Abstract
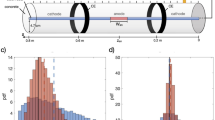
Electrochemical water treatment processes (EWTPs) are widely applied in the fields of urban and industrial water treatment. However, there are few reports on the corrosion problem of metal caused by the electrolysis process. This study undertook a comprehensive exploration of the long-term corrosion behavior of EWTP on carbon steel (CS) equipment under diverse working voltages and elucidated its corrosion mechanism. This study indicated that the severity of general corrosion, including pitting corrosion and electrochemical corrosion increases proportionally with the elevation of the working voltage. Among these, the most severe pitting corrosion rate has increased by 4.8 times. The primary corrosion mechanism lies in the fact that the ClO- formed through the anodic oxidation of Cl- in EWTP reduces the energy barrier for the corrosion reaction of Fe atoms. The secondary mechanism is that the reduction in the content of CaCO3 in the corrosion products decreases the protective effect, and the decrease in solution pH is conducive to the occurrence of corrosion reactions. This study holds significant guiding implications for the corrosion risk assessment of metal equipment, pipelines, structures in water supply systems that adopt EWTP and the development of relevant corrosion control technologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to confidentiality policy, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Pan, Y. et al. Constructing FeNiPt@C trifunctional catalyst by high spin-induced water oxidation activity for Zn-Air battery and anion exchange membrane water electrolyzer. Adv. Sci. 11, 1–10 (2024).
Ren, J. T., Chen, L., Wang, H. Y., Tian, W. W. & Yuan, Z. Y. Water electrolysis for hydrogen production: from hybrid systems to self-powered/catalyzed devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 17, 49–113 (2023).
Veeramani, K. et al. Hydrogen and value-added products yield from hybrid water electrolysis: a critical review on recent developments. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 177, 113227 (2023).
Yuan, X., Liu, B., Mecklenburg, M. & Li, Y. Ultrafast deposition of faceted lithium polyhedra by outpacing SEI formation. Nature 620, 86–91 (2023).
Wu, J. et al. Influence of electrochemical descaling treatment in simulated cooling water on the corrosion behavior of stainless steel. J. Clean. Prod. 451, 142066 (2024).
Yanjin, Z. et al. Case analysis of electrochemical water quality stabilization technology for circulating cooling water system. Ind. Water Treat. 44, 184–189 (2024).
Lu, S. et al. Electrochemical effects on carbon steel in circulating cooling water systems: Scaling, corrosion and chemicals synergies. J. Water Process Eng. 63, 2142–2150 (2024).
Zhang, S., Wang, D., Li, G., Dong, X. & Jiang, H. Experimental study on the combined effect of electromagnetic and electrochemical processes on descaling and anticorrosion. Water 16, 1644 (2024).
Shixin, Z. et al. Research on inhibition of microbial corrosion in industrial circulating water by electrolytic treatment. Mod. Chem. Ind. 43, 110–115 (2023).
Shiwen, W. et al. Industrial application of electrochemical treatment technology to the circulating water system in Daxie Petrochemical Co Ltd. Ind. Water Treat. 38, 96–99 (2018).
Wang, J. et al. Improvement of electrochemical water softening treatment using activated carbon plates in high hardness and low alkalinity water: Enhancing the electrochemical treatment effect while reducing the corrosiveness of the water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 13, 115490 (2025).
Lu, S. et al. Electrochemical effects on carbon steel in circulating cooling water systems: scaling, corrosion and chemicals synergies. J. Water Process Eng. 63, 105337 (2024).
Zhao, S., Jing, Y., Liu, T., Zhao, W. & Li, F. Corrosion behavior and mechanism of carbon steel in industrial circulating cooling water system operated by electrochemical descaling technology. J. Clean. Prod. 434, 139817 (2024).
Liu, Y., Wang, F., Cao, G. & Gao, S. Research and application of electrochemical scale removal technology for circulating water in chemical enterprises. China Chlor–Alkali 04, 20–23 (2021).
Zhang, H. et al. Early period corrosion and scaling characteristics of ductile iron pipe for ground water supply with sodium hypochlorite disinfection. Water Res. 176, 115742 (2020).
Wang, M. Y. et al. Understanding and probing progression of localized corrosion on inner walls of steel pipelines: an overview. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 32, 1–18 (2025).
Zhang, S. et al. A study on the interaction between chloride ions and CO2 towards carbon steel corrosion. Corros. Sci. 167, 108531 (2020).
Hu, Q. et al. Mechanisms of corrosion and corrosion scale formation in water supply networks: a review. J. Water Process Eng. 75, 107975 (2025).
Zhong, H. et al. Corrosion of pipelines in urban water systems: current research status and future trends based on bibliometric analysis. J. Water Process Eng. 56, 104288 (2023).
Zhao, Q. et al. Research on pulse current cathodic protection technology for long-distance pipeline: a review. Mater. Corros. 76, 20–28 (2025).
Xie, F. et al. Stress corrosion cracking behavior induced by sulfate-reducing bacteria and cathodic protection on X80 pipeline steel. Constr. Build. Mater. 308, 125093 (2021).
