Abstract
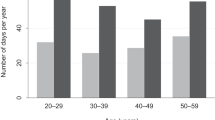
Most research on psychosocial consequences of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) has focused on the relationship between disease factors and cognitive functioning. NF1 may impair domains of learning and attention, resulting in low academic performance. This study is the first nationwide population-based cohort study to investigate educational attainment and delay in completing mandatory school by persons with NF1. Educational information was collected from 550 persons at the age of 30 (born 1965–1984). They were diagnosed with NF1 in Denmark and compared to a cohort of NF1-free persons matched on gender and age (n = 4295). Multinomial logistic models were applied to estimate odds ratios (ORs) for obtaining short (≤9 years) or medium (10–12 years) education compared to long education (>12 years) by the age of 30 years. We calculated the probability of graduating 9th year of mandatory school at different ages in 932 persons with NF1 and 7962 NF1-free persons (born 1965–2000) using quantile regression. The OR of educational completion for short- and medium-term education was three fold (95% CI 2.55–3.99) and 1.29 fold (95% CI 0.99–1.69) higher, respectively, for persons with NF1 than NF1-free persons after adjusting for birth year, gender, psychiatric and somatic morbidity and mother’s education. Persons with NF1 were significantly delayed in graduating mandatory school education compared to NF1-free persons. When 90% of persons have graduated, persons with NF1 were 1.2 times older than the NF1-free persons. Experiencing delays in mandatory school likely affect further educational achievements and may impair employment and entering work force.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Williams VC, Lucas J, Babcock MA, Gutmann DH, Korf B, Maria BL. Neurofibromatosis type 1 revisited. Pediatrics. 2009;123:124–33.
D Gareth R Evans, Catherine O’Hara, Anna Wilding, Sarah L Ingham, Elizabeth Howard, John Dawson, et al. Mortality in neurofibromatosis 1: in North West England: an assessment of actuarial survival in a region of the UK since 1989. Eur J Hum Genet. 2011;19:1187–91.
Tu Anh Duong, Emilie Sbidian, Laurence Valeyrie-Allanore, Cédric Vialette, Salah Ferkal, Smaïl Hadj-Rabia, et al. Mortality associated with neurofibromatosis 1: a cohort study of 1895 patients in 1980-2006 in France. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2011;6:18.
Rasmussen Sa, Yang Q, Friedman JM. Mortality in neurofibromatosis 1: an analysis using U.S. death certificates. Am J Hum Genet. 2001;68:1110–8.
Ferner RE. Neurofibromatosis 1 and neurofibromatosis 2: a twenty first century perspective. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:340–51.
Ozonoff S. Cognitive impairment in neurofibromatosis type 1. Am J Med Genet. 1999;89:45–52.
Boyd K, Korf B, Theos A. Neurofibromatosis type 1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:1–16.
Friedman JM, Birch PH. Type 1 neurofibromatosis: a descriptive analysis of the disorder in 1,728 patients. Am J Med Genet. 1997;143:138–43.
Costa RM, Silva AJ. Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the cognitive deficits associated with neurofibromatosis 1. J Child Neurol. 2002;17:646–51. 622–9
Garwood MM, Bernacki JM, Fine KM, Hainsworth KR, Davies WH, Klein-Tasman BP. Physical, cognitive, and psychosocial predictors of functional disability and health-related quality of life in adolescents with neurofibromatosis-1. Pain Res Treat. 2012;2012:975364.
Lianne C Krab, Femke K Aarsen, Arja de Goede-Bolder, Coriene E Catsman-Berrevoets, Willem F Arts, Henriette A Moll, et al. Impact of neurofibromatosis type 1 on school performance. J Child Neurol. 2008;23:1002–10.
Hyman SL, Shores A, North KN. The nature and frequency of cognitive deficits in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Neurology. 2005;65:1037-44.
Descheemaeker M, Plasschaert E, Frijns J, Legius E. Neuropsychological profile in adults with neurofibromatosis type 1 compared to a control group. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2012;1:1–13.
Kenborg L, Duun-Henriksen AK, Dalton SO, Bidstrup PE, Doser K, Rugbjerg K, et al. Rates and Nature of Hospitalisations in Neurofibromatosis 1: A Danish population-based cohort study. 2019 (in preparation).
Orraca-Castillo M, Estévez-Pérez N, Reigosa-Crespo V. Neurocognitive profiles of learning disabled children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014;8:386.
Cutting LE, Levine TM. Cognitive profile of children with neurofibromatosis and reading disabilities. Child Neuropsychol. 2010;16:417–32.
Gilboa Y, Rosenblum S, Fattal-Valevski A, Toledano-Alhadef H, Josman N. Is there a relationship between executive functions and academic success in children with neurofibromatosis type 1? Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2014;2011:1–18.
Watt SE, Shores A, North KN. An examination of lexical and sublexical reading skills in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Child Neuropsychol. 2008;14:401–18.
