Abstract
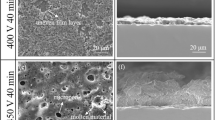
This study investigated the influence of process-induced surface features, porosity, and microstructure on the corrosion behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by different additive manufacturing (AM) technologies, including emerging sinter-based material extrusion (MEX), well-established electron beam melting (EBM) and laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), and wrought reference material. The investigated manufacturing routes produced sensibly different surfaces, porosity, and microstructures. Potentiodynamic and potentiostatic polarization tests in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) revealed stable passivity and excellent corrosion performance for all AM alloys, both in the as-built and polished conditions. After polishing, modest variations were detected among manufacturing technologies, suggesting a possible deleterious effect of the intrinsic porosity once exposed to the environment. Immersion tests performed in neutral and acidified isotonic solutions highlighted the onset of selective corrosion phenomena between the α and β phases under deoxygenated acidic conditions, consistent with Volta potential measurements. Long-term immersion in acidified isotonic solution confirmed the detrimental influence of porosity on the corrosion behavior of Ti-6Al-4V, especially for the MEX-produced alloy, where the presence of a macro-defect network promoted localized corrosion propagation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Nguyen, H. D. et al. A critical review on additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V alloy: microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 18, 4641–4661 (2022).
Trevisan, F. et al. Additive manufacturing of titanium alloys in the biomedical field: processes, properties and applications. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 16, 57–67 (2018).
Chen, Q. & Thouas, G. A. Metallic implant biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. Rep. 87, 1–57 (2015).
Liu, S. & Shin, Y. C. Additive manufacturing of Ti6Al4V alloy: a review. Mater. Des. 164, 107552 (2019).
Mahmoud, D. & Elbestawi, M. A. Lattice Structures and Functionally Graded Materials Applications in Additive Manufacturing of Orthopedic Implants: A Review. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 1, 2 (2017).
Majumdar, T., Eisenstein, N., Frith, J. E., Cox, S. C. & Birbilis, N. Additive manufacturing of titanium alloys for orthopedic applications: a materials science viewpoint. Adv. Eng. Mater. 20, 1800172 (2018).
Davoodi, E. et al. Additively manufactured metallic biomaterials. Bioact. Mater. 15, 214–249 (2021).
Altıparmak, S. C., Yardley, V. A., Shi, Z. & Lin, J. Extrusion-based additive manufacturing technologies: state of the art and future perspectives. J. Manuf. Process. 83, 607–636 (2022).
Sergi, C. et al. Ti6Al4V components by bound metal deposition and competitive with metal injection molded parts: optimization of the printing parameters. Adv. Eng. Mater. 27, 2402813 (2025).
Nurhudan, A. I., Supriadi, S., Whulanza, Y. & Saragih, A. S. Additive manufacturing of metallic based on extrusion process: a review. J. Manuf. Process. 66, 228–237 (2021).
Ramazani, H. & Kami, A. Metal FDM, a new extrusion-based additive manufacturing technology for manufacturing of metallic parts: a review. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 7, 609–626 (2022).
Lorenzi, S. et al. Effect of the deposition strategy and endogenous defect pattern on the plastic deformability and the fracture mechanism of 316L stainless steel obtained using material extrusion. Eng. Fail. Anal. 171, 109395 (2025).
Carrozza, A. et al. A comparative analysis between material extrusion and other additive manufacturing techniques: defects, microstructure and corrosion behavior in nickel alloy 625. Mater. Des. 225, 111545 (2023).
Cabrini, M. et al. Influence of surface finishing and heat treatments on the corrosion resistance of LPBF-produced Ti-6Al-4V alloy for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 308, 117730 (2022).
Carrozza, A., Cabrini, M., Lorenzi, S., Lombardi, M. & Pastore, T. Improving the corrosion performance of LPBF- and EBM-processed Ti-6Al-4V by chemical pickling. Eng. Sci. 26, 985 (2023).
