Abstract
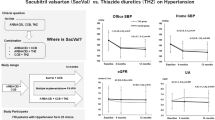
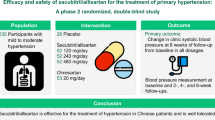
There is substantial evidence demonstrating that angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors (Sacubitril/Valsartan – Sac/Val) significantly reduce sitting blood pressure (BP). However, comprehensive pooled analyses evaluating their effects on out-of-office BP in patients with systemic hypertension remain limited. We conducted a systematic literature search of PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Embase, and ClinicalTrials.gov for randomized and non-randomized studies comparing Sac/Val with other antihypertensive agents in the treatment of systemic hypertension, from inception to the end of May 2024. Outcomes included nighttime, daytime and 24-h mean ambulatory (ma) systolic/diastolic BP (maSBP/maDBP), ambulatory pulse pressure (PP), and office BP. Safety outcomes were also assessed. Fifteen randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and 4 observational studies representing 7548 patients were included. In RCTs, Sac/Val therapy was associated with greater reductions in out-of-office blood pressure compared to angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and calcium channel blockers (CCBs). This included nighttime maSBP (mean difference [MD] −3.61 mmHg; 95% confidence intervals [CI] −4.86 to −2.36; p < 0.001) and maDBP (−2.11 mmHg; [−2.69 to −1.53]; p < 0.001); as well as daytime maSBP (−3.39 mmHg; [−4.58 to −2.21]; p < 0.001) and maDBP (−1.82 mmHg; [−2.82 to −0.82]; p < 0.001). Similarly, significant reductions in 24-h maSBP/maDBP, ambulatory PP, and office BP were observed with Sac/Val. Observational studies also demonstrated that Sac/Val significantly reduced office BP compared with ARBs and thiazide diuretics (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences in the incidence of adverse events between groups. In conclusion, Sac/Val effectively reduces both out-of-office and office BP and is well tolerated throughout the follow-up period.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data underlying this project are available in the article, in its online supplementary material and with the request to the corresponding authors of the paper.
References
WHO. Hypertension. 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension.
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:3021–104.
Katsuya T, Ishikawa K, Sugimoto K, Rakugi H, Ogihara T. Salt sensitivity of Japanese from the viewpoint of gene polymorphism. Hypertens Res. 2003;26:521–5.
Kario K, Shin J, Chen CH, Buranakitjaroen P, Chia YC, Divinagracia R, et al. Expert panel consensus recommendations for ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in Asia: The HOPE Asia Network. J Clin Hypertens. 2019;21:1250–83.
Kario K, Chia YC, Siddique S, Turana Y, Li Y, Chen CH, et al. Seven-action approaches for the management of hypertension in Asia - The HOPE Asia network. J Clin Hypertens. 2022;24:213–23.
McEvoy JW, McCarthy CP, Bruno RM, Brouwers S, Canavan MD, Ceconi C, et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2024;45:3912–4018.
Umemura S, Arima H, Arima S, Asayama K, Dohi Y, Hirooka Y, et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens Res. 2019;42:1235–481.
Benowitz NL. Antihypertensive agents. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Lange; 2001. pp. 155–80.
Hermida RC, Crespo JJ, Otero A, Domínguez-Sardiña M, Moyá A, Ríos MT, et al. Asleep blood pressure: significant prognostic marker of vascular risk and therapeutic target for prevention. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:4159–71.
Kikuya M, Ohkubo T, Asayama K, Metoki H, Obara T, Saito S, et al. Ambulatory blood pressure and 10-year risk of cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality: the Ohasama study. Hypertension. 2005;45:240–5.
Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Mojon A, Fernandez JR. Decreasing sleep-time blood pressure determined by ambulatory monitoring reduces cardiovascular risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58:1165–73.
Muxfeldt ES, Cardoso CR, Salles GF. Prognostic value of nocturnal blood pressure reduction in resistant hypertension. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169:874–80.
Ohkubo T, Hozawa A, Yamaguchi J, Kikuya M, Ohmori K, Michimata M, et al. Prognostic significance of the nocturnal decline in blood pressure in individuals with and without high 24-h blood pressure: the Ohasama study. J Hypertens. 2002;20:2183–9.
Ito S, Satoh M, Tamaki Y, Gotou H, Charney A, Okino N, et al. Safety and efficacy of LCZ696, a first-in-class angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor, in Japanese patients with hypertension and renal dysfunction. Hypertens Res. 2015;38:269–75.
Supasyndh O, Wang J, Hafeez K, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Rakugi H. Efficacy and safety of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) compared with olmesartan in elderly asian patients (>/=65 Years) with systolic hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2017;30:1163–9.
McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:3599–726.
Wang TD, Tan RS, Lee HY, Ihm SH, Rhee MY, Tomlinson B, et al. Effects of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) on natriuresis, diuresis, blood pressures, and NT-proBNP in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension. 2017;69:32–41.
