Abstract
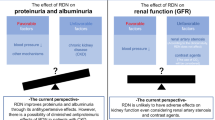
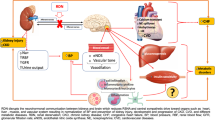
Proteinuria, especially albuminuria, serves as an independent risk factor for progression in cardiovascular and renal diseases. Clinical and experimental studies have demonstrated that renal nerves contribute to renal dysfunction in arterial hypertension (AH). This study hypothesizes that renal nerves mediate the mechanisms of protein endocytosis by proximal tubule epithelial cells (PTEC) and glomerular function; with dysregulation of the renal nerves contributing to proteinuria in Wistar rats with renovascular hypertension (2-kidney, 1-clip model, 2K-1C). Reduced albumin uptake and increased internalization of endocytic receptor megalin in PTEC were found in both the clipped and contralateral kidneys of 2K-1C rats. Renal denervation (DNx) or hydralazine treatment restored these parameters. Moreover, DNx, but not hydralazine, reduced serum creatinine and recovered podocyte numbers in the contralateral kidney of 2K-1C rats. Thus, our data suggest that renal nerves and high arterial pressure contribute to decreased albumin reabsorption by cellular redistribution of megalin in PTEC, while renal nerves remarkably drive glomerular dysfunction in renovascular hypertension, independently of their effect on blood pressure.

Created with BioRender.com
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barroso WKS, Rodrigues CIS, Borbolotto LA, Mota-Gomes MA, Brandão AA, Feitosa AD, et al. Brazilian guidelines of hypertension—2020. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2021;116:516–658.
Yugar-Toledo JC, Júnior HM, Gus M, Rosito GB, Scala LC, Muxfeldt ES, et al. Posicionamento brasileiro sobre hipertensão arterial resistente—2020. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2020;114:576–96.
Reyes KG, Rader F. Long-term safety and antihypertensive effects of renal denervation: current insights. Integr Blood Press control. 2023;16:59–70.
Camafort M, Ihm SH, Ruilope LM. Renal denervation for the treatment of hypertension and kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2023;32:544–50.
Lauder L, Azizi M, Kirtane AJ, Bohm M, Mahfoud F. Device-based therapies for arterial hypertension. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17:614–28.
Kiuchi MG, Esler MD, Fink GD, Osborn JW, Banek CT, Bohm M, et al. Renal denervation update from the international sympathetic nervous system summit: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73:3006–17.
Yamazaki D, Konishi Y, Kitada K. Effects of renal denervation on the kidney: albuminuria, proteinuria, and renal function. Hypertens Res. 2024;47:2659–64.
Lees JS, Welsh CE, Celis-Morales CA, Mackay D, Lewsey J, Gray SR, et al. Glomerular filtration rate by differing measures, albuminuria and prediction of cardiovascular disease, mortality and end-stage kidney disease. Nat med. 2019;25:1753–60.
Chazot R, Botelho-Neves E, Mariat C, Frésard A, Cavalier E, Lucht F, et al. Cystatin C and urine albumin to creatinine ratio predict 5-year mortality and cardiovascular events in people living with HIV. J Infect Dis. 2021;223:885–92.
Park S, Lee S, Lee A, Paek JH, Chin HJ, Na KY, et al. Preoperative dipstick albuminuria and other urine abnormalities predict acute kidney injury and patient outcomes. Surgery. 2018;163:1178–85.
Schmieder RE, Mann JF, Schumacher H, Gao P, Mancia G, Weber MA, et al. Changes in albuminuria predict mortality and morbidity in patients with vascular disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:1353–64.
Toblli JE, Bevione P, Gennaro FD, Madalena L, Cao G, Angerosa M. Understanding the mechanisms of proteinuria: therapeutic implications. Int J Nephrol. 2012;2012:546039.
Weisz OA. Endocytic adaptation to functional demand by the kidney proximal tubule. J Physiol. 2021;599:3437–46.
