Abstract
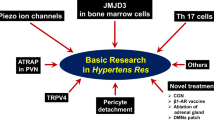
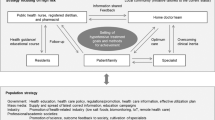
This mini-review article presents a comprehensive update on recent advancements in blood pressure management, based on original research published between 2023 and 2024. As part of the “Hypertension Research 2024 Update and Perspectives”, the review integrates insights from the JSH2024 Fukuoka Declaration, emphasizing the concept of “NEO-HYPERTENSION harmonized with society”. The strategies proposed in this review aim to realize this concept by promoting lifelong blood pressure management, preemptive medicine, and leveraging digital health technologies. Key strategies include adherence to treatment guidelines, overcoming clinical inertia, and the utilization of new digital tools and novel antihypertensive agents. Additionally, the review explores the significance of multidisciplinary collaboration and non-pharmacological therapies, as well as the importance of setting individualized treatment goals tailored to patients’ unique backgrounds. By aligning with the JSH’s vision, this review offers a fresh perspective on contemporary clinical practices and future directions. These updates aim to contribute to improved patient outcomes and global health advancements in hypertension care.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Node K, Tanaka A, Nishiyama A, Kario K. JSH2024 Fukuoka Declaration “NEO-HYPERTENSION harmonized with society”. Hypertens Res. 2024;47:3287.
Wang TD, Ohkubo T, Bunyi ML, Chadachan VM, Chia YC, Kario K, et al. Current realities of home blood pressure monitoring from physicians’ perspectives: results from Asia HBPM survey 2020. Hypertens Res 2023;46:1638–49.
Umishio W, Ikaga T, Kario K, Fujino Y, Suzuki M, Ando S, et al. Role of housing in blood pressure control: a review of evidence from the Smart Wellness Housing survey in Japan. Hypertens Res. 2023;46:9–18.
Collaboration NCDRF. Long-term and recent trends in hypertension awareness, treatment, and control in 12 high-income countries: an analysis of 123 nationally representative surveys. Lancet 2019;394:639–51.
Collaboration NCDRF. Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021;398:957–80.
Sakima A, Yamazato M, Kohagura K, Ishida A, Matayoshi T, Tana T, et al. Achievement rate of target blood pressure in patients with hypertension treated by hypertension specialists and non-specialists in a real-world setting. Hypertens Res. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-023-01362-3.
He J, Ouyang N, Guo X, Sun G, Li Z, Mu J, et al. Effectiveness of a non-physician community health-care provider-led intensive blood pressure intervention versus usual care on cardiovascular disease (CRHCP): an open-label, blinded-endpoint, cluster-randomised trial. Lancet. 2023;401:928–38.
Neal B, Wu Y, Feng X, Zhang R, Zhang Y, Shi J, et al. Effect of Salt Substitution on Cardiovascular Events and Death. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:1067–77.
Yuan Y, Jin A, Neal B, Feng X, Qiao Q, Wang H, et al. Salt substitution and salt-supply restriction for lowering blood pressure in elderly care facilities: a cluster-randomized trial. Nat Med. 2023;29:973–81.
Zhang X, Yuan Y, Li C, Feng X, Wang H, Qiao Q, et al. Effect of a Salt Substitute on Incidence of Hypertension and Hypotension Among Normotensive Adults. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024;83:711–22.
Kaya E, Solak Y, Sahin M, Kurt B, Vural Solak GT, Ucer H. Is YouTube useful as a source of information for approaches to reducing blood pressure and hypertension treatment? Hypertens Res. 2023;46:386–94.
Kario K, Nomura A, Harada N, Okura A, Nakagawa K, Tanigawa T, et al. Efficacy of a digital therapeutics system in the management of essential hypertension: the HERB-DH1 pivotal trial. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:4111–22.
Kario K, Tomitani N, Harada N, Okura A, Hisaki F, Tanigawa T, et al. Home blood pressure-lowering effect of digital therapeutics in hypertension: impact of body weight and salt intake. Hypertens Res. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-023-01245-7.
Hisaki F, Aga M, Tomitani N, Okawara Y, Harada N, Kario K. Daily self-reported behavioural efficacy records on hypertension digital therapeutics as digital metrics associated with the reduction in morning home blood pressure: post-hoc analysis of HERB-DH1 trial. Hypertens Res. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-023-01434-4.
Nozato Y, Yamamoto K. The effects of smartphone apps expected in self-management for hypertension management. Hypertens Res. 2024;47:564–5.
Han M, Lee YR, Park T, Ihm SH, Pyun WB, Burkard T, et al. Feasibility and measurement stability of smartwatch-based cuffless blood pressure monitoring: A real-world prospective observational study. Hypertens Res. 2023;46:922–31.
Kario K, Williams B, Tomitani N, McManus RJ, Schutte AE, Avolio A, et al. Innovations in blood pressure measurement and reporting technology: International Society of Hypertension position paper endorsed by the World Hypertension League, European Society of Hypertension, Asian Pacific Society of Hypertension, and Latin American Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2024;42:1874–88.
Freeman MW, Halvorsen YD, Marshall W, Pater M, Isaacsohn J, Pearce C, et al. Phase 2 Trial of Baxdrostat for Treatment-Resistant Hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2023;388:395–405.
Desai AS, Webb DJ, Taubel J, Casey S, Cheng Y, Robbie GJ, et al. Zilebesiran, an RNA Interference Therapeutic Agent for Hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2023;389:228–38.
Bakris GL, Saxena M, Gupta A, Chalhoub F, Lee J, Stiglitz D, et al. RNA Interference With Zilebesiran for Mild to Moderate Hypertension: The KARDIA-1 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024;331:740–9.
Pickersgill SJ, Msemburi WT, Cobb L, Ide N, Moran AE, Su Y, et al. Modeling global 80-80-80 blood pressure targets and cardiovascular outcomes. Nat Med. 2022;28:1693–9.
Liu J, Li Y, Ge J, Yan X, Zhang H, Zheng X, et al. Lowering systolic blood pressure to less than 120mm Hg versus less than 140mm Hg in patients with high cardiovascular risk with and without diabetes or previous stroke: an open-label, blinded-outcome, randomised trial. Lancet 2024;404:245–55.
Liu X, Steinman MA, Lee SJ, Peralta CA, Graham LA, Li Y, et al. Systolic blood pressure, antihypertensive treatment, and cardiovascular and mortality risk in VA nursing home residents. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71:2131–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nozato, Y. Hypertension research 2024 update and perspectives: blood pressure management. Hypertens Res 48, 1733–1738 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-025-02130-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-025-02130-1