Ormellese, M., Beretta, S., Brugnetti, F. & Brenna, A. Effects of non-stationary stray current on carbon steel buried pipelines under cathodic protection. Constr. Build. Mater. 281, 122645 (2021).
Li, Z. et al. Advances on electrochemical disinfection research: mechanisms, influencing factors and applications. Sci. Total Environ. 912, 169043 (2024).
Atrashkevich, A., Alum, A., Stirling, R., Abbaszadegan, M. & Garcia-Segura, S. Approaching easy water disinfection for all: can in situ electrochlorination outperform conventional chlorination under realistic conditions? Water Res. 250, 121014 (2024).
Zhang, L. N. et al. Advanced hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts promising sustainable hydrogen and chlor-alkali co-production. Energy Environ. Sci. 14, 6191–6210 (2021).
Sun, R. et al. A self-deoxidizing electrolyte additive enables highly stable aqueous zinc batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202303557 (2023).
Xu, D. et al. Insight into the effect of oxygen content on the corrosion behavior of X70 pipeline steel in a typical simulated soil solution by dissolution-diffusion-deposition model. Corros. Sci. 240, 112478 (2024).
Shah, A. A., Walia, S. & Kazemian, H. Advancements in combined electrocoagulation processes for sustainable wastewater treatment: a comprehensive review of mechanisms, performance, and emerging applications. Water Res. 252, 121248 (2024).
Martínez-Huitle, C. A., Rodrigo, M. A., Sirés, I. & Scialdone, O. A critical review on latest innovations and future challenges of electrochemical technology for the abatement of organics in water. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 328, 122430 (2023).
Sun, Y. et al. A smart composite coating with photothermal response, anti-UV and anti-corrosion properties. Chem. Eng. J. 452, 138983 (2023).
Mahmood, S., Bruns, M. P., Gallagher, C., Virtanen, S. & Engelberg, D. L. Correlating X-ray computed tomography observations with respirometric measurement of aluminium alloy 6063 corrosion under FeCl3 droplets. Corros. Sci. 227, 111704 (2024).
Jia, G. et al. Hydrogen embrittlement in hydrogen-blended natural gas transportation systems: a review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 48, 32137–32157 (2023).
Behvar, A., Haghshenas, M. & Djukic, M. B. Hydrogen embrittlement and hydrogen-induced crack initiation in additively manufactured metals: a critical review on mechanical and cyclic loading. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 58, 1214–1239 (2024).
Lee, S. et al. Quantitative estimation of corrosion rate in 3C steels under seawater environment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 11, 681–686 (2021).
Valdez-Salas, B. et al. Pitting corrosion of austenitic stainless steels in electroactivated water. Int. J. Corros. 2024, 5591969 (2024).
LeBaron, T. W., Sharpe, R. & Ohno, K. Electrolyzed–reduced water: review I. molecular hydrogen is the exclusive agent responsible for the therapeutic effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 14750 (2022).
Gjertsen, S., Seiersten, M., Palencsar, A. & Hemmingsen, T. The effect of weak acids on active corrosion rate in top-of-line corrosion. Corros. Sci. 236, 112253 (2024).
Messinese, E., Ormellese, M. & Brenna, A. A predictive model for corrosion of carbon steel exposed to organic acids: theory and validation in formic, azelaic and citric acid. Corros. Sci. 235, 112160 (2024).
Setiawan, A. R., Fausia, P. I. U., Jannah, M. & Ramelan, A. Unveiling the combined effects of soil acidity and ammonium sulfate on the corrosion behavior of x60 steel pipelines in Indonesian regions. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 78, 1–13 (2025).
Liu, W. et al. Influence of initial pH and sulfate-reducing bacteria concentration on the microbiologically influenced corrosion of buried pipeline steel. Mater. Corros. 75, 1193–1203 (2024).
Su, Y. M., Xie, F. & Wang, D. Synergistic effect of factors influencing the external corrosion of heavy oil pipelines in reed pond soil. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30, 3556–3567 (2021).
Arana Juve, J. M., Christensen, F. M. S., Wang, Y. & Wei, Z. Electrodialysis for metal removal and recovery: a review. Chem. Eng. J. 435, 134857 (2022).
Tan, C. & Liu, H. Inhibition of hexavalent chromium release from drinking water distribution systems: effects of water chemistry-based corrosion control strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 57, 18433–18442 (2023).
Jiang, B. et al. Electrochemical water softening technology: from fundamental research to practical application. Water Res. 250, 121077 (2024).
Mahidashti, Z., Rezaei, M. & Asfia, M. P. Internal under-deposit corrosion of X60 pipeline steel upon installation in a chloride-containing soil environment. Colloids Surf. A 602, 125120 (2020).
Wang, X. & Melchers, R. E. Long-term under-deposit pitting corrosion of carbon steel pipes. Ocean Eng. 133, 231–243 (2017).
Fayyad, E. M. et al. Assessing underdeposit corrosion inhibitor performance for carbon steel in CO2/sulfide environment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 28, 1433–1451 (2024).