Edwards A, Long KR, Baty CJ, Shipman KE, Weisz OA. Modelling normal and nephrotic axial uptake of albumin and other filtered proteins along the proximal tubule. J Physiol. 2022;600:1933–52.
Rbaibi Y, Long KR, Shipman KE, Ren Q, Baty CJ, Kashlan OB, et al. Megalin, cubilin, and Dab2 drive endocytic flux in kidney proximal tubule cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2023;34:ar74.
Long KR, Rbaibi Y, Kashlan OB, Weisz OA. Receptor-associated protein impairs ligand binding to megalin and megalin-dependent endocytic flux in proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2023;325:F457–64.
D’Amico G, Bazzi C. Pathophysiology of proteinuria. Kidney Int. 2003;63:809–25.
Lopes NR, Milanez MI, Martins BS, Veiga AC, Ferreira GR, Gomes GN, et al. Afferent innervation of the ischemic kidney contributes to renal dysfunction in renovascular hypertensive rats. Pflüg Arch. 2020;472:325–34.
Dickson LE, Wagner MC, Sandoval RM, Molitoris BA. The proximal tubule and albuminuria: really! J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25:443–53.
Silva-Aguiar RP, Bezerra NC, Lucena MC, Sirtoli GM, Sudo RT, Zapata-Sudo G, et al. O-GlcNAcylation reduces proximal tubule protein reabsorption and promotes proteinuria in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Biol Chem. 2018;293:12749–58.
Ren Q, Weyer K, Rbaibi Y, Long KR, Tan RJ, Nielsen R, et al. Distinct functions of megalin and cubilin receptors in recovery of normal and nephrotic levels of filtered albumin. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2020;318:F1284–F1294.
Tojo A, Onozato ML, Ha H, Kurihara H, Sakai T, Goto A, et al. Reduced albumin reabsorption in the proximal tubule of early-stage diabetic rats. Histochem Cell Biol. 2001;116:269–76.
Nishi EE, Lopes NR, Gomes GN, Perry JC, Simões-Sato AY, Naffah-Mazzacoratti MG, et al. Renal denervation reduces sympathetic overactivation, brain oxidative stress, and renal injury in rats with renovascular hypertension independent of its effects on reducing blood pressure. Hypertens Res. 2019;42:628–40.
Veiga GL, Nishi EE, Estrela HF, Lincevicius GS, Gomes GN, Simões-Sato AY, et al. Total renal denervation reduces sympathoexcitation to different target organs in a model of chronic kidney disease. Auton Neurosci. 2017;204:81–87.
de Oliveira TL, Lincevicius GS, Shimoura CG, Simões-Sato AY, Garcia ML, Bergamaschi CT, et al. Effects of renal denervation on cardiovascular, metabolic and renal functions in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2021;278:119534.
Page IH, Heuer GJ. The effect of renal denervation on patients suffering from nephritis. J Clin Investig. 1935;14:443–58.
Birn H, Christensen EI. Renal albumin absorption in physiology and pathology. Kidney Int. 2006;69:440–9.
Birn H, Nielsen R, Weyer K. Tubular albumin uptake: is there evidence for a quantitatively important, receptor-independent mechanism? Kidney Int. 2023;104:1069–73.
Kuwahara S, Saito SA. The endocytic receptor megalin and its associated proteins in proximal tubule epithelial cells. Membranes. 2014;4:333–55.
Perez Bay AE, Schreiner R, Benedicto I, Marzolo MP, Banfelder J, Weinstein AM, et al. The fast-recycling receptor Megalin defines the apical recycling pathway of epithelial cells. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11550.
Sun J, Hultenby K, Axelsson J, Nordström J, He B, Wernerson A, et al. Proximal tubular expression patterns of megalin and cubilin in proteinuric nephropathies. Kidney Int Rep. 2017;2:721–32.
