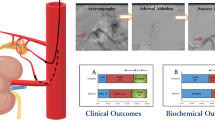
Abstract
To date, no systematic review has examined whether adrenalectomy (ADX) or mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) treatment is more effective in patients with unilateral primary aldosteronism (uPA). Comparing clinical and biochemical data before and after treatment, we performed a systematic review to determine whether either ADX or MRA treatment is superior to the other in patients with uPA. Article search was performed using the PubMed, Cochrane Library, and ICHUSHI electronic databases. A comparative analysis was performed when at least 3 articles were available in each outcome. The collected data were used to calculate the effect measures represented as mean difference (MD) or odds ratio (OR). Our search strategy identified 526 abstracts, of which 7 research papers were finally included in the analysis. ADX for uPA patients significantly reduced the incidence of cerebro-cardiovascular disease (OR 0.63 [95% confidence interval 0.46, 0.85]), lowered the systolic BP (−8.78 mmHg [−11.61, −5.95]), and increased the serum potassium levels (0.43 mmol/L [0.35, 0.51]) compared to MRAs. In conclusion, ADX is more effective than MRA treatment in patients with uPA, but with higher risk of increased serum potassium levels.

Graphical abstract: ADX adrenalectomy, MRAs mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, PA primary aldosteronism, SBP systolic blood pressure.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mulatero P, Stowasser M, Loh KC, Fardella CE, Gordon RD, Mosso L, et al. Increased diagnosis of primary aldosteronism, including surgically correctable forms, in centers from five continents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:1045–50.
Rossi GP, Bernini G, Caliumi C, Desideri G, Fabris B, Ferri C, et al. A prospective study of the prevalence of primary aldosteronism in 1,125 hypertensive patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:2293–300.
Funder JW, Carey RM, Mantero F, Murad MH, Reincke M, Shibata H, et al. The management of primary aldosteronism: case detection, diagnosis, and treatment: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101:1889–916.
Yoon M, Hong N, Ha J, Lee CJ, Ku CR, Rhee Y, et al. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of primary aldosteronism in a tertiary-care center in Korea. Hypertens Res. 2022;45:1418–29.
Born-Frontsberg E, Reincke M, Rump LC, Hahner S, Diederich S, Lorenz R, et al. Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular comorbidities of hypokalemic and normokalemic primary aldosteronism: results of the German Conn’s Registry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:1125–30.
Ohno Y, Sone M, Inagaki N, Yamasaki T, Ogawa O, Takeda Y, et al. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease and its risk factors in primary aldosteronism: a multicenter study in Japan. Hypertension. 2018;71:530–7.
Amar L, Baguet JP, Bardet S, Chaffanjon P, Chamontin B, Douillard C, et al. SFE/SFHTA/AFCE primary aldosteronism consensus: Introduction and handbook. Ann Endocrinol. 2016;77:179–86.
Naruse M, Katabami T, Shibata H, Sone M, Takahashi K, Tanabe A, et al. Japan Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of primary aldosteronism 2021. Endocr J. 2022;69:327–59.
Satoh M, Maruhashi T, Yoshida Y, Shibata H. Systematic review of the clinical outcomes of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist treatment versus adrenalectomy in patients with primary aldosteronism. Hypertens Res. 2019;42:817–24.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700.
Medical Information Network Distribution Service (Minds) Manual Developing Committee (ed). Minds manual for guideline development 2020 ver 3.0. Tokyo: Japan Council for Quality Health Care; 2021.
Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d4002.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–60.
Park KS, Kim JH, Yang YS, Hong AR, Lee DH, Moon MK, et al. Outcomes analysis of surgical and medical treatments for patients with primary aldosteronism. Endocr J. 2017;64:623–32.
Katabami T, Fukuda H, Tsukiyama H, Tanaka Y, Takeda Y, Kurihara I, et al. Clinical and biochemical outcomes after adrenalectomy and medical treatment in patients with unilateral primary aldosteronism. J Hypertens. 2019;37:1513–20.
Kishimoto S, Oki K, Maruhashi T, Kajikawa M, Hashimoto H, Takaeko Y, et al. A comparison of adrenalectomy and eplerenone on vascular function in patients with aldosterone-producing adenoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:3474–85.
Puar TH, Loh LM, Loh WJ, Lim DST, Zhang M, Tan PT, et al. Outcomes in unilateral primary aldosteronism after surgical or medical therapy. Clin Endocrinol. 2021;94:158–67.
Nakamaru R, Yamamoto K, Akasaka H, Rakugi H, Kurihara I, Yoneda T, et al. Age-stratified comparison of clinical outcomes between medical and surgical treatments in patients with unilateral primary aldosteronism. Sci Rep. 2021;11:6925.
Wu VC, Wang SM, Huang KH, Tsai YC, Chan CK, Yang SY, et al. Long-term mortality and cardiovascular events in patients with unilateral primary aldosteronism after targeted treatments. Eur J Endocrinol. 2021;186:195–205.
Chen ZW, Liao CW, Pan CT, Tsai CH, Chang YY, Chang CC, et al. Reversal of arterial stiffness in medically and surgically treated unilateral primary aldosteronism. J Hypertens. 2024;42:538–45.
