Abstract
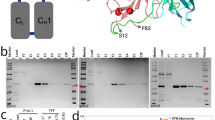
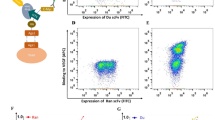
Anti-idiotype antibodies have been considered for vaccination approaches against different diseases, including cancers. Based on that, we previously described an anti-bevacizumab idiotype monoclonal antibody, 10.D7, that revealed detectable antitumor effects on a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-dependent tumor model. Herein, we evaluated the possible applicability of a single-chain variable fragment (scFv) for the 10.D7 antibody in a gene immunization strategy. After checking that mammalian cells transfected to express the 10.D7 scFv are recognized by bevacizumab, it was explored the ability of our scFv construction, in a gene-based scheme, to elicit an immune response containing VEGF-binding antibodies. The results provide evidence that the designed 10.D7 scFv construct maintains the anti-bevacizumab idiotype features and has potential to activate an immune response recognizing VEGF.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the reported results are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Jerne NK. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris). 1974;125C:373–89.
Pan SY, Chia YC, Yee HR, Fang Cheng AY, Anjum CE, Kenisi Y, et al. Immunomodulatory potential of anti-idiotypic antibodies for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Future Sci OA. 2020;7:648. https://doi.org/10.2144/fsoa-2020-0142.
Cowton VM, Owsianka AM, Fadda V, Ortega-Prieto AM, Cole SJ, Potter JA, et al. Development of a structural epitope mimic: an idiotypic approach to HCV vaccine design. NPJ Vaccines. 2021;6:7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41541-020-00269-1.
Stanova AK, Ryabkova VA, Utekhin SV, Shoenfeld VJ, Churilov LP, Shoenfeld Y. Anti-Idiotypic agonistic antibodies: candidates for the role of universal remedy. Antibodies (Basel). 2020;9:19. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib9020019.
Saha A, Chatterjee SK. Dendritic cells pulsed with an anti-idiotype antibody mimicking Her-2/neu induced protective antitumor immunity in two lines of Her-2/neu transgenic mice. Cell Immunol. 2010;263:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2010.02.010.
Ladjemi MZ, Chardes T, Corgnac S, Garambois V, Morisseau S, Robert B, et al. Vaccination with human anti-trastuzumab anti-idiotype scFv reverses HER2 immunological tolerance and induces tumor immunity in MMTV.f.huHER2(Fo5) mice. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr2826.
Kohler H, Pashov A, Kieber-Emmons T. The promise of anti-idiotype revisited. Front Immunol. 2019;10:808. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00808.
Ladjemi MZ. Anti-idiotypic antibodies as cancer vaccines: achievements and future improvements. Front Oncol. 2012;2:158. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2012.00158.
Ascoli CA, Aggeler B. Overlooked benefits of using polyclonal antibodies. Biotechniques. 2018; https://doi.org/10.2144/btn-2018-0065.
Bemani P, Mohammadi M, Hakakian A. ScFv improvement approaches. Protein Pept Lett. 2018; https://doi.org/10.2174/0929866525666171129225436.
Ye X, Gaucher JF, Vidal M, Broussy S. A structural overview of vascular endothelial growth factors pharmacological ligands: from macromolecules to designed peptidomimetics. Molecules. 2021; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26226759.
Garcia J, Hurwitz HI, Sandler AB, Miles D, Coleman RL, Deurloo R, et al. Bevacizumab (Avastin®) in cancer treatment: a review of 15 years of clinical experience and future outlook. Cancer Treat Rev. 2020;86:102017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102017.
Sanches Jde S, de Aguiar RB, Parise CB, Suzuki JM, Chammas R, de Moraes JZ. Anti-bevacizumab idiotype antibody vaccination is effective in inducing vascular endothelial growth factor-binding response, impairing tumor outgrowth. Cancer Sci. 2016; https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12903.
Pignatari GC, Takeshita D, Parise CB, Soares FA, de Moraes JZ, Han SW. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) mimicry by an anti-idiotypic scFv isolated from anti-Id 6.C4 hybridoma. J Biotechnol. 2007;127:615–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.08.007.
de Aguiar RB, da Silva TA, Costa BA, Machado MFM, Yamada RY, Braggion C, et al. Generation and functional characterization of a single-chain variable fragment (scFv) of the anti-FGF2 3F12E7 monoclonal antibody. Sci Rep. 2021; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80746-8.
National Research Council, Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed., Nat Acad Press,Washington (DC), 2011.
Li L, Petrovsky N. Molecular mechanisms for enhanced DNA vaccine immunogenicity. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2016; https://doi.org/10.1586/14760584.2016.1124762.