Sun Y, Lu X, Danser AHJ. Megalin: a novel determinant of renin-angiotensin system activity in the kidney? Curr Hypertens Rep. 2020;22:30.
Goldblatt H, Lynch J, Hanzal RF, Summerville WW. Studies on experimental hypertension: I. the production of persistent elevation of systolic blood pressure by means of renal ischemia. J Exp Med. 1934;59:347–79.
Mulder J, Hokfelt T, Knuepfer MM, Kopp UC. Renal sensory and sympathetic nerves reinnervate the kidney in a similar time-dependent fashion after renal denervation in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013;304:R675–82.
Intengan HD, Schiffrin EL. Disparate effects of carvedilol versus metoprolol treatment of stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats on endothelial function of resistance arteries. J Cardiovasc Pharm. 2000;35:763–8.
Queiroz-Madeira EP, Lara LS, Wengert M, Landgraf SS, Líbano-Soares JD, Zapata-Sudo G, et al. Na(+)-ATPase in spontaneous hypertensive rats: possible AT(1) receptor target in the development of hypertension. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1798:360–6.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54.
Peres RAS, Silva-Aguiar RP, Teixeira DE, Peruchetti DB, Alves SAS, Leal ABC, et al. Gold nanoparticles reduce tubule-interstitial injury and proteinuria in a murine model of subclinical acute kidney injury. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2023;1867:130314.
Peres RAS, Peruchetti DB, Silva-Aguiar RP, Teixeira DE, Gomes CP, Takiya CM, et al. Rapamycin treatment induces tubular proteinuria: role of megalin-mediated protein reabsorption. Front Pharm. 2023;14:1194816.
Schuh CD, Polesel M, Platonova E, Haenni D, Gassama A, Tokonami N, et al. Combined structural and functional imaging of the kidney reveals major axial differences in proximal tubule endocytosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29:2696–712.
Veiga AC, Milanez MI, Ferreira GR, Lopes NR, Santos CP, De Angelis K, et al. Selective afferent renal denervation mitigates renal and splanchnic sympathetic nerve overactivity and renal function in chronic kidney disease-induced hypertension. J Hypertens. 2020;38:765–73.
Peruchetti DB, Silva-Filho JL, Silva-Aguiar RP, Teixeira DE, Takiya CM, Souza MC, et al. IL-4 receptor α chain protects the kidney against tubule-interstitial injury induced by albumin overload. Front Physiol. 2020;11:172.
Fan L, Gao W, Nguyen BV, Jefferson JR, Liu Y, Fan F, et al. Impaired renal hemodynamics and glomerular hyperfiltration contribute to hypertension-induced renal injury. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2020;319:F624–F635.
Endres BT, Sandoval RM, Rhodes GJ, Campos-Bilderback SB, Kamocka MM, McDermott-Roe C, et al. Intravital imaging of the kidney in a rat model of salt-sensitive hypertensive. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2017;313:F163–F173.
Teixeira DE, Peruchetti DB, Souza MC, Henriques MG, Pinheiro AA, Caruso-Neves C. A high salt diet induces tubular damage associated with a pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic response in a hypertension-independent manner. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866:165907.
Fels J, Scharner B, Zarbock R, Guevara IPZ, Lee WK, Barbier OC, et al. Cadmium complexed with β2-microglubulin, albumin and lipocalin-2 rather than metallothionein cause megalin: cubilin dependent toxicity of the renal proximal tubule. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:2379.
Lincevicius GS, Shimoura CG, Nishi EE, Perry JC, Casarini DE, Gomes GN, et al. Aldosterone contributes to sympathoexcitation in renovascular hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2015;28:1083–90.
Pontes RB, Crajoinas RO, Nishi EE, Oliveira-Sales EB, Girardi AC, Campos RR, et al. Renal nerve stimulation leads to the activation of the Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 via angiotensin II type I receptor. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2015;308:F848–56.