Wu VC, Wang SM, Chang CH, Hu YH, Lin LY, Lin YH, et al. Long term outcome of Aldosteronism after target treatments. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32103.
Hundemer GL, Curhan GC, Yozamp N, Wang M, Vaidya A. Cardiometabolic outcomes and mortality in medically treated primary aldosteronism: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:51–9.
Nanba K, Baker JE, Blinder AR, Bick NR, Liu CJ, Lim JS, et al. Histopathology and genetic causes of primary aldosteronism in young adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107:2473–82.
Huang C, Chang LY, Sheu JY, Huang YT, Chen JY, Lai CF, et al. Exploring the high prevalence, comorbidities, and indicators of mild autonomous cortisol secretion in primary aldosteronism: a cohort study and systematic review. Hypertens Res. 2025;48:1716–1729.
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, Rothstein HR. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods. 2010;1:97–111.
Marzano L, Colussi G, Sechi LA, Catena C. Adrenalectomy is comparable with medical treatment for reduction of left ventricular mass in primary aldosteronism: meta-analysis of long-term studies. Am J Hypertens. 2015;28:312–8.
Jing Y, Liao K, Li R, Yang S, Song Y, He W, et al. Cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in surgically or medically treated primary aldosteronism: a Meta-analysis. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2021;22:14703203211003781.
Tsai CH, Chen YL, Pan CT, Lin YT, Lee PC, Chiu YW, et al. New-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with primary aldosteronism receiving different treatment strategies: systematic review and pooled analysis of three studies. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:646933.
Huang WC, Chen YY, Lin YH, Chueh JS. Composite cardiovascular outcomes in patients with primary aldosteronism undergoing medical versus surgical treatment: a meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:644260.
Chen SY, Chen JY, Huang WC, Puar THK, Chin Kek P, Chueh JS, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes and all-cause mortality in primary aldosteronism after adrenalectomy or mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist treatment: a meta-analysis. Eur J Endocrinol. 2022;187:S47–S58.
Oguro S, Morimoto R, Seiji K, Ota H, Kinoshita T, Kawabata M, et al. Safety and feasibility of radiofrequency ablation using bipolar electrodes for aldosterone-producing adenoma: a multicentric prospective clinical study. Sci Rep. 2022;12:14090.
Liu SY, Chu CM, Kong AP, Wong SK, Chiu PW, Chow FC, et al. Radiofrequency ablation compared with laparoscopic adrenalectomy for aldosterone-producing adenoma. Br J Surg. 2016;103:1476–86.
Oguro S, Ota H, Yanagaki S, Kawabata M, Kamada H, Omata K, et al. Transvenous radiofrequency catheter ablation for an aldosterone-producing tumor of the left adrenal gland: a first in human case report. Cardiovasc Interv Radio. 2023;46:1666–73.
Sun F, Liu X, Zhang H, Zhou X, Zhao Z, He H, et al. Catheter-based adrenal ablation: an alternative therapy for patients with aldosterone-producing adenoma. Hypertens Res. 2023;46:91–9.
Qiu J, Li N, Xiong HL, Yang J, Li YD, Hu CK, et al. Superselective adrenal arterial embolization for primary aldosteronism without lateralized aldosterone secretion: an efficacy and safety, proof-of-principle study. Hypertens Res. 2023;46:1297–310.
Zhou Y, Wang X, Hou J, Wan J, Yang Y, Liu S, et al. A controlled trial of percutaneous adrenal arterial embolization for hypertension in patients with idiopathic hyperaldosteronism. Hypertens Res. 2024;47:311–21.
Lai ZQ, Fu Y, Liu JW, Zhang HJ, Zhang H, Liang NP, et al. The impact of superselective adrenal artery embolization on renal function in patients with primary aldosteronism: a prospective cohort study. Hypertens Res. 2024;47:944–58.
Li X, Xiao S, Yu Y, Liu W, Xi H, Wang G, et al. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic adrenalectomy (RARLA): what advantages and disadvantages compared to retroperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy (RLA)? Front Endocrinol. 2023;14:1145820.
Mulatero P, Wuerzner G, Groessl M, Sconfienza E, Damianaki A, Forestiero V, et al. Safety and efficacy of once-daily dexfadrostat phosphate in patients with primary aldosteronism: a randomised, parallel group, multicentre, phase 2 trial. EClinicalMedicine. 2024;71:102576.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all members involved in the creation of JSH2025 for their inspiring discussions and technical assistance.
Funding
YY received funding from Grand-in-Aid for the Intractable Adrenal Disorders Research by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare 23FC1041. KK received funding from Terumo Life Science Foundation, The Grants for Basic Research of The Japanese Society of Hypertension, and The Salt Science Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, Y., Kinouchi, K., Nagai, S. et al. A systematic review to compare adrenalectomy and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in patients with unilateral primary aldosteronism. Hypertens Res 48, 2368–2375 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-025-02273-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-025-02273-1
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension 2025 (JSH2025)
Hypertension Research (2026)
-
Treatment for patients with unilateral aldosteronism: surgical or medical treatment
Hypertension Research (2025)
-
The JSH Morning Hypertension Eradication Program Project
Hypertension Research (2025)