Prestat, M., Vucko, F., Holzer, L. & Thierry, D. Microstructural aspects of Ti6Al4V degradation in H2O2-containing phosphate buffered saline. Corros. Sci. 190, 109640 (2021).
Xu, W. et al. Mechanically-assisted crevice corrosion and its effect on materials degradation. Corros. Commun. 11, 23–32 (2023).
Kurtz, M. A., Khullar, P. & Gilbert, J. L. Cathodic activation and inflammatory species are critical to simulating in vivo Ti-6Al-4V selective dissolution. Acta Biomater. 149, 399–409 (2022).
Toledano-Serrabona, J. et al. Ion release and local effects of titanium metal particles from dental implants: an experimental study in rats. J. Periodontol. 94, 119–129 (2023).
Kawahara, M. & Kato-Negishi, M. Link between aluminum and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer′s disease: the integration of the aluminum and amyloid cascade hypotheses. Int. J. Alzheimer’s. Dis. 2011, 276393 (2011).
Sander, G. et al. Corrosion of additively manufactured alloys: a review. Corrosion 74, 1318–1350 (2018).
Xu, C., Qi, J., Zhang, L., Liu, Q. & Ren, L. Material extrusion additive manufacturing of Ti6Al4V bio-inspired bone implants with tunable Young’s modulus. Addit. Manuf. 78, 103884 (2023).
García de la Cruz, L., Alvaredo, P., Torralba, J. M. & Campos, M. Material extrusion: a promising tool for processing CoCrMo alloy with excellent wear resistance for biomedical applications. Mater. Des. 244, 113089 (2024).
Cabanettes, F. et al. Topography of as built surfaces generated in metal additive manufacturing: a multi scale analysis from form to roughness. Precis. Eng. 52, 249–265, (2018).
Kayacan, M. C. et al. Monitoring the osseointegration process in porous Ti6Al4V implants produced by additive manufacturing: an experimental study in sheep. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 16, 68–75 (2018).
Le Guehennec, L. et al. Osteoblastic cell behaviour on different titanium implant surfaces. Acta Biomater. 4, 535–543 (2008).
Mas-Moruno, C., Su, B. & Dalby, M. J. Multifunctional coatings and nanotopographies: toward cell instructive and antibacterial implants. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 8, 1801103 (2019).
Wennerberg, A. & Albrektsson, T. Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: a systematic review. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 20, 172–184 (2009).
Palmquist, A., Jolic, M., Hryha, E. & Shah, F. A. Complex geometry and integrated macro-porosity: clinical applications of electron beam melting to fabricate bespoke bone-anchored implants. Acta Biomater. 156, 125–145 (2023).
Anselme, K. & Bigerelle, M. Topography effects of pure titanium substrates on human osteoblast long-term adhesion. Acta Biomater. 1, 211–222 (2005).
Suwanpreecha, C. & Manonukul, A. A review on material extrusion additive manufacturing of metal and how it compares with metal injection moulding. Metals 12, 3 (2022).
Quarto, M. & Giardini, C. Additive manufacturing of metal filament: when it can replace metal injection moulding. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 8, 561–570 (2023).
Sadaf, M., Bragaglia, M., Slemenik Perše, L. & Nanni, F. Advancements in metal additive manufacturing: a comprehensive review of material extrusion with highly filled polymers. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 8, 14 (2024).
Kim, Y.-K., Youn, S.-J., Lim, K.-R. & Na, Y.-S. Fused deposition modeling of Inconel 625 alloy: effect of hot isostatic pressing on the microstructure and tensile properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 897, 146328 (2024).
Eickhoff, R., Antusch, S., Nötzel, D. & Hanemann, T. New partially water-soluble feedstocks for additive manufacturing of Ti6Al4V parts by material extrusion. Materials 16, 8 (2023).
Brennan, M. C., Keist, J. S. & Palmer, T. A. Defects in metal additive manufacturing processes. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30, 4808–4818 (2021).
Ren, X. P. et al. A comparative study on mechanical properties of Ti–6Al–4V alloy processed by additive manufacturing vs. traditional processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 817, 141384 (2021).