Denapoli PMA, Zanetti BF, Dos Santos AA, de Moraes JZ, Han SW. Preventive DNA vaccination against CEA-expressing tumors with anti-idiotypic scFv6.C4 DNA in CEA-expressing transgenic mice. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017;66:333–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-016-1940-4.
de Aguiar RB, Parise CB, Souza CR, Braggion C, Quintilio W, Moro AM, et al. Blocking FGF2 with a new specific monoclonal antibody impairs angiogenesis and experimental metastatic melanoma, suggesting a potential role in adjuvant settings. Cancer Lett. 2016;371:151–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.11.030.
Liu MA. DNA vaccines: an historical perspective and view to the future. Immunol Rev. 2011;239:62–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2010.00980.x.
Jorritsma SHT, Gowans EJ, Grubor-Bauk B, Wijesundara DK. Delivery methods to increase cellular uptake and immunogenicity of DNA vaccines. Vaccine. 2016;34:5488–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.09.062.
Francisco JA, Gilliland LK, Stebbins MR, Norris NA, Ledbetter JA, Siegall CB. Activity of a single-chain immunotoxin that selectively kills lymphoma and other B-lineage cells expressing the CD40 antigen. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3099–104.
Tripathi PK, Qin H, Deng S, Xu C, Bhattacharya-Chatterjee M, Foon KA, et al. Antigen mimicry by an anti-idiotypic antibody single chain variable fragment. Mol Immunol. 1998;35:853–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-5890(98)00072-8.
Liu A, Ye Y, Chen W, Wang X, Chen F. Expression of V(H)-linker-V(L) orientation-dependent single-chain Fv antibody fragment derived from hybridoma 2E6 against aflatoxin B1 in Escherichia coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015; https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1570-9.
Mir LM, Bureau MF, Gehl J, Rangara R, Rouy D, Caillaud JM, et al. High-efficiency gene transfer into skeletal muscle mediated by electric pulses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:4262–7. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.8.4262.
Parise CB, Lisboa B, Takeshita D, Sacramento CB, de Moraes JZ, Han SW. Humoral immune response after genetic immunization is consistently improved by electroporation. Vaccine. 2008;26:3812–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.05.029.
Lee YH, Lim H, Lee JA, Kim SH, Hwang YH, In HJ, et al. Optimization of Zika DNA vaccine by delivery systems. Virology. 2021;559:10–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2021.03.005.
Fomsgaard A, Liu MA. The key role of nucleic acid vaccines for one health. Viruses. 2021;13:258. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020258.
Coelho M, Gauthier P, Pugnière M, Roquet F, Pèlegrin A, Navarro-Teulon I. Isolation and characterisation of a human anti-idiotypic scFv used as a surrogate tumour antigen to elicit an anti-HER-2/neu humoral response in mice. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:2032–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6601825.
Ghosh S, Maity P. Augmented antitumor effects of combination therapy with VEGF antibody and cisplatin on murine B16F10 melanoma cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2007;7:1598–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2007.08.017.
Grimmett E, Al-Share B, Alkassab MB, Zhou RW, Desai A, Rahim MMA, et al. Cancer vaccines: past, present and future; a review article. Discov Oncol. 2022;13:31 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12672-022-00491-4.
Inogès S, Rodrìguez-Calvillo M, Zabalegui N, Lòpez-Dìaz de Cerio A, Villanueva H, Soria E, et al. Clinical benefit associated with idiotypic vaccination in patients with follicular lymphoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:1292–301. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djj358.
Schuster SJ, Neelapu SS, Gause BL, Janik JE, Muggia FM, Gockerman JP, et al. Vaccination with patient-specific tumor-derived antigen in first remission improves disease-free survival in follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:2787–94. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.33.3005.
Meleshko AN, Petrovskaya NA, Savelyeva N, Vashkevich KP, Doronina SN, Sachivko NV. Phase I clinical trial of idiotypic DNA vaccine administered as a complex with polyethylenimine to patients with B-cell lymphoma. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017;13:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/21645515.2017.1285477.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP; Grant Number 16/14358-2), and the Brazilian National Research Council (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RBA and JZM conceived the experiments. TAS and GEM performed the assays. BH offered technical support. MM and MFMM contributed to scFv construction. All authors analyzed the results. RBA and JZM wrote and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Animal procedures were approved by the ethics committee (CEUA) of the “Universidade Federal de São Paulo” (Protocol no. 6710130416).
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, T.A., Aguiar, R.B., Mori, M. et al. Potential of an anti-bevacizumab idiotype scFv DNA-based immunization to elicit VEGF-binding antibody response. Gene Ther 30, 598–602 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-022-00376-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-022-00376-9