Hilda A Crawford, Belinda Barton, Meredith J Wilson, Yemima Berman, Valerie J McKelvey-Martin, Patrick J Morrison, et al. The impact of neurofibromatosis type 1 on the health and wellbeing of Australian adults. J Genet Couns. 2015;24:931–44.
Barton B, North K. Social skills of children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2004;46:553–63.
Coudé FX, Mignot C, Lyonnet S, Munnich A. Academic impairment is the most frequent complication of neurofibromatosis type-1 (NF1) in children. Behav Genet. 2006;36:660–4.
Granström S, Friedrich RE, Langenbruch AK, Augustin M, Mautner VF. Influence of learning disabilities on the tumour predisposition syndrome NF1—Survey from adult patients’ perspective. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:3675–81.
Pedersen CB, Gøtzsche H, Møller JO, Mortensen PB. The Danish Civil Registration System. a cohort of eight million persons. Dan Med Bull. 2006;53:441–9.
Lynge E, Sandegaard JL, Rebolj M. The Danish National Patient Register. Scand J Public Health. 2011;39:30–3.
Jensen VM, Rasmussen AW. Danish education registers. Scand J Public Health. 2011;39:91–4.
EaGE M for C. Overview of the Danish education system. 2016. http://eng.uvm.dk/general-overview/overview-of-the-danish-education-system. Accessed 09 February 2019.
UNESCO. International standard classification of education ISCED 1997. p.48. (UNESCO Institute for Statistics: Montreal, Quebec, Canada) 2006.
Mors O, Perto GP, Mortensen PB. The Danish Psychiatric Central Research Register. Scand J Public Health. 2011;39:54–7.
Williams RL, Box PO, Carolina N. A note on robust variance estimation for cluster-correlated data. Biometrics. 2000;56:645–6.
Cohen JS, Levy HP, Sloan J, Dariotis J, Biesecker BB. Depression among adults with neurofibromatosis type 1: prevalence and impact on quality of life. Clin Genet. 2015;88:425–30.
Augusto Pasini, Adriana Lo-Castro, Loredana Di Carlo, Mariabernarda Pitzianti, Martina Siracusano, Caterina Rosa, et al. Detecting anxiety symptoms in children and youths with neurofibromatosis type I. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2012;159B:869–73.
StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 14. College Station, TX: StataCorp LP. 2015.
SAS Institute Inc. SAS 9.1.3. SAS Institute Inc. 2005.
Granstrom S, Friedrich RE, Langenbruch AK, Augustin M, Mautner V-F. Influence of learning disabilities on the tumour predisposition syndrome NF1--survey from adult patients’ perspective. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:3675–81.
Hyman S, Shores A, North KN. Learning disabilities in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: subtypes, cognitive profile, and attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2006;48:973–7.
Descheemaeker MJ, Ghesquière P, Symons H, Fryns JP, Legius E. Behavioural, academic and neuropsychological profile of normally gifted Neurofibromatosis type 1 children. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2005;49:33–46.
Ginsberg Y, Beusterien KM, Amos K, Jousselin C, Asherson P. The unmet needs of all adults with ADHD are not the same: a focus on Europe. Expert Rev Neurother. 2014;14:799–812.
Coudé FX, Mignot C, Lyonnet S, Munnich A. Early grade repetition and inattention associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. J Atten Disord. 2007;11:101–5.
Pride NA, Payne JM, North KN. The Impact of ADHD on the cognitive and academic functioning of children with NF1. Dev Neuropsychol. 2012;37:590–600.
European Commission. Education and training monitor 2017 Denmark. Education and training. Vol. 2. Luxemburg: Publications Office of the European Union. 2017.
Koch S, Kejs AMT, Engholm G, Johansen C, Schmiegelow K. Educational attainment among survivors of childhood cancer: a population-based cohort study in Denmark. Br J Cancer. 2004;91:923–8.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command, through the Neurofibromatosis Research Program under Award No. W81XWH-14-1-0054. Opinions, interpretations, conclusions and recommendations are those of the author and are not necessarily endorsed by the U.S. Army.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doser, K., Kenborg, L., Andersen, E.W. et al. Educational delay and attainment in persons with neurofibromatosis 1 in Denmark. Eur J Hum Genet 27, 857–868 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-019-0359-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-019-0359-8
This article is cited by
-
Neurocognitive functioning in adults with neurofibromatosis type 1- a nationwide population-based study
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2024)
-
The contribution of morbidity and unemployment for the reduced labor market participation of individuals with neurofibromatosis 1 in Finland
European Journal of Human Genetics (2024)
-
Employment, occupation, and income in adults with neurofibromatosis 1 in Denmark: a population- and register-based cohort study
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2023)
-
School performance of children with neurofibromatosis 1: a nationwide population-based study
European Journal of Human Genetics (2022)
-
Forming and ending marital or cohabiting relationships in a Danish population-based cohort of individuals with neurofibromatosis 1
European Journal of Human Genetics (2020)