Carrozza, A. et al. Effect of aging and cooling path on te Super β-transus heat-treated Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced via electron beam melting (EBM). Materials 15, 4067 (2022).
de Formanoir, C., Michotte, S., Rigo, O., Germain, L. & Godet, S. Electron beam melted Ti–6Al–4V: microstructure, texture and mechanical behavior of the as-built and heat-treated material. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 652, 105–119 (2016).
Zhang, T. & Liu, C.-T. Design of titanium alloys by additive manufacturing: a critical review. Adv. Powder Mater. 1, 100014 (2022).
Hooper, P. A. Melt pool temperature and cooling rates in laser powder bed fusion. Addit. Manuf. 22, 548–559 (2018).
Xu, W. et al. Additive manufacturing of strong and ductile Ti–6Al–4V by selective laser melting via in situ martensite decomposition. Acta Mater. 85, 74–84 (2015).
Cui, Y.-W. et al. Metastable pitting corrosion behavior of laser powder bed fusion produced Ti-6Al-4V in Hank’s solution. Corros. Sci. 203, 110333 (2022).
Li, J., He, Y., Shi, W., Xiang, S. & Gao, W. Different passivation behavior between α and β phases of Ti-6Al-4V in HCl solutions under oxygenated/deoxygenated conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 604, 154539 (2022).
Zeng, L. R., Chen, H. L., Li, X., Lei, L. M. & Zhang, G. P. Influence of alloy element partitioning on strength of primary α phase in Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34, 782–787 (2018).
Sharma, A., Oh, M. C., Kim, J.-T., Srivastava, A. K. & Ahn, B. Investigation of electrochemical corrosion behavior of additive manufactured Ti–6Al–4V alloy for medical implants in different electrolytes. J. Alloy. Compd. 830, 154620 (2020).
Cigada, A., Cabrini, M. & Pedeferri, P. Increasing of the corrosion resistance of the Ti6Al4V alloy by high thickness anodic oxidation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 3, 408–412 (1992).
Metalnikov, P., Ben-Hamu, G. & Eliezer, D. Corrosion behavior of AM-Ti-6Al-4V: a comparison between EBM and SLM. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 7, 509–520 (2022).
Fojt, J. et al. Corrosion behaviour and cell interaction of Ti-6Al-4V alloy prepared by two techniques of 3D printing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 93, 911–920 (2018).
Zhang, H. et al. Different corrosion behaviors between α and β phases of Ti6Al4V in fluoride-containing solutions: influence of alloying element Al. Corros. Sci. 169, 108605 (2020).
Örnek, C., Leygraf, C. & Pan, J. On the Volta potential measured by SKPFM – fundamental and practical aspects with relevance to corrosion science. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 54, 185–198 (2019).
Acknowledgements
Financed by the European Union - NextGenerationEU (National Sustainable Mobility Center CN00000023, Italian Ministry of University and Research Decree n. 1033 - 17/06/2022, Spoke 5 - Light vehicle and active mobility, and Spoke 11 - Innovative Materials & Lightweighting). The opinions expressed are those of the authors only and should not be considered as representative of the European Union or the European Commission’s official position. Neither the European Union nor the European Commission can be held responsible for them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.L.: conceptualization, methodology, project administration, resources, supervision, validation, funding acquisition, writing – review & editing. L.N.: data curation, investigation, methodology, visualization, validation, writing – original draft. T.P.: data curation, investigation, validation, writing – original draft. M.L.: conceptualization, resources, writing – review & editing. F.S.: conceptualization, resources, funding acquisition, writing – review & editing. C.S.: conceptualization, resources, writing – review & editing. M.C.: conceptualization, methodology, project administration, resources, supervision, validation, writing – review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Lorenzi, S., Nani, L., Persico, T. et al. A comparative study on the corrosion resistance of Ti-6Al-4V produced via material extrusion and other additive manufacturing technologies. npj Mater Degrad (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-026-00745-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-026-00745-4