Abstract
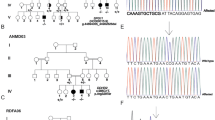
Mitochondrial membrane protein-associated neurodegeneration (MPAN) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder characterized by spastic paraplegia, parkinsonism and psychiatric and/or behavioral symptoms caused by variants in gene encoding chromosome-19 open reading frame-12 (C19orf12). We present here seven patients from six unrelated families with detailed clinical, radiological, and genetic investigations. Childhood-onset patients predominantly had a spastic ataxic phenotype with optic atrophy, while adult-onset patients were presented with cognitive, behavioral, and parkinsonian symptoms. Levodopa induced choreiform dyskinesia was observed in one patient who showed a response to levodopa. Brain magnetic resonance imaging showed mineralization in all patients and cerebellar atrophy in one patient. The “pallidal splitting sign” was found in two patients and additional caudate and putamen mineralization was noted in two patients. Exome sequencing identified six variants in the C19orf12 gene, including two novel splice-site variants, four previously reported missense variants. Transcript analysis using RT-PCR followed by Sanger sequencing was performed on a splice site variant (c.194-2delA) to understand the splice defect and its consequences. This analysis confirmed the splice defect and use of an alternate cryptic splice site in the downstream exonic region. The variants identified in this study expand the spectrum of clinical and genetic knowledge on MPAN patients, highlighting the importance of genetic testing in the diagnosis and management of this disorder.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data is available with the corresponding author with reasonable request.
References
Gregory A, Hayflick S. Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation Disorders Overview. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews((R)). Seattle (WA) 1993.
Svetel M, Dragasevic N, Petrovic I, Novakovic I, Tomic A, Kresojevic N, et al. NBIA Syndromes: A Step Forward from the Previous Knowledge. Neurol India. 2021;69:1380–8.
Olgiati S, Dogu O, Tufekcioglu Z, Diler Y, Saka E, Gultekin M, et al. The p.Thr11Met mutation in c19orf12 is frequent among adult Turkish patients with MPAN. Park Relat Disord. 2017;39:64–70.
Hartig MB, Iuso A, Haack T, Kmiec T, Jurkiewicz E, Heim K, et al. Absence of an orphan mitochondrial protein, c19orf12, causes a distinct clinical subtype of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Am J Hum Genet. 2011;89:543–50.
Hogarth P, Gregory A, Kruer MC, Sanford L, Wagoner W, Natowicz MR, et al. New NBIA subtype: genetic, clinical, pathologic, and radiographic features of MPAN. Neurology. 2013;80:268–75.
Gregory A, Klopstock T, Kmiec T, Hogarth P, Hayflick SJ. Mitochondrial Membrane Protein-Associated Neurodegeneration. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, et al., editors. GeneReviews((R)). Seattle (WA) 1993.
Hartig M, Prokisch H, Meitinger T, Klopstock T. Mitochondrial membrane protein-associated neurodegeneration (MPAN). Int Rev Neurobiol. 2013;110:73–84.
Gore E, Appleby BS, Cohen ML, DeBrosse SD, Leverenz JB, Miller BL, et al. Clinical and imaging characteristics of late onset mitochondrial membrane protein-associated neurodegeneration (MPAN). Neurocase. 2016;22:476–83.
Lehericy S, Roze E, Goizet C, Mochel F. MRI of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Curr Opin Neurol. 2020;33:462–73.
Gregory A, Lotia M, Jeong SY, Fox R, Zhen D, Sanford L, et al. Autosomal dominant mitochondrial membrane protein-associated neurodegeneration (MPAN). Mol Genet Genom Med. 2019;7:e00736.
Remiche G, Vandernoot I, Sadeghi-Meibodi N, Desmyter L. SPG43 and ALS-like syndrome in the same family due to compound heterozygous mutations of the C19orf12 gene: a case description and brief review. Neurogenetics. 2021;22:95–101.
Ramesh R, Deenadayalu A, Bhattacharjee S, Paramanandam V. C19orf12 mutation causing mitochondrial membrane-protein Associated Neurodegeneration masquerading as spastic paraplegia. Park Relat Disord. 2021;89:146–7.
Hayflick SJ, Kurian MA, Hogarth P. Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;147:293–305.
Muthusamy B, Selvan LDN, Nguyen TT, Manoj J, Stawiski EW, Jaiswal BS, et al. Next-generation sequencing reveals novel mutations in x-linked intellectual disability. OMICS. 2017;21:295–303.
Sim NL, Kumar P, Hu J, Henikoff S, Schneider G, Ng PC. SIFT web server: predicting effects of amino acid substitutions on proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:W452–7.
Schwarz JM, Cooper DN, Schuelke M, Seelow D. MutationTaster2: mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat Methods. 2014;11:361–2.
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods. 2010;7:248–9.
Ioannidis NM, Rothstein JH, Pejaver V, Middha S, McDonnell SK, Baheti S, et al. REVEL: an ensemble method for predicting the pathogenicity of rare missense variants. Am J Hum Genet. 2016;99:877–85.
Panteghini C, Zorzi G, Venco P, Dusi S, Reale C, Brunetti D, et al. C19orf12 and FA2H mutations are rare in Italian patients with neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2012;19:75–81.
Skowronska M, Kmiec T, Czlonkowska A, Kurkowska-Jastrzebska I. Transcranial sonography in mitochondrial membrane protein-associated neurodegeneration. Clin Neuroradiol. 2018;28:385–92.
Nagarjunakonda S, Daggumati R, Uppala V, Gajula R, Amalakanti S. A novel mutation in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation - a case report. Neurol India. 2019;67:1341–3.
Venco P, Bonora M, Giorgi C, Papaleo E, Iuso A, Prokisch H, et al. Mutations of C19orf12, coding for a transmembrane glycine zipper containing mitochondrial protein, cause mis-localization of the protein, inability to respond to oxidative stress and increased mitochondrial Ca(2)(+). Front Genet. 2015;6:185.
Dogu O, Krebs CE, Kaleagasi H, Demirtas Z, Oksuz N, Walker RH, et al. Rapid disease progression in adult-onset mitochondrial membrane protein-associated neurodegeneration. Clin Genet. 2013;84:350–5.
Deschauer M, Gaul C, Behrmann C, Prokisch H, Zierz S, Haack TB. C19orf12 mutations in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation mimicking juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol. 2012;259:2434–9.
Mercan S, Ugur Iseri SA, Yigiter R, Akcakaya NH, Saka E, Yapici Z. Two cases with mitochondrial membrane protein-associated neurodegeneration: genetic features and long-term clinical follow-up. Neurocase. 2022;28:37–41.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their families to participating in this study.
Funding
This study is funded for a research project (54/12/2019-HUM/BMS) from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi. Riyanka Kumari is a recipient of Senior Research Fellowship from CSIR, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PKP; VVH; NS; NK; AA; RY; JS:- clinical assessments, radiological investigations, manuscript review. BM; VVH; GA; RK:- data analysis, BM; RK; VVH:- results interpretation, wrote initial draft of the manuscript review. All authors: Review and critical input to improve the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the institutional ethics committee at NIMHANS, Bangalore.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, R., Holla, V.V., Sriram, N. et al. C19orf12 gene variants causing mitochondrial membrane protein-associated neurodegeneration (MPAN). Eur J Hum Genet 33, 878–886 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-024-01778-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-024-01778-6
This article is cited by
-
Summer reading 2025 in EJHG
European Journal of Human Genetics (2025)