Abstract
Objective
To assess clinical factors leading to recurrent retinal detachment (RD) and characteristics of recurrence in patients with Stickler Syndrome.
Methods
Retrospective case series study of patients with clinical diagnosis of Stickler Syndrome who underwent rhegmatogenous RD repair. Recurrent RD after initial surgery was categorized as “early” if the recurrence was within 1 year or “late” if greater than 1 year.
Results
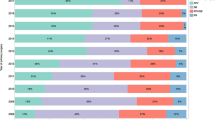
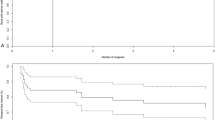
Thirty eyes from 22 patients underwent rhegmatogenous RD repair. For initial repair, 13 eyes underwent pars plana vitrectomy combined with scleral buckling (PPV/SB), 16 eyes underwent primary scleral buckling (SB), and 1 eye underwent pneumatic retinopexy (PnR). Recurrent RD occurred in 6 (46%) PPV/SB eyes (5 early and 1 late), 10 (63%) SB eyes (3 early and 7 late), and 0 (0%) PnR eyes (p = 0.61). PPV/SB was preferred for eyes presenting with total detachment (82%), giant retinal tears (100%), and proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR) (80%). For eyes with early recurrent RD, 6 (75%) had PVR leading to recurrence. For eyes with late recurrent RD, 7 (87.5%) developed a new retinal break leading to recurrence, including 4 with a break posterior to the buckle indentation apex. At last follow-up, median LogMAR visual acuity was 0.68 for eyes with recurrent RD compared to 0.29 for eyes without recurrence (p = 0.27).
Conclusions
Early recurrent RD was mostly caused by PVR, while late recurrent RD was mostly due to new retinal breaks. Eyes with seemingly uncomplicated rhegmatogenous RD repair with primary SB remained at high risk for late re-detachment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Carroll C, Papaioannou D, Rees A, Kaltenthaler E. The clinical effectiveness and safety of prophylactic retinal interventions to reduce the risk of retinal detachment and subsequent vision loss in adults and children with Stickler syndrome: a systematic review. Health Technol Assess. 2011;15:1–62.
Snead MP, McNinch AM, Poulson AV, Bearcroft P, Silverman B, Gomersall P, et al. Stickler syndrome, ocular-only variants and a key diagnostic role for the ophthalmologist. Eye. 2011;25:1389–400.
Coussa RG, Sears J, Traboulsi EI. Stickler syndrome: exploring prophylaxis for retinal detachment. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2019;30:306.
Yonekawa Y, Reddy D, Thomas B, Nudleman E, Williams G. Long-term surgical outcomes of retinal detachment in patients with Stickler syndrome. Clin Ophthalmol. 2016;10:1531–4.
Day AC, Donachie PHJ, Sparrow JM, Johnston RL. The Royal College of Ophthalmologists National Ophthalmology Database study of cataract surgery: report 1, visual outcomes and complications. Eye. 2015;29:552–60.
Ryan EH, Ryan CM, Forbes NJ, Yonekawa Y, Wagley S, Mittra RA, et al. Primary retinal detachment outcomes study report number 2. Ophthalmology. 2020;127:1077–85.
Starr MR, Boucher N, Sharma C, Wakabayashi T, Sivalingam M, Klufas MA, et al. The state of pediatric retinal detachment surgery in the United States: a nationwide aggregated health record analysis. Retina. 2023;43:717.
Abdi F, Aghajani A, Hemmati S, Moosavi D, Gordiz A, Chaibakhsh S, et al. Pediatric rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: a meta-analysis of clinical features, surgical success rate, and prognostic factors. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023;71:717.
Abeysiri P, Bunce C, da Cruz L. Outcomes of surgery for retinal detachment in patients with Stickler syndrome: a comparison of two sequential 20-year cohorts. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007;245:1633–8.
Al Rashaed S, Alshahrani S, Ghazi N. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachments associated to Stickler syndrome in a tertiary eye care center in Saudi Arabia. Clin Ophthalmol. 2015;10:1–6.
Taylor K, Su M, Richards Z, Mamawalla M, Rao P, Chang E. Outcomes in retinal detachment repair and laser prophylaxis for syndromes with optically empty vitreous. Ophthalmol Retin. 2023;7:848–56.
Errera MH, Liyanage SE, Moya R, Wong SC, Ezra E. Primary scleral buckling for pediatric rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Retina. 2015;35:1441–9.
Lincoff H, Kreissig I. Extraocular repeat surgery of retinal detachment: a minimal approach. Ophthalmology.1996;103:1586–92.
Fincham GS, Pasea L, Carroll C, McNinch AM, Poulson AV, Richards AJ, et al. Prevention of retinal detachment in stickler syndrome: the Cambridge prophylactic cryotherapy protocol. Ophthalmology. 2014;121:1588–97.
Linton E, Jalil A, Sergouniotis P, Moussa G, Black G, Charles S, et al. Laser prophylaxis in stickler syndrome: the Manchester protocol. Retina. 2023;43:88–93.
Funding
This work was supported by NIH CORE Grant P30 EY08098 to the Department of Ophthalmology, the Eye and Ear Foundation of Pittsburgh, the Children’s Foundation, and an unrestricted grant from Research to Prevent Blindness, New York, NY.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: THC, MF, KKN, and JNM. Data Collection: THC, MA, HLS, and KST. Analysis and interpretation: THC, MF, MA, HLS, KST, KKN, and JNM. Overall Responsibility: THC, MF, MA, HLS, KST, KKN, and JNM.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, T.H., Fooladi, M.I., Alabek, M. et al. Recurrent retinal detachment in Stickler Syndrome. Eye 39, 170–174 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-024-03402-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-024-03402-9