA. Combinatorial study with vancomycin suggested synergistic effect. Mechanistic investigations revealed membrane disruption of MRSA by the peptide. This study suggested that peptide P3 could be an effective therapeutic option to resist the emergence of MRSA-related infections.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Plotted and analysed data in support of the research article were included along with supporting information. The raw data produced throughout the present investigation are accessible from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ferrara F, Castagna T, Pantolini B, Campanardi MC, Roperti M, Grotto A, et al. The challenge of antimicrobial resistance (AMR): Current status and future prospects. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharm. 2024;397:9603–15.
Ahmed SK, Hussein S, Qurbani K, Ibrahim RH, Fareeq A, Mahmood KA, Mohamed MG. Antimicrobial resistance: impacts, challenges, and future prospects. J Med, Surg, Public Health. 2024;2:100081.
Algammal AM, Hetta HF, Elkelish A, Alkhalifah D, Hozzein WN, Batiha GE, El Nahhas N, Mabrok MA. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): one health perspective approach to the bacterium epidemiology, virulence factors, antibiotic-resistance, and zoonotic impact. Infect Drug Resistance. 2020;13:3255–65.
Robinson DA, Enright MC. Evolutionary models of the emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. 2003;47:3926–34.
Savitskaya A, Masso-Silva J, Haddaoui I, Enany S. Exploring the arsenal of antimicrobial peptides: Mechanisms, diversity, and applications. Biochimie. 2023;214:216–27.
Wang L, Wang N, Zhang W, Cheng X, Yan Z, Shao G, Wang X, Wang R, Fu C. Therapeutic peptides: current applications and future directions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7:48.
Drayton M, Kizhakkedathu JN, Straus SK. Towards robust delivery of antimicrobial peptides to combat bacterial resistance. Molecules. 2020;25:3048.
Mahlapuu M, Håkansson J, Ringstad L, Björn C. Antimicrobial peptides: an emerging category of therapeutic agents. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016;6:194.
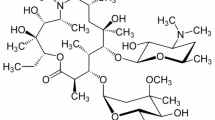
Ma C, He N, Ou Y, Feng W. Design and synthesis of new vancomycin derivatives. ChemistrySelect. 2020;5:6670–3.
Wu Z-C, Isley NA, Boger DL. N-Terminus alkylation of vancomycin: Ligand binding affinity, antimicrobial activity, and site-specific nature of quaternary trimethylammonium salt modification. ACS Infect Dis. 2018;4:1468–74.
Velkov T, Thompson PE, Nation RL, Li J. Structure− activity relationships of polymyxin antibiotics. J Med Chem. 2010;53:1898–916.
Wang M, Rakesh KP, Leng J, Fang WY, Ravindar L, Channe Gowda D, Qin HL. Amino acids/peptides conjugated heterocycles: a tool for the recent development of novel therapeutic agents. Bioorg Chem. 2018;76:113–29.
De Zoysa GH, Cameron AJ, Hegde VV, Raghothama S, Sarojini V. Antimicrobial peptides with potential for biofilm eradication: synthesis and structure activity relationship studies of battacin peptides. J Med Chem. 2015;58:625–39.
Wani NA, Singh G, Shankar S, Sharma A, Katoch M, Rai R. Short hybrid peptides incorporating β-and γ-amino acids as antimicrobial agents. Peptides. 2017;97:46–53.
Kumar D, Rahman Sarkar A, Iqbal Andrabi N, Assim Haq S, Ahmed M, Kumar Shukla S, Ahmed Z, Rai R. Synthesis, characterization, and anti-inflammatory activity of tetrahydropiperine, piperic acid, and tetrahydropiperic acid via down regulation of NF-κB pathway. Cytokine. 2024;178:156578.
Ur Rahim J, Singh G, Shankar S, Katoch M, Rai R. Tetrahydropiperic acid (THPA) conjugated cationic hybrid dipeptides as antimicrobial agents. J Antibiotics. 2021;74:480–3.
Humphries R, Bobenchik AM, Hindler JA, Schuetz AN. Overview of changes to the clinical and laboratory standards institute performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, M100. J Clin Microbiol. 2021;59:10–1128.
Lambert R, Pearson J. Susceptibility testing: accurate and reproducible minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and non-inhibitory concentration (NIC) values. J Appl Microbiol. 2000;88:784–90.
Pandey BK, Ahmad A, Asthana N, Azmi S, Srivastava RM, Srivastava S, Verma R, Vishwakarma AL, Ghosh JK. Cell-selective lysis by novel analogues of melittin against human red blood cells and Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 2010;49:7920–9.
Chowdhary R, Rathore A, Sarkar AR, Kumari J, Manhas R, Firdous S, Mahapa A, Rai R. Antibacterial activity of 2-(4-aminopiperidin-4-yl) acetic acid (β3, 3-Pip) and Its peptide conjugated with lauric acid through the side chain against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Micro Pathogenesis. 2025;205:107693.
