Abstract
Background/Objectives
FACE-Q Craniofacial Module is a validated patient-reported outcome measure for appearance. This study aimed to assess the content validity of FACE-Q Craniofacial Module for use in patients treated for corneal anaesthesia.
Subjects/Methods
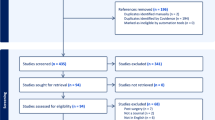
This was a qualitative, prospective observational study. Cognitive debriefing interviews were conducted with patients ≥8 years old who had surgical treatment for corneal anaesthesia at least six months before time of study. Two rounds of interviews gathered feedback on the comprehensibility, comprehensiveness, and relevance of three eye scales and checklists and four health-related quality-of-life scales. Based on the input from participants, ophthalmologists, scientists, and patient advocates, the scales and checklists were modified, then further refined.
Results
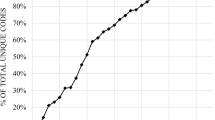
Feedback on the FACE-Q scales and checklists was obtained from 10 participants. Instructions for the scales were modified to enhance comprehensibility. Eleven items were revised for enhanced comprehensibility and relevance. Twelve items were added to enhance comprehensiveness. Four items were removed due to their irrelevance to appearance or corneal anaesthesia. Modifications to the eye and health-related quality-of-life scales were generally condition-specific and generic, respectively. A comment section was added to the end of each scale and checklist.
Conclusions
The FACE-Q demonstrates strong potential for adaptation to measure appearance outcomes in corneal anaesthesia patients. With lived expertise, clinical, and scientific input, the content validity of FACE-Q was improved for use in corneal anaesthesia patients. The modified FACE-Q is now ready for psychometric evaluation and further validation.
Meeting Presentations: Poster Presentation at 2023 Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) Annual Meeting in New Orleans, LA, April 23-27, 2023.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 18 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $14.39 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Zhang J, Barmettler A. Corneal neurotization: a narrative review of techniques, outcomes, and surgical considerations. Ann Eye Sci. 2023;8:7–7.
Dragnea DC, Krolo I, Koppen C, Faris C, Van den Bogerd B, Ní Dhubhghaill S. Corneal neurotization—indications, surgical techniques and outcomes. J Clin Med. 2023;12:2214.
Catapano J, Fung SSM, Halliday W, Jobst C, Cheyne D, Ho ES, et al. Treatment of neurotrophic keratopathy with minimally invasive corneal neurotisation: long-term clinical outcomes and evidence of corneal reinnervation. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019;103:1724–31.
Feroze KB, Patel BC Neurotrophic Keratitis. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 31]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK431106/.
James H, Jenkinson E, Harrad R, Ezra DG, Newman S. Collaboration (ARC) members of the AR. Appearance concerns in ophthalmic patients. Eye. 2011;25:1039.
Kingsley C, Patel S. Patient-reported outcome measures and patient-reported experience measures. BJA Educ. 2017;17:137–44.
Braithwaite T, Calvert M, Gray A, Pesudovs K, Denniston AK. The use of patient-reported outcome research in modern ophthalmology: impact on clinical trials and routine clinical practice. Patient Relat Outcome Measures. 2019;10:9.
Clarke A, Rumsey N, Collin JRO, Wyn-Williams M. Psychosocial distress associated with disfiguring eye conditions. Eye (Lond). 2003;17:35–40.
Murray LT, McCormack J, Grobeiu I, Wiklund I, Kimel M, Van Nooten F. Development of the neurotrophic keratopathy questionnaire: qualitative research. J Patient Rep Outcomes. 2020;4:30.
Terwee CB, Gerding MN, Dekker FW, Prummel MF, Wiersinga WM. Development of a disease specific quality of life questionnaire for patients with Graves’ ophthalmopathy: the GO-QOL. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998;82:773–9.
FACE-Q | Craniofacial - Q-Portfolio MEASURING WHAT MATTERS TO PATIENTS [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Jun 7]. Available from: https://qportfolio.org/face-q/craniofacial/.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services FDA Center for Devices and Radiological Health. Guidance for industry: patient-reported outcome measures: use in medical product development to support labeling claims: draft guidance. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2006;4:79.
Terwee CB, Prinsen CAC, Chiarotto A, Westerman MJ, Patrick DL, Alonso J, et al. COSMIN methodology for evaluating the content validity of patient-reported outcome measures: a Delphi study. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1159–70.
Patrick DL, Burke LB, Gwaltney CJ, Leidy NK, Martin ML, Molsen E, et al. Content validity-establishing and reporting the evidence in newly developed patient-reported outcomes (PRO) instruments for medical product evaluation: ISPOR PRO good research practices task force report: part 1-eliciting concepts for a new PRO instrument. Value Health. 2011;14:967–77.
