Abstract
Purpose
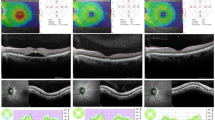
To compare retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) and ganglion cell complex (GCC) thickness in patients with unilateral exfoliation syndrome (XFS) and age-matched controls using spectral domain-optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT).
Materials and methods
This prospective case–control study included 54 eyes (the XFS-affected and the fellow eyes) of 27 unilateral XFS patients and 27 eyes of 27 age-matched control subjects. The RNFL and GCC thicknesses were measured using SD-OCT (RT-Vue 100, Optovue, Fremont, CA) after pupillary dilation. RNFL and GCC thicknesses were compared between case and control groups.
Results
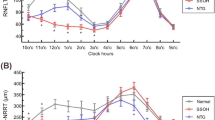
The mean age of XFS patients was 73.3 years and that of age-matched controls was 74.3 years. Both groups demonstrated a male preponderance. Superior RNFL thickness of XFS-affected eyes were significantly thinner than those of the healthy age-matched controls (P = 0.002 by ANOVA). There were no statistically significant differences in the RNFL thickness between both eyes of unilateral XFS patients. Moreover, superior GCC thickness of both eyes in unilateral XFS patients were thinner than those in controls (P = 0.002 by ANOVA).
Conclusions
Thinner RNFL and GCC thicknesses were observed in unilateral XFS patients without visual field defects. These findings imply that XFS itself might be a risk factor for development of glaucomatous optic disc and RNFL damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ritch R, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U, Konstas AG. Why is glaucoma associated with exfoliation syndrome? Prog Retinal Eye Res. 2003;22:253–75.
Ritch R, Schlotzer-Schrehardt U. Exfoliation syndrome. Surv Ophthalmol. 2001;45:265–315.
Citirik M, Acaroglu G, Batman C, Yildiran L, Zilelioglu O. A possible link between the pseudoexfoliation syndrome and coronary artery disease. Eye. 2007;21:11.
Holló G. Exfoliation syndrome and systemic cardiovascular diseases. J Glaucoma. 2014;23:S9–S11.
Wang W, He M, Zhou M, Zhang X. Ocular pseudoexfoliation syndrome and vascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS One. 2014;9:e92767.
Khalil AK, Kubota T, Tawara A, Inomata H. Early changes in iris blood vessels in exfoliation syndrome. Curr Eye Res. 1998;17:1124–34.
Prata T, Rozenbaum I, De Moraes C, Lima V, Liebmann J, Ritch R. Retinal vascular occlusions occur more frequently in the more affected eye in exfoliation syndrome. Eye. 2010;24:658.
Repo LP, Suhonen MT, Teräsvirta ME, Koivisto KJ. Color Doppler imaging of the ophthalmic artery blood flow spectra of patients who have had a transient ischemic attack: correlations with generalized iris transluminance and pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Ophthalmology. 1995;102:1199–205.
Yüksel N, Karabaş VL, Arslan A, Demirci A, Çağlar Y. Ocular hemodynamics in pseudoexfoliation syndrome and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2001;108:1043–9.
Sibour G, Finazzo C, Carenini AB. Monolateral pseudoexfoliatio capsulae: a study of choroidal blood flow. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1997;75:13–4.
Altintaş Ö, Maral H, Yüksel N, Karabaş VL, Dillioğlugil MÖ, Çağlar Y. Homocysteine and nitric oxide levels in plasma of patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome, pseudoexfoliation glaucoma, and primary open-angle glaucoma. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005;243:677–83.
Aydin D, Kusbeci T, Uzunel UD, Orsel T, Yuksel B. Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer and ganglion cell complex thickness in unilateral exfoliation syndrome using optical coherence tomography. J Glaucoma. 2016;25:523–7.
Lalezary M, Medeiros FA, Weinreb RN, Bowd C, Sample PA, Tavares IM, et al. Baseline optical coherence tomography predicts the development of glaucomatous change in glaucoma suspects. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;142:576–82. e571.
Curcio CA, Allen KA. Topography of ganglion cells in human retina. J Comp Neurol. 1990;300:5–25.
Eltutar K, Acar F, Kayaarası Öztürker Z, Ünsal E, Özdoğan Erkul S. Structural changes in pseudoexfoliation syndrome evaluated with spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Curr Eye Res. 2016;41:513–20.
Feuer WJ, Anderson DR. Static threshold asymmetry in early glaucomatous visual field loss. Ophthalmology. 1989;96:1285–97.
Seong M, Sung KR, Choi EH, Kang SY, Cho JW, Um TW, et al. Macular and peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer measurements by spectral domain optical coherence tomography in normal-tension glaucoma. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51:1446–52.
Yu J-g HuangQ, Zhou X-f, Ding Y, Li J, Xiang Y. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness changes in the pseudoexfoliation syndrome: a meta-analysis of case–control studies. Ophthalmic Res. 2018;59:14–23.
