Abstract
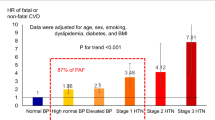
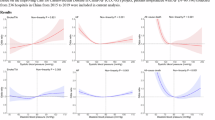
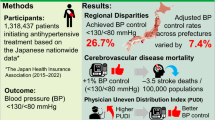
This study aimed to use real-world data obtained from a claim database based on the general population to indicate the optimal blood pressure (BP) level for preventing cardiovascular disease and bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) undergoing anticoagulant therapy. We conducted a retrospective cohort study using claims data and health checkup data collected from multiple health insurance companies in Japan. A total of 4039 AF patients with health examination data who were receiving anticoagulant therapy were analyzed. BP is classified the Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension 2025 (JSH 2025). Primary outcome was cardiovascular disease, Safety outcomes were intracranial bleeding and extracranial bleeding. During a mean follow-up period of 2.80 years, 133 cardiovascular disease events, 33 intracranial and 152 extracranial bleeding were observed. The incidence rates of cardiovascular disease and intracranial bleeding patients increased with the elevation of BP levels. The incidence of cardiovascular disease was lowest in those with BP levels <120/80 mmHg. The incidence of intracranial bleeding was lowest in those with BP < 130/80 mmHg. Extracranial bleeding found no clear association with BP. This real-world data of AF patients undergoing anticoagulant therapy, optimal systolic BP levels was <120-130 mmHg for prevention of cardiovascular disease and of intracranial bleeding.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K, Singh D, Rienstra M, Benjamin EJ, et al. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2014;129:837–47.
Inoue H, Fujiki A, Origasa H, Ogawa S, Okumura K, Kubota I, et al. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation in the general population of Japan: an analysis based on periodic health examination. Int J Cardiol. 2009;137:102–7.
Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV, et al. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults. JAMA. 2001;285:2370–5.
Meng X, Xu X. What is the ideai blood pressure treatment target for primary prevention and management of atrial fibrillation?. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020;7:586183.
McCabe JJ, Cheung Y, Foley M, Brennan SO, Buckley J, Renom PC, et al. Residual risk of recurrent stroke despite anticoagulation in patients with atrial fibrillation. A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2025;82:696–705.
Arima H, Hart RG, Colman S, Chalmers J, Anderson C, Rodgers A, et al. Perindopril-based blood pressure–lowering reduces major vascular events in patients with atrial fibrillation and prior stroke or transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2005;36:2164–9.
Jiang C, Lai Y, Du X, Wang Y, Li S, He L, et al. Effects of intensive blood pressure control on cardiovascular and cognitive outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation: insights from the SPRINT trial. Europace. 2022;24:1560–8.
Lip GYH, Frison L, Grind M. Effect of hypertension on anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:752–9.
Vemulapalli S, Hellkamp AS, Jones WS, Piccini JP, Mahaffey KW, Becker RC, et al. Blood pressure control and stroke or bleeding risk in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation: results from the ROCKET AF Trial. Am Heart J. 2016;178:74–84.
Ho LY, Siu CW, Yue WS, Lau CP, Lip GY, Tse HF. Safety and efficacy of oral anticoagulation therapy in Chinese patients with concomitant atrial fibrillation and hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2011;25:304–10.
Kario K, Hasebe N, Okumura K, Yamashita T, Akao M, Atarashi H, et al. Anticoagulant therapy and home blood pressure-associated risk for stroke/bleeding events in elderly patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: the sub-cohort study of ANAFIE registry. Hypertens Res. 2023;46:2575–82.
Maeda T, Nishi T, Funakoshi S, Tada K, Tsuji M, Satoh A, et al. Risks of bleeding and stroke based on CHA2DS2-VASc scores in Japanese patients with atrial fibrillation: a large-scale observational study using real-world data. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020;9:e014574.
Maeda T, Nishi T, Funakoshi S, Tada K, Tsuji M, Satoh A, et al. Increased incident ischemic stroke risk in advanced kidney disease: a large-scale real-worid data study. Am J Nephrol. 2020;51:659–68.
Maeda T, Nishi T, Funakoshi S, Tada K, Tsuji M, Satoh A, et al. Risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation according to sex in patients aged younger than 75 years: a large-scale, observational study using real-world data. Heart Lung Circ. 2021;30:963–70.
Maeda T, Nishi T, Funakoshi S, Tada K, Tsuji M, Satoh A, et al. Residual risks of ischaemic stroke and systemic embolism among atrial fibrillation patients with anticoagulation: large-scale real-world data (F-CREATE project). Heart. 2021;107:217–22.
Umemura S, Arima H, Arima S, Asayama K, Dohi Y, Hirooka Y, et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens Res. 2019;42:1235–481.
Araki E, Goto A, Kondo T, Noda M, Noto H, Origasa H, et al. Japanese clinical practice guideline for diabetes 2019. Diabetol Int. 2020;11:165–223.
Arima H, Anderson C, Omae T, Woodward M, MacMahon S, Mancia G, et al. Effects of blood pressure lowering on intracranial and extracranial bleeding in patients on antithrombotic therapy. The PROGRESS trial. Stroke. 2012;43:1675–7.
Toyoda K, Yasaka M, Uchiyama S, Nagao T, Gotoh J, Nagata K, et al. Blood pressure levels and bleeding events during antithrombotic therapy. The Bleeding with Antithrombotic Therapy (BAT) study. Stroke. 2010;41:1440–4.
Kimura T, Sugitani T, Nishimura T, Ito M. Validation and recalibration of Charlson and Elixhauser comorbidity indices based on data from a Japanese insurance claims database. J. Pharmacoepidemiol./Yakuzai ekigaku. 2019;24:53–64.
Hara K, Tomio J, Svensson T, Ohkuma R, Svensson AK, Yamazaki T. Association measures of claims-based algorithms for common chronic conditions were assessed using regularly collected data in Japan. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;99:84–95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ishida, S., Maeda, T., Fujii, T. et al. Optimal blood pressure levels for patients with atrial fibrillation who are on undergoing anticoagulant therapy: a large-scale real-world data (F-CREATE project). Hypertens Res 49, 407–415 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-025-02441-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-025-02441-3