Abstract
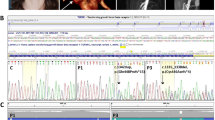
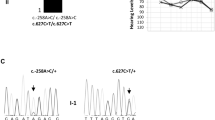
Variants in TGFBR1 have been reported to induce two completely distinct diseases, namely Loeys–Dietz syndrome (LDS) and multiple self-healing squamous epithelioma (MSSE). However, detailed mechanisms underlying this effect remain unknown. We report a Japanese familial case of LDS with a novel splice donor site variant in TGFBR1 gene (c.973 + 1 G > A; NG_007461.1). The intronic variant was predicted to mediate in-frame exon 5 skipping within the serine/threonine kinase (STK) domain, which may also be mediated by a similar TGFBR1 variant of a splice acceptor site in intron 4 (c.806-2 A > C), identified in a British familial case of MSSE. Therefore, ex vivo splicing and functional assays were performed in mammalian cells to evaluate the effect of these sequence variants. The MSSE variant activated a cryptic acceptor site at 76 bp downstream of the 3′ natural splice acceptor site, which produced an out-of-frame transcript (r.807_882del, p.Asn270Thrfs*8). In contrast, the LDS variant generated two types of in-frame transcription products, r.[806_973del, 965_973 del], and produced two functionally inactivated proteins, p.[Asp269_Gln324del, Thr323_Gly325del], as a result of exon 5 skipping and the activation of a cryptic donor splice site at 9 bp upstream of the 5′ natural splice donor site, respectively. Our results support the previously proposed but not yet approved mechanism that dominant-negative and truncating variants in STK domain induce LDS and MSSE, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Loeys BL, Chen J, Neptune ER, et al. A syndrome of altered cardiovascular, craniofacial, neurocognitive and skeletal development caused by mutations in TGFBR1 or TGFBR2. Nat Genet. 2005;37:275–281.
Roman MJ, Devereux RB, Kramer-Fox R, O’Loughlin J. Two-dimensional echocardiographic aortic root dimensions in normal children and adults. Am J Cardiol. 1989;64:507–512.
Loeys BL, Schwarze U, Holm T, et al. Aneurysm syndromes caused by mutations in the TGF-beta receptor. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:788–798.
Cardoso S, Robertson SP, Daniel PB. TGFBR1 mutations associated with Loeys-Dietz syndrome are inactivating. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2012;32:150–155.
Horbelt D, Guo G, Robinson PN, Knaus P. Quantitative analysis of TGFBR2 mutations in Marfan-syndrome-related disorders suggests a correlation between phenotypic severity and Smad signaling activity. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:4340–4350.
Goudie DR, D’Alessandro M, Merriman B, et al. Multiple self-healing squamous epithelioma is caused by a disease-specific spectrum of mutations in TGFBR1. Nat Genet. 2011;43:365–369.
Robertson SJ, Bashir SJ, Pichert G, Robson A, Whittaker S. Severe exacerbation of multiple self-healing squamous epithelioma (Ferguson-Smith disease) with radiotherapy, which was successfully treated with acitretin. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35:e100–e102.
Takeda N, Morita H, Fujita D, et al. A deleterious MYH11 mutation causing familial thoracic aortic dissection. Hum Genome Var. 2015;2:15028.
Hara H, Takeda N, Morita H, et al. Three novel BMPR2 mutations associated with advanced pulmonary arterial hypertension. Hum Genome Var. 2017;4:17010.
Muro AF, Caputi M, Pariyarath R, Pagani F, Buratti E, Baralle FE. Regulation of fibronectin EDA exon alternative splicing: possible role of RNA secondary structure for enhancer display. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:2657–2671.
Shapiro MB, Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987;15:7155–7174.
Stenson PD, Mort M, Ball EV, et al. The Human Gene Mutation Database: 2008 update. Genome Med. 2009;1:13.
Zhu X, Need AC, Petrovski S, Goldstein DB. One gene, many neuropsychiatric disorders: lessons from Mendelian diseases. Nat Neurosci. 2014;17:773–781.
Takeshima Y, Yagi M, Okizuka Y, et al. Mutation spectrum of the dystrophin gene in 442 Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy cases from one Japanese referral center. J Hum Genet. 2010;55:379–388.
Malan V, Rajan D, Thomas S, et al. Distinct effects of allelic NFIX mutations on nonsense-mediated mRNA decay engender either a Sotos-like or a Marshall-Smith syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2010;87:189–198.
Akhurst RJ. The paradoxical TGF-beta vasculopathies. Nat Genet. 2012;44:838–839.
Takeda N, Yagi H, Hara H, et al. Pathophysiology and Management of Cardiovascular Manifestations in Marfan and Loeys-Dietz Syndromes. Int Heart J. 2016;57:271–277.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the patient and her family for their participation in this study. This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Research on Rare and Intractable Diseases from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (N.T.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara, T., Takeda, N., Hara, H. et al. Distinct variants affecting differential splicing of TGFBR1 exon 5 cause either Loeys–Dietz syndrome or multiple self-healing squamous epithelioma. Eur J Hum Genet 26, 1151–1158 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-018-0127-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-018-0127-1
This article is cited by
-
Truncating variants in the penultimate exon of TGFBR1 escaping nonsense-mediated mRNA decay cause Loeys-Dietz syndrome
European Journal of Human Genetics (2023)
-
The implications of alternative pre-mRNA splicing in cell signal transduction
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
Association of gene polymorphisms in MYH11 and TGF-β signaling with the susceptibility and clinical outcomes of DeBakey type III aortic dissection
Mammalian Genome (2022)
-
Activation of TGF-β signaling in an aortic aneurysm in a patient with Loeys-Dietz syndrome caused by a novel loss-of-function variant of TGFBR1
Human Genome Variation (2019)