Cheung DG, Aizenberg D, Gorbunov V, Hafeez K, Chen CW, Zhang J. Efficacy and safety of sacubitril/valsartan in patients with essential hypertension uncontrolled by olmesartan: a randomized, double-blind, 8-week study. J Clin Hypertens. 2018;20:150–8.
Almarjan AI, Almarjan SA, Masoud AT. Different doses of sacubitril/valsartan compared with olmesartan in patients with essential hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2023;30:207–18.
Zheng L, Xia B, Zhang X, Zhao Y. A meta-analysis on the effect and safety of LCZ696 in the treatment of hypertension. Cardiol Res Pr. 2021;2021:8867578.
Chua SK, Lai WT, Chen LC, Hung HF. The antihypertensive effects and safety of LCZ696 in patients with hypertension: a systemic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Med. 2021;10:2824.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Higgins J. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. England; Cochrane Collaboration and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.; 2008.
Sterne JAC, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. 2016; https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i4919.
Rakugi H, Kario K, Yamaguchi M, Sasajima T, Gotou H, Zhang J. Efficacy of sacubitril/valsartan versus olmesartan in Japanese patients with essential hypertension: a randomized, double-blind, multicenter study. Hypertens Res. 2022;45:824–33.
Izzo JL Jr, Zappe DH, Jia Y, Hafeez K, Zhang J. Efficacy and safety of crystalline valsartan/sacubitril (LCZ696) compared with placebo and combinations of free valsartan and sacubitril in patients with systolic hypertension: the RATIO study. J Cardiovasc Pharm. 2017;69:374–81.
Huo Y, Li W, Webb R, Zhao L, Wang Q, Guo W. Efficacy and safety of sacubitril/valsartan compared with olmesartan in Asian patients with essential hypertension: a randomized, double-blind, 8-week study. J Clin Hypertens. 2019;21:67–76.
Ruilope LM, Dukat A, Böhm M, Lacourcière Y, Gong J, Lefkowitz MP. Blood-pressure reduction with LCZ696, a novel dual-acting inhibitor of the angiotensin II receptor and neprilysin: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, active comparator study. Lancet. 2010;375:1255–66.
Schmieder RE, Wagner F, Mayr M, Delles C, Ott C, Keicher C, et al. The effect of sacubitril/valsartan compared to olmesartan on cardiovascular remodelling in subjects with essential hypertension: the results of a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:3308–17.
Williams B, Cockcroft JR, Kario K, Zappe DH, Brunel PC, Wang Q, et al. Effects of sacubitril/valsartan versus olmesartan on central hemodynamics in the elderly with systolic hypertension: the PARAMETER study. Hypertension. 2017;69:411–20.
Lyu TJ, Liu Y, Zhang H, Li LY, He RQ, Gao JQ, et al. Clinical observation of sacubitril valsartan sodium in the treatment of resistant hypertension: a randomized clinical trial. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:1099043.
Zhang S, Yin Z, Li ZF, Zhang WJ, Sui YG, Xu YL, et al. The Effects of sacubitril/valsartan compared to olmesartan on the blood pressure and glucolipid metabolism in DM patients with primary hypertension. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024;38:1349–58.
Wang X, Song F, Jiang L, Huang Z, Luo S, Li X, et al. Efficacy and safety of sacubitril/valsartan in chronic type B aortic dissection combined with mild hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2024;37:612–20.
Chen J, Pei Y, Wang Q, Li C, Liang W, Yu J. Effect of sacubitril/valsartan or valsartan on ventricular remodeling and myocardial fibrosis in perimenopausal women with hypertension. J Hypertens. 2023;41:1077–83.
Jordan J, Stinkens R, Jax T, Engeli S, Blaak EE, May M, et al. Improved insulin sensitivity with angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibition in individuals with obesity and hypertension. Clin Pharm Ther. 2017;101:254–63.
Yamamoto K, Yarimizu D, Shimanishi A, Eguchi S, Iekushi K, Takami Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of sacubitril/valsartan versus amlodipine in japanese patients with essential hypertension: a randomized, multicenter, open-label, noninferiority study (PARASOL study). J Clin Hypertens. 2025;27:e14938.
Ye Q, Sheng Y, He X. Comparative analysis of sacubitril/valsartan and losartan potassium in the treatment of hypertension: efficacy, adverse reactions, and observations. Am J Transl Res. 2023;15:5715–22.
Mitsuno R, Uchiyama K, Nakayama T, Takahashi R, Yoshimoto N, Yamaguchi S, et al. Comparison of the effects of angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors and thiazide diuretic/renin-angiotensin system inhibitor combination therapy in hypertensive patients: a retrospective cohort study. J Hum Hypertens. 2023;37:1049–55.
Li X, Zuo C, Chen C, Tian D, Li J, Fan L, et al. Effectiveness and safety evaluation of sacubitril/valsartan in blood pressure control and clinical outcomes for elderly patients with heart failure and hypertension: a prospective cohort study. Int J Cardiol. 2023;371:244–51.