Upadhyay A, Pal D, Kumar A. Development of an innovative method of Salmonella Typhi biofilm quantification using Tetrahydrofuran and Response Surface Methodology. Micro Pathogenesis. 2025;208:107992.
Syal K. Novel method for quantitative estimation of biofilms. Curr Microbiol. 2017;74:1194–9.
Manhas R, Rathore A, Havelikar U, Mahajan S, Gandhi SG, Mahapa A. Uncovering the potentiality of quinazoline derivatives against Pseudomonas aeruginosa with antimicrobial synergy and SAR analysis. J Antibiotics. 2024;77:365–81.
Hall M, Middleton R, Westmacott D. The fractional inhibitory concentration (FIC) index as a measure of synergy. J Antimicrobial Chemother. 1983;11:427–33.
Firdous S, Sarkar AR, Manhas R, Chowdhary R, Rathore A, Kumari J, Rai R, Mahapa A. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of urea-containing α/β hybrid peptides against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. ACS Omega. 2025;10:2102–15.
Huo S, Chen C, Lyu Z, Zhang S, Wang Y, Nie B, Yue B. Overcoming planktonic and intracellular Staphylococcus aureus-associated infection with a cell-penetrating peptide-conjugated antimicrobial peptide. ACS Infect Dis. 2020;6:3147–62.
Oyama LB, Olleik H, Teixeira A, Guidini MM, Pickup JA, Hui B, Vidal N, Cookson AR, Vallin H, Wilkinson T, Bazzolli D, Richards J, Wootton M, Mikut R, Hilpert K, Maresca M, Perrier J, Hess M, Mantovani HC, Fernandez-Fuentes N, Creevey CJ, Huws SA. In silico identification of two peptides with antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. npj Biofilms Microbiomes. 2022;8:58.
Sarkar AR, Kumari J, Rathore A, Chowdhary R, Manhas R, Firdous S, Mahapa A, Rai R. Antimicrobial activity of α/β hybrid peptides incorporating tBu-β3, 3Ac6c against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antibiotics. 2024;77:794–801.
Shankar S, Jyothi D, Rahim J, Pal PC, Singh UP, Rai R. Conformation of achiral α/β hybrid peptides containing glycine and 1-aminocyclohexaneacetic acid. ChemistrySelect. 2022;7:e202104453.
Ur Rahim J, Ahmad SM, Amin T, Chowdhary R, Goswami A, Rai R. Synthesis, conformation and cytotoxic activity of short hybrid peptides containing conformationally constrained 1-(aminomethyl) cyclohexanecarboxylic acid and gabapentin. Peptides. 2022;158:170897.
Xiong J, Ashraf U, Ye J, Cao S. Extracellular vesicles in pathogenic infection, transmission, and immunity. Engineering. 2024;43:228–40.
Álvarez A, Fernández L, Gutiérrez D, Iglesias B, Rodríguez A, García P. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in hospitals: Latest trends and treatments based on bacteriophages. J Clin Microbiol. 2019;57:10–1128.
Guo X, An Y, Yan T, Jia Y, Jiao R, Cai X, Yang W, Bao G, Sun W, Yang W, Lu N, Xie J. Halogenated sulfono-γ-AApeptides modified cationic AMPs have enhanced stability and therapeutic potential against clinically important MDR infections. ACS Infect Dis. 2025;11:2018–36.
Chen N, Jiang C. Antimicrobial peptides: structure, mechanism, and modification. Eur J Med Chem. 2023;255:115377.
Sharif S, Yadav AK. Bacterial biofilm and its role in antibiotic resistance. Microbe. 2025;7:100356.
Acknowledgements
RR acknowledges support by the research project GAP-3102 under the NDTL initiative. AM acknowledges Indian Council of Medical Research, India (ICMR) Research Grant IIRP2023-0715, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) CSIR-MMP075202 and ANRF-SRG SRG/2023/000145 projects for financial support. The authors thank the CSIR-Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (CSIR-IIIM), Jammu, for providing the necessary environment, facilities, and instrumentation. AR, JK, and SF thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India, and the University Grant Commission (UGC), India, for providing the fellowship grants. RM thanks the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) for providing the project fellowship. The authors acknowledge Dr. Ramajayan Pandian for providing the Rabbit’s blood sample for the hemolysis assay (Institutional Animal Ethics Committee IAEC No.406/85/8/2024). The manuscript have assigned an institutional communication no. CSIR-IIIM/IPR/00957.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AR and BR contributed correspondingly to the research. AR and BR accomplished the experiments and analyzed the whole data. ARS, JK, RM, BS and SF aided in experimentation, data collection, analysis, and interpretation. RC and FM provided additional support in experimental execution and helped with preliminary data processing. RR and AM contributed to conceptualization, methodology expansion, overall guidance, critical revision of the manuscript and supervision. RR and AM equally supervised the whole research. All authors in the article read and accepted the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rathore, A., Rashid, B., Sarkar, A.R. et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of optimized THPA conjugated dipeptides against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antibiot 79, 15–29 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-025-00877-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-025-00877-w