Abstract
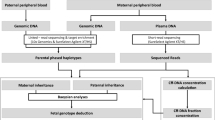
Direct haplotyping enables noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT) without analyzing proband, which is a promising strategy for pregnancies at risk of an inherited single-gene disorder. Here, we aimed to expand the scope of single-gene disorders that NIPT using linked-read direct haplotyping would be applicable to. Three families at risk of myotonic dystrophy type 1, lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy were recruited. All cases exhibited distinct characteristics that are often encountered as hurdles (i.e., repeat expansion, identical variants in both parents, and novel variants with retrotransposon insertion) in the universal clinical application of NIPT. Direct haplotyping of parental genomes was performed by linked-read sequencing, combined with allele-specific PCR, if necessary. Target DMPK, STAR, and FKTN genes in the maternal plasma DNA were sequenced. Posterior risk calculations and an Anderson–Darling test were performed to deduce the maternal and paternal inheritance, respectively. In all cases, we could predict the inheritance of maternal mutant allele with > 99.9% confidence, while paternal mutant alleles were not predicted to be inherited. Our study indicates that direct haplotyping and posterior risk calculation can be applied with subtle modifications to NIPT for the detection of an expanded range of diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lo YM, Corbetta N, Chamberlain PF, Rai V, Sargent IL, Redman CW, et al. Presence of fetal DNA in maternal plasma and serum. Lancet. 1997;350:485–7.
Hudecova I, Chiu RW. Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis of thalassemias using maternal plasma cell free DNA. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;39:63–73.
Wong FC, Lo YM. Prenatal diagnosis innovation: genome sequencing of maternal plasma. Annu Rev Med. 2016;67:419–32.
Chitty LS, Lo YM. Noninvasive prenatal screening for genetic diseases using massively parallel sequencing of maternal plasma DNA. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015;5:a023085.
Chiu EKL, Hui WWI, Chiu RWK. cfDNA screening and diagnosis of monogenic disorders - where are we heading? Prenat Diagn. 2018;38:52–58.
Wong AI, Lo YM. Noninvasive fetal genomic, methylomic, and transcriptomic analyses using maternal plasma and clinical implications. Trends Mol Med. 2015;21:98–108.
Hui WW, Jiang P, Tong YK, Lee WS, Cheng YK, New MI, et al. Universal haplotype-based noninvasive prenatal testing for single gene diseases. Clin Chem. 2017;63:513–24.
Zheng GX, Lau BT, Schnall-Levin M, Jarosz M, Bell JM, Hindson CM, et al. Haplotyping germline and cancer genomes with high-throughput linked-read sequencing. Nat Biotechnol. 2016;34:303–11.
Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1754–60.
Bishara A, Liu Y, Weng Z, Kashef-Haghighi D, Newburger DE, West R, et al. Read clouds uncover variation in complex regions of the human genome. Genome Res. 2015;25:1570–80.
Lo YM, Chan KC, Sun H, Chen EZ, Jiang P, Lun FM, et al. Maternal plasma DNA sequencing reveals the genome-wide genetic and mutational profile of the fetus. Sci Transl Med. 2010;2:61ra91.
Vermeulen C, Geeven G, de Wit E, Verstegen M, Jansen RPM, van Kranenburg M, et al. Sensitive monogenic noninvasive prenatal diagnosis by targeted haplotyping. Am J Hum Genet. 2017;101:326–39.
Lim BC, Lee S, Shin JY, Hwang H, Kim KJ, Hwang YS, et al. Molecular diagnosis of congenital muscular dystrophies with defective glycosylation of alpha-dystroglycan using next-generation sequencing technology. Neuromuscul Disord. 2013;23:337–44.
Lim BC, Ki CS, Kim JW, Cho A, Kim MJ, Hwang H, et al. Fukutin mutations in congenital muscular dystrophies with defective glycosylation of dystroglycan in Korea. Neuromuscul Disord. 2010;20:524–30.
Jang SS, Lim BC, Yoo SK, Shin JY, Kim KJ, Seo JS, et al. Targeted linked-read sequencing for direct haplotype phasing of maternal DMD alleles: a practical and reliable method for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis. Sci Rep. 2018;8:8678.
Christenson LK, Strauss JF 3rd. Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) and the intramitochondrial translocation of cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1529:175–87.
Kim CJ. Congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2014;19:179–83.
Xia LC, Bell JM, Wood-Bouwens C, Chen JJ, Zhang NR, Ji HP. Identification of large rearrangements in cancer genomes with barcode linked reads. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:e19.
Camunas-Soler J, Lee H, Hudgins L, Hintz SR, Blumenfeld YJ, El-Sayed YY, et al. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of single-gene disorders by use of droplet digital PCR. Clin Chem. 2018;64:336–45.
Acknowledgements
Funding
This study was supported by grant 03-2016-0050 from the Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
41431_2020_759_MOESM6_ESM.docx
Supplemental Table 5. Expected haplotype representations in maternal plasma for each given fractional fetal concentration
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JS., Lee, K.B., Song, H. et al. Noninvasive prenatal test of single-gene disorders by linked-read direct haplotyping: application in various diseases. Eur J Hum Genet 29, 463–470 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-00759-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-00759-9
This article is cited by
-
Linked-read sequencing for detecting short tandem repeat expansions
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases induced by triplet repeat expansion by linked read haplotyping and Bayesian approach
Scientific Reports (2022)