Patrick DL, Burke LB, Gwaltney CJ, Leidy NK, Martin ML, Molsen E, et al. Content validity-establishing and reporting the evidence in newly developed patient-reported outcomes (PRO) instruments for medical product evaluation: ISPOR PRO Good Research Practices Task Force report: part 2-assessing respondent understanding. Value Health. 2011;14:978–88.
Mokkink LB, de Vet HCW, Prinsen CAC, Patrick DL, Alonso J, Bouter LM, et al. COSMIN risk of bias checklist for systematic reviews of patient-reported outcome measures. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1171–9.
Harris PA, Taylor R, Minor BL, Elliott V, Fernandez M, O’Neal L, et al. The REDCap consortium: Building an international community of software platform partners. J Biomed Inf. 2019;95:103208.
Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inf. 2009;42:377–81.
Longmire NM, Riff KWYW, O’Hara JL, Aggarwala S, Allen GC, Bulstrode NW, et al. Development of a new module of the FACE-Q for children and young adults with diverse conditions associated with visible and/or functional facial differences. Facial Plast Surg. 2017;33:499–508.
Cheng KKF, Clark AM. Qualitative methods and patient-reported outcomes: measures development and adaptation. Int J Qualitative Methods. 2017;16:1609406917702983.
Flesch Kincaid Calculator | Good Calculators [Internet]. [cited 2023 Jun 21]. Available from: https://goodcalculators.com/flesch-kincaid-calculator/.
Harris DL, Carr AT. The Derriford Appearance Scale (DAS59): a new psychometric scale for the evaluation of patients with disfigurements and aesthetic problems of appearance. Br J Plast Surg. 2001;54:216–22.
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1983;67:361–70.
Hatt SR, Leske DA, Bradley EA, Cole SR, Holmes JM. Development of a quality-of-life questionnaire for adults with strabismus. Ophthalmology. 2009;116:139–44.e5.
Hatt SR, Leske DA, Castañeda YS, Wernimont SM, Liebermann L, Cheng-Patel CS, et al. Development of pediatric eye questionnaires for children with eye conditions. Am J Ophthalmol. 2019;200:201–17.
Hatt SR, Leske DA, Yamada T, Bradley EA, Cole SR, Holmes JM. Development and initial validation of quality-of-life questionnaires for intermittent exotropia. Ophthalmology. 2010;117:163–8.e1.
Elbaz U, Bains R, Zuker RM, Borschel GH, Ali A. Restoration of corneal sensation with regional nerve transfers and nerve grafts: a new approach to a difficult problem. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014;132:1289–95.
Elalfy M, Maqsood S, Hau S, Kannan RY, Nduka C, Hamada S, et al. Functional and structural changes following corneal neurotisation in the management of neurotrophic keratopathy: UK single centre series. Clin Ophthalmol. 2021;15:2149–60.
Rafailov L, Kim JS, Wisely CE, Espana EM, Soifer M, Leyngold IM. Clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction after corneal neurotization. Cornea. 2021;40:1377–86.
Samoilă O, Samoilă L, Petrescu L. Corneal neurotization, recent progress, and future perspectives. Biomedicines. 2025;13:961.
Goldstein JE, Bradley C, Gross AL, Jackson M, Bressler N, Massof RW. The NEI VFQ-25C: calibrating items in the national eye institute visual function questionnaire-25 to enable comparison of outcome measures. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022;11:10.
Acknowledgements
Author FK is supported by the Vision Science Research Program Award and the Ontario Graduate Scholarship. A special thanks to the Dimaras Lab members, Dr. Sarah Wheeler, and patient advocates Ava Beatty, Ivana Ristevski, and Michelle Prunier for their valuable insights throughout the study.
Funding
Author FK is supported by the University of Toronto Vision Science Research Program Award and the Ontario Graduate Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FK: Design, Acquisition of Data, Analysis and Interpretation, Drafting, Final Approval. RN: Acquisition of Data, Revising, Final Approval. SW: Acquisition of Data, Revising, Final Approval. AS: Analysis and Interpretation, Revising, Final Approval. KWYW-R: Design, Analysis and Interpretation, Revising, Final Approval. AA: Design, Analysis and Interpretation, Revising, Final Approval. HD: Design, Analysis and Interpretation, Revising, Final Approval.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, F., Noronha, R., Williams, S. et al. Health-related quality of life questionnaire for corneal anaesthesia patients: a content validity assessment. Eye 39, 2780–2786 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-025-03969-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-025-03969-x
This article is cited by
-
Assessing patient engagement approaches in the development of patient reported outcome measures
Journal of Patient-Reported Outcomes (2026)