Abstract
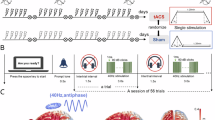
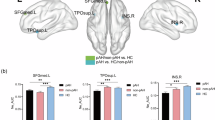
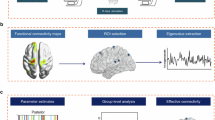
One-third of schizophrenia patients exhibit treatment resistance, underscoring the need for mechanism-based interventions. We report that deep brain stimulation of the substantia nigra pars reticulata has acutely alleviated persistent auditory hallucinations by 64% in a treatment-resistant schizophrenia patient. Deep brain stimulation normalized hallucination-correlated elevation of intraoperative electrocortical theta–gamma phase–amplitude coupling at language-related cortical areas. These findings suggest aberrant cortical synchronization may be involved in the generation of verbal hallucinations and highlight subcortical modulation as a potential therapeutic strategy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data used in this study is part of an ongoing clinical trial and therefore not public yet.
References
Cascella, N. et al. Deep brain stimulation of the substantia nigra pars reticulata for treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a case report. Biol. Psychiatry 90, e57–e59 (2021).
Canolty, R. T. & Knight, R. T. The functional role of cross-frequency coupling. Trends Cogn. Sci. 14, 506–515 (2010).
Lega, B., Burke, J., Jacobs, J. & Kahana, M. J. Slow-theta-to-gamma phase–amplitude coupling in human hippocampus supports the formation of new episodic memories. Cereb. Cortex 26, 268–278 (2016).
Lizarazu, M., Carreiras, M. & Molinaro, N. Theta-gamma phase-amplitude coupling in auditory cortex is modulated by language proficiency. Hum. Brain Mapp. 44, 2862–2872 (2023).
Hyafil, A., Fontolan, L., Kabdebon, C., Gutkin, B. & Giraud, A. L. Speech encoding by coupled cortical theta and gamma oscillations. eLife 4, e06213 (2015).
Papaioannou, O. & Erickson, M. Theta-gamma phase-amplitude coupling as a marker of cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. J. Vis. 23, 5483 (2023).
Ponzi, A., Dura-Bernal, S. & Migliore, M. Theta-gamma phase amplitude coupling in a hippocampal CA1 microcircuit. PLOS Comput. Biol. 19, e1010942 (2023).
Lee, T. H. et al. Relationship between resting-state theta phase-gamma amplitude coupling and neurocognitive functioning in patients with first-episode psychosis. Schizophr. Res. 216, 154–160 (2020).
Torrey, E. F. Schizophrenia and the inferior parietal lobule. Schizophr. Res. 97, 215–225 (2007).
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. et al. Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage 15, 273–289 (2002).
Zmigrod, L., Garrison, J. R., Carr, J. & Simons, J. S. The neural mechanisms of hallucinations: a quantitative meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neurosci. Biobehav Rev. 69, 113–123 (2016).
Kompus, K. et al. The role of the primary auditory cortex in the neural mechanism of auditory verbal hallucinations. Front Hum. Neurosci. [Internet]. 2013 Apr 24 [cited 2025 Mar 6];7. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/human-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00144/full.
Kuhn, J. et al. Deep brain stimulation in schizophrenia. Fortschr. Neurol. Psychiatr. 79, 632–641 (2011).
van Lutterveld, R. et al. Oscillatory cortical network involved in auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia. PLoS One 7, e41149 (2012).
Kim, M. J. et al. Effective stimulation sites and networks for substantia nigra pars reticulata deep brain stimulation for auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia [Internet]. medRxiv; 2025 [cited 2025 Apr 20]. p. 2025.04.09.25325419. Available from: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.04.09.25325419v1.
Angelopoulos, E., Koutsoukos, E., Maillis, A., Papadimitriou, G. N. & Stefanis, C. Cortical interactions during the experience of auditory verbal hallucinations. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 23, 287–293 (2011).
Koutsoukos, E., Angelopoulos, E., Maillis, A., Papadimitriou, G. N. & Stefanis, C. Indication of increased phase coupling between theta and gamma EEG rhythms associated with the experience of auditory verbal hallucinations. Neurosci. Lett. 534, 242–245 (2013).
Steinmann, S., Leicht, G., Andreou, C., Polomac, N. & Mulert, C. Auditory verbal hallucinations related to altered long-range synchrony of gamma-band oscillations. Sci. Rep. 7, 8401 (2017).
Sisterson, N. D. et al. Electrocorticography during deep brain stimulation surgery: safety experience from 4 centers within the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Research Opportunities in Human Consortium. Neurosurgery 88, E420–E426 (2021).
Ashkan, K., Rogers, P., Bergman, H. & Ughratdar, I. Insights into the mechanisms of deep brain stimulation. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 13, 548–554 (2017).
Antal, M., Beneduce, B. M. & Regehr, W. G. The substantia nigra conveys target-dependent excitatory and inhibitory outputs from the basal ganglia to the thalamus. J. Neurosci. 34, 8032–8042 (2014).
van Hooijdonk, C. F. M. et al. The substantia nigra in the pathology of schizophrenia: a review on post-mortem and molecular imaging findings. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 68, 57–77 (2023).
Walker, C. K., Roche, J. K., Sinha, V. & Roberts, R. C. Substantia nigra ultrastructural pathology in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 197, 209–218 (2018).
Lio, G., Thobois, S., Ballanger, B., Lau, B. & Boulinguez, P. Removing deep brain stimulation artifacts from the electroencephalogram: issues, recommendations and an open-source toolbox. Clin. Neurophysiol. 129, 2170–2185 (2018).
Acknowledgements
We extend our gratitude to the participant and his family. We also thank Ms. Yukiko Lema for her suggestions for formatting the figures and her role in research management.Dr. Sawa reports having received research funding from the National Institutes of Health Grant (No. P50MH136297). Dr. Cascella reports having received research funding from the National Institutes of Health Grant (No. U01 MH130625).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.S., W.A., K.M., and N.C. contributed substantially to the conception and design of the study. A.S., Y.S., M.F., N.C., and A.B. contributed to data analysis and interpretation. W.A., K.M., and N.C. were responsible for data acquisition. A.S., W.A., K.M., A.B., M.F., M.J.K., M.B., and N.C. drafted the manuscript or revised it critically for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript. N.C. agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work, ensuring that questions related to accuracy or integrity were appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
W.S.A. reports having received royalty from Globus Medical, and he is a compensated consultant for Iota Biosciences. All other authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, A., Salimpour, Y., Butala, A. et al. Substantia nigra pars reticulata involvement in auditory hallucinations of treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a deep brain stimulation case report. Schizophr (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41537-026-00732-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41537-026-00732-3