Abstract
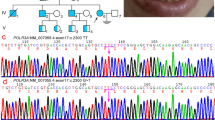
Neonatal progeroid syndrome or Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome (WRS; MIM 264090) is a rare genetic disorder that has clinical symptoms including premature aging, lipodystrophy, and variable mental impairment. Until recently genetic background of the disease was unclear. However, recent studies have indicated that WRS patients have compound heterozygote variations in the POLR3A (RNA polymerase III subunit 3A; MIM 614258) gene that might be responsible for the disease phenotype. In this study we report a WRS patient that has compound heterozygote variations in the POLR3A gene. One of the reported variations in our patient, c.3568C>T, p.(Gln1190Ter), is a novel variation that was not reported before. The other variant, c.3337-11T>C, was previously shown in WRS patients in trans with other variations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Arboleda G, Morales LC, Quintero L, Arboleda H. Neonatal progeroid syndrome (Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome): report of three affected sibs. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155a:1712–5.
Arboleda G, Ramirez N, Arboleda H. The neonatal progeroid syndrome (Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch): a model for the study of human aging?. Exp Gerontol. 2007;42:939–43.
Akawi N, Ali B, Al Gazali L. A progeroid syndrome with neonatal presentation and long survival maps to 19p13.3p13.2. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2013;97:456–62.
Wambach JA, Wegner DJ, Patni N, Kircher M, Willing MC, Baldridge D, et al. Bi-allelic POLR3A loss-of-function variants cause autosomal-recessive Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2018;103:968–75.
Bernard G, Vanderver A. POLR3-Related Leukodystrophy. 2012 Aug 2 [Updated 2017 May 11]. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al., editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2020. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK99167.
Bernard G, Chouery E, Putorti ML, Tetreault M, Takanohashi A, Carosso G, et al. Mutations of POLR3A encoding a catalytic subunit of RNA polymerase Pol III cause a recessive hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 2011;89:415–23.
Paolacci S, Bertola D, Franco J, Mohammed S, Tartaglia M, Wollnik B, et al. Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome: a phenotype analysis. Am J Med Genet A. 2017;173:1763–72.
Jay AM, Conway RL, Thiffault I, Saunders C, Farrow E, Adams J, et al. Neonatal progeriod syndrome associated with biallelic truncating variants in POLR3A. Am J Med Genet A. 2016;170:3343–6.
Lessel D, Ozel AB, Campbell SE, Saadi A, Arlt MF, McSweeney KM, et al. Analyses of LMNA-negative juvenile progeroid cases confirms biallelic POLR3A mutations in Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch-like syndrome and expands the phenotypic spectrum of PYCR1 mutations. Hum Genet. 2018;137:921–39.
Minnerop M, Kurzwelly D, Wagner H, Soehn AS, Reichbauer J, Tao F, et al. Hypomorphic mutations in POLR3A are a frequent cause of sporadic and recessive spastic ataxia. Brain. 2017;140:1561–78.
Gauquelin L, Tetreault M, Thiffault I, Farrow E, Miller N, Yoo B, et al. POLR3A variants in hereditary spastic paraplegia and ataxia. Brain. 2018;141:e1.
Minnerop M, Kurzwelly D, Rattay TW, Timmann D, Hengel H, Synofzik M, et al. Reply: POLR3A variants in hereditary spastic paraplegia and ataxia. Brain. 2018;141:e2.
Báez-Becerra CT, Valencia-Rincón E, Velásquez-Méndez K, Ramírez-Suárez N, Guevara C, Sandoval-Hernandez A, et al. Nucleolar disruption, activation of P53 and premature senescence in POLR3A-mutated Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome fibroblasts. BioRxiv. 2020. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.29.925131v1.full.
Marceddu G, Dallavilla T, Guerri G, Manara E, Chiurazzi P, Bertelli M, et al. PipeMAGI: an integrated and validated workflow for analysis of NGS data for clinical diagnostics. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:6753–65.
Stenson PD, Mort M, Ball EV, Evans K, Hayden M, Heywood S, et al. The Human Gene Mutation Database: towards a comprehensive repository of inherited mutation data for medical research, genetic diagnosis and next-generation sequencing studies. Hum Genet. 2017;136:665–77.
Sim NL, Kumar P, Hu J, Henikoff S, Schneider G, Ng PC. SIFT web server: predicting effects of amino acid substitutions on proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:W452–7.
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods. 2010;7:248–9.
Schwarz JM, Cooper DN, Schuelke M, Seelow D. MutationTaster2: mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat Methods. 2014;11:361–2.
Reva B, Antipin Y, Sander C. Predicting the functional impact of protein mutations: application to cancer genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:e118.
Webb B, Sali A. Comparative protein structure modeling using MODELLER. Curr Protoc Bioinform. 2016;54:5.6.1–37.
Marti-Renom MA, Stuart AC, Fiser A, Sanchez R, Melo F, Sali A. Comparative protein structure modeling of genes and genomes. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2000;29:291–325.
Ding Z, Kihara D. Computational methods for predicting protein-protein interactions using various protein features. Curr Protoc Protein Sci. 2018;93:e62.
DeLano WL. The PyMOL molecular graphics system. 2008. http://pymol.org.
Paolacci S, Li Y, Agolini E, Bellacchio E, Arboleda-Bustos CE, Carrero D, et al. Specific combinations of biallelic POLR3A variants cause Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome. J Med Genet. 2018;55:837–46.
Dauwerse JG, Dixon J, Seland S, Ruivenkamp CA, van Haeringen A, Hoefsloot LH, et al. Mutations in genes encoding subunits of RNA polymerases I and III cause Treacher Collins syndrome. Nat Genet. 2011;43:20–2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Temel, S.G., Ergoren, M.C., Manara, E. et al. Unique combination and in silico modeling of biallelic POLR3A variants as a cause of Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 28, 1675–1680 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-0673-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-0673-1
This article is cited by
-
POLR3A mutations cause nucleolus abnormalities and aberrant telomerase RNA metabolism in induced pluripotent stem cells from Wiedemann-Rautenstrauch premature aging syndrome patient
Biogerontology (2025)
-
POLR3A variants in hereditary spastic paraparesis and ataxia: clinical, genetic, and neuroradiological findings in a cohort of Italian patients
Neurological Sciences (2022)
-
In Silico Study of the Structure and Ligand Preference of Pyruvate Kinases from Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2021)