Song L, Yang H, Ning X, Ma Y, Xue A, Du Y, et al. Sacubitril/valsartan reversal of left ventricular remodeling is associated with improved hemodynamics in resistant hypertension. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2024:20240404; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hjc.2024.03.012.
Reed DNCCKPPM. Sacubitril-Valsartan. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507904/ (2024).
Parcha V, Patel N, Gutierrez OM, Li P, Gamble KL, Musunuru K, et al. Chronobiology of natriuretic peptides and blood pressure in lean and obese individuals. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77:2291–303.
King JB, Bress AP, Reese AD, Munger MA. Neprilysin inhibition in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a clinical review. Pharmacotherapy. 2015;35:823–37.
De la Sierra A, Redon J, Banegas JR, Segura J, Parati G, Gorostidi M, et al. Prevalence and factors associated with circadian blood pressure patterns in hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 2009;53:466–72.
Kario K, Pickering TG, Matsuo T, Hoshide S, Schwartz JE, Shimada K. Stroke prognosis and abnormal nocturnal blood pressure falls in older hypertensives. Hypertension. 2001;38:852–7.
Fujiwara T, Hoshide S, Kanegae H, Kario K. Cardiovascular event risks associated with masked nocturnal hypertension defined by home blood pressure monitoring in the J-HOP nocturnal blood pressure study. Hypertension. 2020;76:259–66.
Verdecchia P, Schillaci G, Guerrieri M, Gatteschi C, Benemio G, Boldrini F, et al. Circadian blood pressure changes and left ventricular hypertrophy in essential hypertension. Circulation. 1990;81:528–36.
Hansen TW, Li Y, Boggia J, Thijs L, Richart T, Staessen JA. Predictive role of the nighttime blood pressure. Hypertension. 2011;57:3–10.
Upadhya B, Kozak PM, Stacey RB, Vasan RS. Newer drugs to reduce high blood pressure and mitigate hypertensive target organ damage. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2022;24:1–20.
Schillaci G, Pucci G, Gavish B. Ambulatory pulse pressure: does it improve cardiovascular risk stratification?. Hypertension. 2014;63:217–9.
Daubert MA, Adams K, Yow E, Barnhart HX, Douglas PS, Rimmer S, et al. NT-proBNP goal achievement is associated with significant reverse remodeling and improved clinical outcomes in HFrEF. JACC Heart Fail. 2019;7:158–68.
Hussain A, Sun W, Deswal A, de Lemos JA, McEvoy JW, Hoogeveen RC, et al. Association of NT-ProBNP, blood pressure, and cardiovascular events: the ARIC study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77:559–71.
Wang B, Wang GH, Ding XX, Tang HX, Zheng J, Liu BC, et al. Effects of sacubitril/valsartan on resistant hypertension and myocardial work in hemodialysis patients. J Clin Hypertens. 2022;24:300–8.
Imamura T, Kinugawa K. Implication of sacubitril/valsartan on N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide levels in hypertensive patients. Ann Palliat Med. 2022;11:2856–61.
Corrao G, Rea F, Monzio Compagnoni M, Merlino L, Mancia G. Protective effects of antihypertensive treatment in patients aged 85 years or older. J Hypertens. 2017;35:1432–41.
Zuo C, Li X, Guan Y, Fan L, Li J, Tian D, et al. Influence of aging on outcomes of sacubitril/valsartan in hypertensive patients with heart failure: a multicenter retrospective study. Anatol J Cardiol. 2024;28:194–200.
Guan Y, Li X, Li H, Ren J, Tang K, Zhang C, et al. Sacubitril/valsartan in heart failure with hypertension patients: real-world experiences on different ages, drug doses, and renal functions. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2023;30:561–72.
Wijkman MO, Claggett B, Vaduganathan M, Cunningham JW, Rørth R, Jackson A, et al. Effects of sacubitril/valsartan on glycemia in patients with diabetes and heart failure: the PARAGON-HF and PARADIGM-HF trials. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022;21:110.
Jackson AM, Jhund PS, Anand IS, Düngen HD, Lam CSP, Lefkowitz MP, et al. Sacubitril-valsartan as a treatment for apparent resistant hypertension in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:3741–52.
Supasyndh O, Sun N, Kario K, Hafeez K, Zhang J. Long-term (52-week) safety and efficacy of sacubitril/valsartan in Asian patients with hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2017;40:472–6.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to state gratitude to the graduate scholarship program for ASEAN or non-ASEAN countries, Chulalongkorn University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: HMN, YK, ASS, BC, SP; data curation: HMN, YK, ASS, BC, WC, AP; data analysis/interpretation: HMN, YK, ASS, BC, FWTC; statistical analysis: HMN, YK, ASS, BC; original manuscript drafting: HMN, YK, ASS, BC; manuscript review and editing: all authors; supervision and mentorship: YK, ASS, BC, FWTC, SP.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Noe, H.M., Sujarit, A.S., Chongmelaxme, B. et al. Angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor for the treatment of hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertens Res 49, 469–485 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-025-02406-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-025-02406-6