Shimoura CG, de, Oliveira TL, Lincevicius GS, Crajoinas RO, Oliveira-Sales EB, et al. The total denervation of the ischemic kidney induces differential responses in sodium transporters’ expression in the contralateral kidney in Goldblatt rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25:6962.
Shipman KE, Baty CJ, Long KR, Rbaibi Y, Cowan IA, Gerges M, et al. Impaired endosome maturation mediates tubular proteinuria in dent disease cell culture and mouse models. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023;34:619–40.
Bobulescu IA, Moe OW. Luminal Na(+)/H (+) exchange in the proximal tubule. Pflug Arch. 2009;458:5–21.
Fan S, Liu J, Wei Y, Yao J, Cheng J, Tong Y, et al. The interference and elimination of nitrite on determination of total urinary protein by Pyrogallol red-molybdate method. Pract Lab Med. 2024;42:e00436. 15
Huber TB, Gloy J, Henger A, Schollmeyer P, Greger R, Mundel P, et al. Catecholamines modulate podocyte function. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:335–45.
Barutta F, Bellini S, Gruden G. Mechanisms of podocyte injury and implications for diabetic nephropathy. Clin Sci. 2022;136:493–520.
Weyer K, Andersen PK, Schmidt K, Mollet G, Antignac C, Birn H, et al. Abolishment of proximal tubule albumin endocytosis does not affect plasma albumin during nephrotic syndrome in mice. Kidney Int. 2018;93:335–42.
Lin H, Geurts F, Hassler L, Batlle D, Colafella KM, Denton KM, et al. Kidney angiotensin in cardiovascular disease: formation and drug targeting. Pharm Rev. 2022;74:462–505.
Martinez-Maldonado. Pathophysiology of renovascular hypertension. Hypertension. 1991;17:707–19.
Lincevicius GS, Shimoura CG, Nishi EE, de, Oliveira TL, Cespedes JG, et al. Differential effects of renal denervation on arterial baroreceptor function in Goldblatt hypertension model. Auton Neurosci. 2017;208:43–50.
Shimoura CG, Lincevicius GS, Nishi EE, Girardi AC, Simon KA, Bergamaschi CT, et al. Increased dietary salt changes baroreceptor sensitivity and intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in Goldblatt hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2017;30:28–36.
Charlton JR, Tan W, Daouk G, Teot L, Rosen S, Bennett KM, et al. Beyond the tubule: pathological variants of LRP2, encoding the megalin receptor, result in glomerular loss and early progressive chronic kidney disease. Am J Phys Ren Phys. 2020;319:F988–F999.
Christensen EI, Kristoffersen IB, Grann B, Thomsen JS, Andreasen A, Nielsen R. A well-developed endolysosomal system reflects protein reabsorption in segment 1 and 2 of rat proximal tubules. Kidney Int. 2021;99:841–53.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the expert technical assistance in histological sections preparation of Jacilene Barbosa from the multi-user facility of Infar-UNIFESP, and the English grammar revision of Dr. Alex Dayton from University of Minnesota.
Funding
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)— Finance Code 001, by the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP 2019/25295-0; 2022/11063-2) and by the Brazilian National Research Council (CNPq 406233/2018-7). ACV was a recipient of FAPESP scholarship (2020/02617-9). RRC and CTB are recipients of the CNPq productive research fellowship. And CCN was supported by CNPq: 46.5656/2014-5 (to CC-N); 30.9112/2021-4 (to CC-N), Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro–FAPERJ: E-26/210.046/2023 (CC-N), E-26/200.900/2021 (to CC-N), Rio Network of Innovation in Nanosystems for Health (Nanohealth/FAPERJ): E-26/010.000983/2019 (CC-N).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Veiga, A.C., Silva-Aguiar, R.P., Milanez, M.I.O. et al. Renal nerves and hypertension contribute to impaired proximal tubule megalin-mediated albumin uptake in renovascular hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res 48, 1491–1502 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-025-02100-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-025-02100-7