Philip S, Najafi A, Tantraworasin A, Chui TY, Rosen RB, Ritch R. Macula vessel density and foveal avascular zone parameters in exfoliation glaucoma compared to primary open-angle glaucoma. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019;60:1244–53.
Yasmeen N, Fatima N. Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in patients having pseudo exfoliation syndrome with healthy adults. Pak J Med Sci. 2016;32:1533.
Yüksel N, Altıntaş Ö, Çelik M, Özkan B, Çağlar Y. Analysis of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome using optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmologica. 2007;221:299–304.
Detorakis ET, Achtaropoulos AK, Drakonaki EE, Kozobolis VP. Hemodynamic evaluation of the posterior ciliary circulation in exfoliation syndrome and exfoliation glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007;245:516–21.
Dayanir V, Topaloğlu A, Ozsunar Y, Keceli M, Okyay P, Harris A. Orbital blood flow parameters in unilateral pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Int Ophthalmol. 2009;29:27–32.
Kozobolis VP, Papatzanaki M, Vlachonikolis IG, Pallikaris IG, Tsambarlakis IG. Epidemiology of pseudoexfoliation in the island of Crete (Greece). Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1997;75:726–9.
Ringvold A. Epidemiology of the pseudo‐exfoliation syndrome, a review. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1999;77:371–5.
Young A, Tang W, Lam D. The prevalence of pseudoexfoliation syndrome in Chinese people. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004;88:193–5.
Lee S-Y, Kim S, Kim JH, Hong S-C, Lee KH, Lee H-S, et al. Prevalence of pseudoexfoliation syndrome in an isolated island population of Korea: the Woodo study. J Glaucoma. 2017;26:730–4.
Wang L, Yu Y, Fu S, Zhao W, Liu P. LOXL1 gene polymorphism with exfoliation syndrome/exfoliation glaucoma: a meta-analysis. J Glaucoma. 2016;25:62–94.
Kim MJ, Park KH, Kim CY, Jeoung JW, Kim SH. The distribution of intraocular pressure and associated systemic factors in a Korean population: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014;92:e507–e513.
Grieshaber MC, Flammer J. Blood flow in glaucoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2005;16:79–83.
Ocakoglu O, Koyluoglu N, Kayiran A, Tamcelik N, Ozkan S. Microvascular blood flow of the optic nerve head and peripapillary retina in unilateral exfoliation syndrome. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2004;82:49–53.
Kim S, Sung KR, Lee JR, Lee KS. Evaluation of lamina cribrosa in pseudoexfoliation syndrome using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography enhanced depth imaging. Ophthalmology. 2013;120:1798–803.
Moghimi S, Mazloumi M, Johari M, Abdi P, Fakhraie G, Mohammadi M, et al. Evaluation of lamina cribrosa and choroid in nonglaucomatous patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57:1293–300.
Braunsmann C, Hammer CM, Rheinlaender J, Kruse FE, Schäffer TE, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U. Evaluation of lamina cribrosa and peripapillary sclera stiffness in pseudoexfoliation and normal eyes by atomic force microscopy. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53:2960–7.
Jonas J. Central retinal artery and vein collapse pressure in eyes with chronic open angle glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 2003;87:949–51.
Hansen E, Sellevold OJ. Pseudoexfoliation of the lens capsule II. Development of the exfoliation syndrome. Acta Ophthalmol. 1969;47:161–73.
Puska PM. Unilateral exfoliation syndrome: conversion to bilateral exfoliation and to glaucoma: a prospective 10-year follow-up study. J Glaucoma. 2002;11:517–24.
Parodi MB, Bondel E, Saviano S, Ravalico G. Iris indocyanine green angiography in pseudoexfoliation syndrome and capsular glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2000;78:437–42.
Tomita G, Puska P, Raitta C. Interocular differences in optic disc configuration in the unilateral exfoliation syndrome. Acta Ophthalmol. 1994;72:162–7.
Puska P, Harju M. Optic nerve head topography in nonglaucomatous, normotensive patients with unilateral exfoliation syndrome. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009;247:1111.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a VHS Medical Center Research Grant, Republic of Korea (Grant number: VHSMC 18016).
Funding
This study was supported by a VHS Medical Center Research Grant, Republic of Korea (Grant number: VHSMC 18016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, SH., Gu, W.M. & Cha, S.C. Comparison of the retinal nerve fiber layer and ganglion cell complex thickness in Korean patients with unilateral exfoliation syndrome and healthy subjects. Eye 34, 1419–1425 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-019-0642-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-019-0642-5
This article is cited by
-
Optical coherence tomography angiography analysis of the fellow eye in unilateral pseudoexfoliation syndrome
BMC Ophthalmology (2024)
-
Evaluation of retina nerve fiber layer, ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer and lamina cribrosa in clinically unilateral exfoliative glaucoma
International Ophthalmology (2020)