Shen, F., Liu, G., Liu, C., Zhang, Y. & Yang, L. Corrosion and oxidation on iron surfaces in chloride contaminated electrolytes: insights from ReaxFF molecular dynamic simulations. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 29, 1305–1312 (2024).
Lai, Z., Huang, F., Wen, L., Zhao, Z. & Jin, Y. Study on microelectrochemical inhomogeneity of an SA508-309L/308L overlay welded joint. Anal. Chem. 95, 18006–18019 (2023).
Wang, Y. et al. High-throughput calculations combining machine learning to investigate the corrosion properties of binary Mg alloys. J. Magnes. Alloy. 12, 1406–1418 (2024).
Bui, H. T., Maekawa, K. & Tan, K. H. Electrochemical corrosion kinetics of steel bars in pseudo-transparent concrete under different alkaline properties and chloride contamination levels. Constr. Build. Mater. 421, 135636 (2024).
Lashgari, S. M. et al. Synthesis of graphene oxide nanosheets decorated by nanoporous zeolite-imidazole (ZIF-67) based metal-organic framework with controlled-release corrosion inhibitor performance: experimental and detailed DFT-D theoretical explorations. J. Hazard. Mater. 404, 124068 (2021).
Ding, C., Tai, Y., Wang, D., Tan, L. & Fu, J. Superhydrophobic composite coating with active corrosion resistance for AZ31B magnesium alloy protection. Chem. Eng. J. 357, 518–532 (2019).
Qiang, Y., Ran, B., Li, M., Xu, Q. & Peng, J. GO-functionalized MXene towards superior anti-corrosion coating. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 642, 595–603 (2023).
Liu, Y. et al. Efficient and green water softening by integrating electrochemically accelerated precipitation and microfiltration with membrane cleaning by periodically anodic polarization. Chem. Eng. J. 449, 137832 (2022).
Niu, Y. Q. et al. Calcium carbonate: controlled synthesis, surface functionalization, and nanostructured materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 51, 7883–7943 (2022).
Wang, Y., Xiao, W., Dai, C., Wang, J. & Pan, F. Enhanced corrosion resistance of Mg alloy embedded in Cl-containing Portland cement with the formation of CaCO3-coated Mg(Al)O passive film via one-step pulse electrodeposition. Corros. Sci. 227, 111751 (2024).
Choi, J. Y., Kinney, K. A. & Katz, L. E. Effect of CaCO3(S) nucleation modes on algae removal from alkaline water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 11694–11703 (2019).
Wei, S., Chen, T., Hou, H. & Xu, Y. Recent advances in electrochemical sterilization. J. Electroanal. Chem. 937, 117419 (2023).
Zhou, E. et al. Direct microbial electron uptake as a mechanism for stainless steel corrosion in aerobic environments. Water Res. 219, 118553 (2022).
Zhou, E. et al. Accelerated biocorrosion of stainless steel in marine water via extracellular electron transfer encoding gene phzH of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Water Res. 220, 118634 (2022).
Li, C. et al. Effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on EH40 steel corrosion in the simulated tidal zone. Water Res. 232, 119708 (2023).
dos Santos, A. J., Kronka, M. S., Fortunato, G. V. & Lanza, M. R. V. Recent advances in electrochemical water technologies for the treatment of antibiotics: a short review. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 26, 100674 (2021).
Brião, G., de, V., da Costa, T. B., Antonelli, R. & Costa, J. M. Electrochemical processes for the treatment of contaminant-rich wastewater: a comprehensive review. Chemosphere 355, 141884 (2024).
Jiang, P. et al. Nitrogen-containing wastewater fuel cells for total nitrogen removal and energy recovery based on Cl•/ClO• oxidation of ammonia nitrogen. Water Res. 235, 119914 (2023).
Yu, D. et al. Electrochemical reduction for chlorinated hydrocarbons contaminated groundwater remediation: mechanisms, challenges, and perspectives. Water Res. 274, 123149 (2025).
Li, Q., Liu, G. hua, Qi, L., Wang, H. & Xian, G. Chlorine-mediated electrochemical advanced oxidation process for ammonia removal: mechanisms, characteristics and expectation. Sci. Total Environ. 896, 165169 (2023).
Cao, K. F. et al. The noteworthy chloride ions in reclaimed water: harmful effects, concentration levels and control strategies. Water Res. 215, 118271 (2022).
Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 59, 1758–1775 (1999).
John, P., Perdew, K. ieron & Burke, M. E. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865–3868 (1996).
Grimme, S., Antony, J., Ehrlich, S. & Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 132, 154104 (2010).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the technical support provided by Henan Qingshuiyuan Technology Co., Ltd. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shichao Zhao: Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, data curation, validation, writing-original draft. Yuanyuan Jing and Xiaoxiao He: Formal analysis, visualization. Fengting Li: Writing—review and editing, formal analysis, supervision. All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, S., Jing, Y., He, X. et al. Effect of electrochemical water treatment processes on carbon steel corrosion in urban water supply system. npj Mater Degrad (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-026-00736-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-026-00736-5